Porter
Title:
Porter
Description:
Inventors. Characteristics of Adopters ... Characteristics of Inventors ... Characteristics of Inventors. Strong R&D department ... –
Number of Views:32
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Porter
1
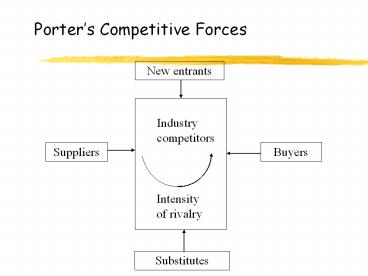
Porters Competitive Forces
New entrants
Industry competitors
Suppliers
Buyers
Intensity of rivalry
Substitutes
2
Strategies for Competitive Advantage
Competitive Advantage
Cost
Differentiation
Broad focus
Cost leadership
Competitive Scope
Differentiation
Narrow focus
Differentiation focus
Cost focus
3
Role of IT in Competitive Strategy
- Raise Barriers to Entry
- offer unique services that are hard to copy
- first mover advantages
- knowledge barriers
4
Role of IT in Competitive Strategy
- Establish Switching Costs
- integrate IT services with other services
- response time and service quality
- value-added services
5
Role of IT in Competitive Strategy
- Generate New Products
- tailor existing products to meet customer needs
- emergence of new IT-based industries
6
Role of IT in Competitive Strategy
- Change cost structure or product/service
offerings - cheaper production, distribution through IT
- use IT to differentiate
7
Role of IT in Competitive Strategy
- Change supplier/buyer relationships
- process automation
- inventory management and JIT
- electronic linkages
- reducing the role of the middleman
8
Role of IT in the Value Chain
- Inbound logistics
- inventory and ordering
- links to suppliers
- Operations
- process control
- on-line processing
- telecommunications
9
Role of IT in the Value Chain
- Outbound logistics
- links to buyers
- Marketing and sales
- customer service
- linking suppliers and buyers
- database marketing
10
Role of IT in the Value Chain
- After-sales service
- on-line support
- expert systems
11
Classification of Companies Use of Information
Systems
- Adopters
- Adapters
- Inventors
12
Characteristics of Adopters
- Use purchased, off-the-shelf systems for routine
applications - Goal is short-term survival or catching up with
competitors
13
Characteristics of Adopters
- Most often found in
- stagnant industries
- areas of depressed economy
- companies with insufficient capital resources
14
Characteristics of Adapters
- IT is an essential element of planning
- Have awareness, capability, and funds to
undertake internal development
15
Characteristics of Adapters
- Have close working relationships with suppliers
to take advantage of developments in which timing
is critical - Invest significantly in maintenance of existing
applications, but also focus on adapting new
technology through expansion and innovation
16
Characteristics of Inventors
- Create new technologies that represent
significant departures from current practice - Can leapfrog the competition
17
Characteristics of Inventors
- Strong RD department
- Ability to market needs and bring products or
services to the market at the right time and at a
competitive cost
18
Information Technology Strategic Development
Cycles
- Assessment Cycle
- Planning/Development/Implementation Cycle
19
Assessment Cycle
- Evaluate position and approach used by
competitors - Identify strong and weak points of competitors
products and services - Identify competitors major applications of IT
- Identify competitors technical and financial
strength and their ability to invest in IT
20
Assessment Cycle
- Evaluate companys current IT status
- should be performed by independent group within
company or outside consultant - develop description of applications of IT to
critical operations or products and identify gaps
in applications ability to meet its objectives
21
Assessment Cycle
- Evaluate companys current IT status (contd)
- appraise skills, methods, and tools of
application developers - review work mix (e.g., percentage of time spent
on maintenance versus new development)
22
Assessment Cycle
- Understand how information technology could be
applied - appraise available IT that could be used for
competitive advantage now - appraise anticipated changes or new developments
that could be used for competitive advantage over
the next 3-5 years
23
Assessment Cycle
- Understand how information technology could be
applied - identify potential applications of current and
future technology -- how will they affect
competition? - identify potential changes in current
applications driven by market demands or
technology development
24
Assessment Cycle
- Assess environmental factors
- technology
- industry structure
- external economic and political forces
25
Planning/Development/Implementation Cycle
- Identify major threats and opportunities
- summary of results of assessment cycle
- what areas would most benefit from improved use
of IT? - relate to business objectives
26
Planning/Development/Implementation Cycle
- Develop an IT strategy
- what areas deserve high-priority attention
- how competitors maximize their use of IT
- how does company respond to competitors
- identify any important new threats
27
Planning/Development/Implementation Cycle
- Develop an IT strategy (contd)
- identify and analyze new uses of IT for products
and services - assess threats and opportunities
- identify parts of company infrastructure that
will need to be improved
28
Planning/Development/Implementation Cycle
- Develop the infrastructure to implement the plans
- Specify
- goals
- strategy
- approach
- expected results
- critical milestones
- requisite resources
29
Planning/Development/Implementation Cycle
- Perform detailed planning and implementation
- improve the IT infrastructure
- begin detailed planning for the application
- establish a steering group to ensure that all
interests are represented during this phase
30
Planning/Development/Implementation Cycle
- Evaluate realized returns on investment
- evaluation may not be possible for months due to
application migration, test marketing, redesign
of business processes - maintain updated estimates on return of
technology investments
31
Planning/Development/Implementation Cycle
- Evaluate realized returns on investment (contd)
- measure return in terms of success criteria
- Reiterate these cycles to improve competitive
position
32
Risks
- Failure to continue investing in new technology
- Lowered barriers to entry
- Litigation
- Dominance of customer or supplier (elimination of
middleman)
33
Risks
- Timing
- Threats to large firms
- Misunderstanding segments
- Cultural lag
34
Management Perspective
- Importance of IT in the strategic plan
- Securing confidentiality
- Evaluating financial and accounting measures for
IT - Partnership with IT specialists