Creating Solid Models Parametric Modeling Concept - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title:
Creating Solid Models Parametric Modeling Concept
Description:
... modeling design program: SolidWorks, Pro-Engineer, Unigraphics (CSG and ... 1 - It is desired to have AB always vertical. 2 - It is required to have AB = CD. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:455
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Creating Solid Models Parametric Modeling Concept
1
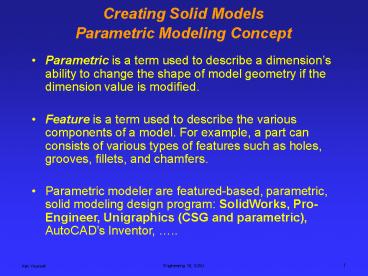
Creating Solid ModelsParametric Modeling Concept
- Parametric is a term used to describe a
dimensions ability to change the shape of model
geometry if the dimension value is modified. - Feature is a term used to describe the various
components of a model. For example, a part can
consists of various types of features such as
holes, grooves, fillets, and chamfers.
- Parametric modeler are featured-based,
parametric, solid modeling design program
SolidWorks, Pro-Engineer, Unigraphics (CSG and
parametric), AutoCADs Inventor, ..
2
Sketching and Features
When discussing the mind-set needed for working
with parametric modelers, there are two topics
that need to be expanded Sketching and Features
- When sketching it is not necessary to create
geometry with accuracy. In other words the
geometry need not be created with exact dimension
in mind.
- When dimensions are added, the sketch will change
size and shape. This is the essence of parametric
modeling.
In short, the sketch need only be the approximate
size and shape of the part being designed. When
dimensions are added, they will drive the size
and the shape of the geometry.
3
Sketching Drawing Tools
2D sketch menu
4
Exiting Sketch
To exit the sketch, right click and select Finish
Sketch
5
Dimensioning Sketch
Select the dimension icon
? select the object to dimension (line), you can
also select two endpoints of a line
6
Editing a Sketch
Browser shows the history of the model
The box was created by sketching a rectangle 1.25
x .75 and then extruded by .5 (depth)
Change the height from .75 to 1.0
.75
7
Editing a Sketch
Double click the dimension to be changed and
enter the new dimension
8
Constraints
Geometric constraints may be added to sketch to
apply behavior to a specific object or to create
a relationship between two objects.
C
B
A
D
9
Constraints
Choose Vertical from the constraint menu and
select the line.
10
Sketching Modifying Tools
Original shape
Creates a duplicate of a selected object at a
specified distance
Offset shape
- Click the Offset tool.
- Click the sketch geometry you want to copy.
- Move the cursor in the direction you want to
place the offset geometry, then click to create
the new geometry. - Click to place the curve at the offset distance.
- If desired, use the Dimension tool to set a
specified offset distance.
- Set the starting point for the move command. Once
selected, you can click anywhere in the graphics
window or select the Precise Input check box to
enter X and Y coordinates of the base point into
the Precise Input toolbar.
11
Sketching Modifying Tools
- Select the geometry to rotate. Click the Select
button, and then select the geometry in the
graphics window. The Select button is on by
default when you open the Rotate tool.
Sketch
12
Sketching Modifying Tools
- Select sketch geometry to mirror.
sketch
- Set the starting reference point for the copy
command. Once selected, you can click anywhere in
the graphics window or select the Precise Input
check box to enter X and Y coordinates of the
base point into the Precise Input toolbar.
13
Sketching Modifying Tools
Use the Trim tool to trim curves or remove
segments.
- Click the Trim tool.
Segment to trim
14
Sketching Modifying Tools
15
Design Intent
- In parametric modeling, dimensions control the
model. - Design intent is how your model will react when
dimension values are changed.
16
Design Intent
The drawing shows the intent of the designer that
the inclined plane (chamfer) should have a flat
area measuring 2.5 inches and that it should
start at a point 1.25 inches from the base of the
drawing. These parameters are what the designer
deemed significant for this model.
2.50
2.50
1.25
4.00
Remember that the placement of dimensions is very
important because they are being used to drive
the shape of the geometry. If the 2.5 in.
vertical dimension increases, the 2.5 in. flat
across the chamfer will be maintained, but its
angle will change.
17
Design Intent
In this drawing, what is important to the
designer is the vertical location and horizontal
dimension of the chamfer, rather than the flat of
the chamfer.
2.125
2.50
1.25
4.00
18
Design Intent
19
Design Notes
- Keep in mind that dimensioning scheme can be
changed at any time. You are not locked into a
specific design. You can also design without
dimensioning, rough out a sketch, and then later
go back and fully define it.
- Do not be concerned with dimensioning to datum or
stacked tolerances in the part. Those issues can
be addressed in the drawing layout. Be more
concerned with your design intent.