Introduction to Optical Electronics - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title:
Introduction to Optical Electronics
Description:
The photoelectric current is proportional to the intensity of the radiation. Photoelectric emission starts with no observable time lag after illumination ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:77
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Introduction to Optical Electronics
1
Introduction to Optical Electronics
2
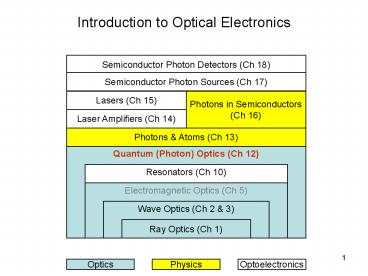
Optics
Ray Optics (Geometrical Optics)
- Focus on location direction of light rays
- Limit of Wave Optics where ? 0
Wave Optics (Gaussian Beam)
- Scalar wave theory (Single scalar wavefunction
describes light)
EM Optics (Geometrical Optics)
- Two mutually coupled vector waves (E M)
Quantum Optics (Photon Optics)
- Describes certain optical phenomena that
arecharacteristically quantum mechanical
3
Chronological Development of Optics
- Michael Faraday (1791 1867)
- James Clerk Maxwell (1831 1879)
- James Bradley (1693 1762)
- Dominque Arago (1786 1853)
- Augustin Jean Fresnel (1788 1827)
- Armand Fizeau (1819 1896)
- Airy (1801 1892)
- Henrik Antoon Lorentz (1853 1928)
- Albert Abraham Michelson (1852 1931)
- Jules Henri Poincare (1854 1921)
- Albert Einstein (1879 1955)
- Max Planck (1858 1947)
- Richard Phillips Feynman (1918 1988)
4
The Photoelectric Effect
A
V
- The photoelectric current is proportional to the
intensity of the radiation - Photoelectric emission starts with no observable
time lag after illumination starts, even if the
intensity is very low - The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted
electrons is independent of the intensity of the
light - There is a linear relation between the stopping
potential (V0) and frequency (?) for any given
metal
The stopping potential V0 is defined as the
magnitude of the potential difference necessary
to reduce the current to zero.
5
Moving from Wave to Particle Nature of Light
- Wave Nature of Light(Classical)
- Light in resonator
- completely characterized by EM field
- Particle Nature of Light(Quantum)
- Light in resonator
- comprised of a set of modes containing an
integral number of photons - Characteristics of the modes taken from classical
and assigned to photon - ?
- spatial distribution
- direction of propagation
- polarization
6
Photon (Quantum) Optics
- Photons
- Energy
- Position
- Momentum
- Polarization
- Interference
- Time
- Photon Streams
- Coherent
- Partially Coherent
- Probability Rules!
- Mean Photon Flux
- Photon-Number Statistics
- Random Partitioning
7
Blackbody Radiation Theory
8
Density of Modes
ky
9
Light as Particles - Photons
- Energy
- Position
- Momentum
- Polarization
- Interference
- Time
10
Quantum Effects
I
?
I
?
11
Photon StreamsStatistics!
Temporal
Spatial
12
Photon Flux
- Mean Photon-Flux Density
- Mean Photon Flux
- Mean Number of Photons
13
Classical vice Quantum Concepts
Spectral Definitions
14
Photon FluxTime-Varying
- Mean Photon-Flux Density
- Mean Photon Flux
- Mean Number of Photons
15
Uncertainty Relationships
Defining Conjugate Pairs
Uncertainty
16
More Uncertainty Relationships
More Conjugate Pairs
Uncertainty
Conjugate Heisenbergs Pairs Uncertainty
17
Photon-Number StatisticsCoherent Light
18
Photon-Number Statistics
- Coherent Light
Poisson Distribution
Mean Variance
Signal-to-Noise Ratio
19
Photon-Number StatisticsThermal Light
20
Photon-Number Statistics
- Thermal Light
- Boltzman Prob. Dist.
Bose-Einstein Distribution
Mean Variance
Signal-to-Noise Ratio
21
Atom Photon Interactions
Next Class!