PowerPoint Presentation - Application Requirements - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
PowerPoint Presentation - Application Requirements
Description:
ITU-T G.823, G.824 traffic masks. Packet based (no 'on-path-support' ... GPS. Applications Requirements: Time synchronization. Application Class. Example applications ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:28
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: PowerPoint Presentation - Application Requirements
1
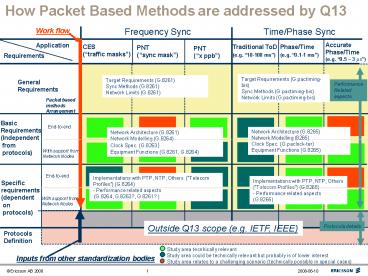
How Packet Based Methods are addressed by Q13
2
Applications Requirements Frequency
synchronization
Application Class Example applications Strandard/Speciifcations/Recommendations Main Sync Methods Identified or Under discussion
Long Term Accuracy GSM, WCDMA FDD, LTE FDD 50 ppb 100 ppb (Pico) 100-250 ppb (Home) Packet based (no on-path-support). Note PDV controlled and/or stable oscillator (OCXO)
Traffic Masks CES (Adaptive methods) ITU-T G.8261 CES Budget (application case 1 and 2) ITU-T G.823, G.824 traffic masks Packet based (no on-path-support). Note PDV controlled and suitable oscillator
Synch Masks Support for CES (Network synchronous, Differential) ITU-T G.823 , G.824 synchronization mask G.8261 (EEC network limits) Timing over Physical layer (e.g. SDH, syncE) GPS
3
Applications Requirements Time synchronization
Application Class Example applications Strandard/Specifications/Recommendations Main Sync Methods Identified or Under discussion
ToD Traditional (10-500 ms) Billing, Alarming, etc. Packet based (no support from the network).
Tens of microseconds-hundreds of microseconds IP delay monitoring LTE TDD (some configurations) Y.1541 3GPP Packet based (no on-path-support). Note PDV controlled and suitable oscillator
0.5 3 microseconds MBSFN WCDMA TDD TD-SCDMA CDMA2000 LTE TDD (some configurations) GPS Packet based (with path support)
Main focus for TICTOC ?
4
Q13 Frequency Sync Recommendations
Recc. Main Contents What is missing
G.8261 Target Requirements Network Limits Sync Methods Detailed model to clarify where the PDV limits apply. PDV metrics and related network limits
G.8262 SyncE Clocks completed
G.8263 Packet based clocks spec Clock model PSC, PEC, specifications New Clocks?
G.8264 Modelling Functional blocks Equipment functions Details on use of protocols for syncE (i.e. SSM) and for packet based (e.g. IEEE1588 Telecom Profiles these could be handled in Annexes, one per application) Details on packet based methods incl. profiles
5
Q13 Time-Phase Sync, Planned Recommendations
Recc. Main Contents
G.pactiming-bis Target Requirements Network Limits Sync Methods
G.paclock-ter Time-Phase clocks spec (e.g. Boundary clock)
G.8265 Functional blocks Modelling Equipment functions Details on use of protocols (e.g. IEEE1588 Telecom Profiles, NTP implementations these could be handled in Annexes, one per application)