Testing Webbased applications - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 57
Title:
Testing Webbased applications
Description:
Testing Web-based applications. Typically, a multi-layered architecture is used. ... (for EE 5), JBoss, BEA, IBM WebSphere, Oracle Application Server, JOnAS, ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:76
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Testing Webbased applications
1
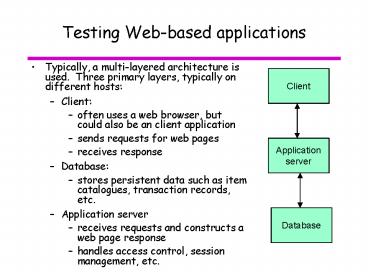
Testing Web-based applications
- Typically, a multi-layered architecture is used.
Three primary layers, typically on different
hosts - Client
- often uses a web browser, but could also be an
client application - sends requests for web pages
- receives response
- Database
- stores persistent data such as item catalogues,
transaction records, etc. - Application server
- receives requests and constructs a web page
response - handles access control, session management, etc.
Client
Application server
Database
2
The Client layer
- Web pages are represented by HTML, the HyperText
Markup Language. - The protocol to send and receive web pages from a
web server is HTTP, the HyperText Transfer
Protocol. - Whats useful to know about HTTP in this context?
- It was intended as a request response protocol
without any state. - It is entirely text-based and (somewhat)
human-readable.
3
Application Servers
- Typical functions
- Management of concurrent sessions and
transactions - Construction of dynamic and static web pages
- Arrange for storage and retrieval of persistent
data - Handling of business logic
- Security
4
The Database interface
- The connection to a database via a programming
language is via a connection protocol API
(application programming interface) - ODBC open database connectivity
- JDBC specific version for Java
- Since databases are not compatible, there are
normally specific drivers loaded in for each type
of database (Oracle, MySQL, etc.) - Specify a URL such as jdbcmysql//ste5007.site.uo
ttawa.ca3306/db to connect, and then provide a
userid and password. - After logging in, SQL (structured query language)
commands are issued to insert, view, update, or
delete data. - Results from the database are loaded into a
O/JDBC object for use.
5
For this presentation
- Some assumptions on the environment for the
purposes of this presentation - Code is based on the Java Enterprise Edition (EE)
software development kit, version 1.4 or earlier
(i.e. not Java EE 5) - Use of a web application server that conforms to
the Java EE specification
6
Java Application Servers
- Java EE servers use the concept of a container
in which processing of a session is handled. - Java classes are deployed into a container, and
then interact with the container to provide
functionality for the server. - The container manages the creation and life cycle
of the objects deployed within, and access to
these objects.
7
Java Application Servers
Container
HTTP request
Servlet
Filter
Enterprise JavaBean (EJB)
Client / Browser
Java Server Page (JSP)
Tag Library
HTTP response, containing HTML
Application server
DB
8
Server options
- Production-capable server
- Apache Tomcat, Sun JAS, Glassfish (for EE 5),
JBoss, BEA, IBM WebSphere, Oracle Application
Server, JOnAS, ... - Simplified server
- Jetty
- No server
- Mock object generator that provides mocks for the
HTTP interface or the DB interface.
9
Testing the client
- If the purpose of testing is to test behaviour at
the client, then various approaches are possible. - Use an actual production-capable application
server (including possibly even the database
layer). - Use an application server (perhaps a with stubs
for web pages - Web pages are empty or nearly so, with no dynamic
content. - Replace the application server with a stub or
mock object that works with the HTTP protocol.
The mock connection is the interface to the
client. - Test client objects directly with JUnit.
10
Testing the client
HTTP request
Embedded Application Server
Client / Browser
JUnit Test Case
HTTP response, containing HTML
11
Testing the client
HTTP request
Mock Connection
Client / Browser
JUnit Test Case
HTTP response, containing HTML
12
HTTP primary commands
- GET request a resource
- GET /awilliam/csi5118 HTTP/1.1Host
www.site.uottawa.ca - POST submit data for processing
- POST /index.html HTTP/1.1Host
www.example.com...Content-type
application/x-www-form-urlencoded...searchwordf
indmeoptionsearchsubmitgo
File to retrieve
File from which data was posted
Form data
13
HTTP responses
- HTTP returns a numeric 3-digit code, header
information, plus content. - Frequent codes
- 200 OK request was satisfied, and message
contains content. - HTTP/1.1 200 OK ... Content-length
43794 Content-type text/html ... lthtmlgt ...
lt/htmlgt - 404 Not found the resource requested could not
be located.
Success
Content information
Web page in HTML
14
Potential test purposesat the Client Interface
- Check that when a user action occurs, the correct
data is put into an HTTP request - Link has correct uniform resource locator (URL)
address. - Data in POST command is as expected, and
formatted correctly. - Check that when an HTTP request is sent to the
server, the response is as expected. - HTTP response is correct
- HTML response is correct
- Search for particular items within a web page to
see if they are included (especially for
dynamically generated pages) - Correct page
- Correct page elements (buttons, etc.)
- Data is as expected.
15
Sample Web client that returnsa string read
from a web server
- public class WebClient
- public String getContent( URL url )
- StringBuffer content new StringBuffer()
- try
- HttpURLConnection connection
- (HttpURLConnection)
url.openConnection( ) - connection.setDoInput( true )
- InputStream is connection.getInputStrea
m( ) - byte buffer new byte2048
- int count
- while ( -1 ! ( count is.read( buffer
) ) ) - content.append( new String( buffer,
0, count ) ) - catch ( IOException e ) return null
16
Client test strategies
- To test this client, we have to arrange for some
known data to appear from the URL, and be sure
that the client reads it correctly. - Two approaches
- Use an embedded server that we can control.
- Use a stub or mock object for the connection.
17
Test strategy 1 Embedded server
HTTP request
Embedded Application Server
Client / Browser
JUnit Test Case
HTTP response, containing HTML
18
Jetty
- Jetty is a small application server that can be
embedded within a Java application. - http//www.mortbay.org/
- For running JUnit, Jetty can be started within
the same virtual machine. - Jetty can be provided with various contexts and
handlers - Essentially, a context defines a relative URL for
which the Jetty server will accept requests. - Handlers tell Jetty how to construct responses.
19
Setup for Embedded Jetty Server
- public class WebClientTest
- private static HttpServer server
- _at_BeforeClass
- public static void setUpBeforeClass( ) throws
Exception - server new HttpServer()
- SocketListener listener new
SocketListener() - listener.setPort( 8080 )
- server.addListener( listener )
- HttpContext context1 new HttpContext()
- context1.setContextPath( "/testGetContentOK"
) - context1.addHandler( new TestGetContentOKHan
dler() ) - server.addContext( context1 )
- HttpContext context2 new HttpContext()
- context2.setContextPath( "/testGetContentNot
Found" ) - context2.addHandler( new NotFoundHandler()
) - server.addContext( context2 )
Handler for requests
URL for the context will be httplocalhost8080/te
stGetContentOK
20
Jetty Handlers
- public class TestGetContentOKHandler extends
AbstractHttpHandler - public void handle( String pathInContext,
String pathParams, - HttpRequest theRequest,
HttpResponse theResponse ) - throws HttpException, IOException
- OutputStream out theResponse.getOutputStre
am( ) - ByteArrayISO8859Writer writer new
ByteArrayISO8859Writer( ) - writer.write( "It works" )
- writer.flush( )
- theResponse.setIntField( HttpFields.__Conten
tLength, - writer.size( ) )
- writer.writeTo( out )
- out.flush( )
- theRequest.setHandled( true )
21
Sample test Teardown
- _at_Test
- public void testGetContentOK( ) throws
MalformedURLException - WebClient client new WebClient( )
- URL url new
- URL("http//localhost8080/testGetConten
tOK") - String expected "It works"
- String actual client.getContent( url )
- assertEquals( expected, actual )
- _at_AfterClass
- public static void tearDownAfterClass( ) throws
Exception - server.stop()
22
Strategy 2 No server
HTTP request
Stub Connection
Client / Browser
JUnit Test Case
HTTP response, containing HTML
23
Strategy 2 Implementation
HTTP request
Client / Browser
Stub URL Stream Handler
JUnit Test Case
URL
Stub URL Connection
HTTP response, containing HTML
Stub Stream Handler Factory
24
Stub for the URL connection
- public class StubHttpURLConnection extends
HttpURLConnection - private boolean isInput true
- protected StubHttpURLConnection( URL url )
- super( url )
- public InputStream getInputStream( ) throws
IOException - ByteArrayInputStream bais
- new ByteArrayInputStream( new String(
"It works" ) - .getBytes( ) )
- return bais
25
Sample test Setup
- _at_BeforeClass
- public static void setUpBeforeClass( ) throws
Exception - URL.setURLStreamHandlerFactory(
- new StubStreamHandlerFactory() )
- _at_Test
- public void testGetContentOK( ) throws
MalformedURLException - WebClient client new WebClient( )
- URL url new
- URL("http//localhost8080/testGetConten
tOK") - String expected "It works"
- String actual client.getContent( url )
- assertEquals( expected, actual )
26
Testing Application Server Classes
- In-container approach
- This is the actual environment in which the class
would be run. - Requires deploying classes to an application
server (complex, time-consuming setup) - Access to classes for test purposes is restricted
by the container. - Out-of-container approach
- Requires stubs or mock objects for interactions
with the container. - Not the actual running environment.
- Once the container environment is simulated,
tests can be run quickly.
27
Java Application Servers (reprise)
Container
HTTP request
Servlet
Filter
Enterprise JavaBean (EJB)
Client / Browser
Java Server Page (JSP)
Tag Library
HTTP response, containing HTML
Application server
DB
28
Servlets
- Servlets are a mechanism for an application
server to construct dynamic web page content. - Example
- User enters a value into a text field on a web
page and clicks a submit button. - An HTTP command is constructed by the browser and
sent to the server. - The application server will parse the HTTP
command, determine which session the command
belongs to, and construct an HttpServletRequest
object containing the request information. - The servlets function is to create an
HttpServletResponse object that contains
information needed to create the HTTP reply that
contains the HTML to be displayed in the users
browser.
29
The Servlet Environment
Container
HTTP request
Servlet
HttpServletRequest
Browser
HttpServletResponse
HTTP response, containing HTML
Application server
DB
30
A (small) Sample Servlet
- Purpose As part of handling a request, this
method checks to see if the session associated
with the request has stored a attribute
indicating that the session was authenticated. - public class SampleServlet extends HttpServlet
- implements Servlet
- public boolean isAuthenticated(
HttpServletRequest request ) - HttpSession session request.getSession(
false ) - if ( session null )
- return false
- String authenticationAttribute ( String )
session - .getAttribute( "authenticated" )
- return Boolean.parseBoolean(
authenticationAttribute )
31
How to test the Servlet?
- Because this method asks for the containers
session parameters, direct JUnit test cases are
not possible in this environment. - The HttpServletRequest object is created by the
container and is only available there. The
request also must return a valid HttpSession to
check the attribute. - To test this code without the container, mock
objects for the HttpServletRequest and
HttpSession objects are needed.
32
Servlet Testing approaches
- Three ways of running test cases for this servlet
will be shown here. - Out of container, using mock objects created by
EasyMock. - In container, using the Apache Tomcat server and
Cactus - In container, using the embeddable Jetty server
and Cactus.
33
Out-of-container Strategy
Servlet
HttpServletRequest
JUnit Test Case
HttpServletResponse
Mock DB
34
The sample servlet, again
- public class SampleServlet extends HttpServlet
- implements Servlet
- public boolean isAuthenticated(
HttpServletRequest request ) - HttpSession session request.getSession(
false ) - if ( session null )
- return false
- String authenticationAttribute ( String )
session - .getAttribute( "authenticated" )
- return Boolean.parseBoolean(
authenticationAttribute )
35
Mock objects test case setup and teardown
- public class MockObjectTest
- private SampleServlet servlet
- private HttpServletRequest theRequest
- private HttpSession theSession
- _at_Before
- public void setUp( ) throws Exception
- servlet new SampleServlet( )
- theRequest
- EasyMock.createMock(HttpServletReques
t.class ) - theSession EasyMock.createMock(
HttpSession.class ) - _at_After
- public void tearDown( ) throws Exception
- EasyMock.verify( theRequest )
36
Mock object test case test method
- _at_Test
- public void testIsAuthenticatedTrue( )
- EasyMock.expect( theRequest.getSession( false
) ) - .andReturn( theSession )
- EasyMock.expect( theSession.getAttribute("authe
nticated") ) - .andReturn("true")
- EasyMock.replay( theRequest )
- EasyMock.replay( theSession )
- boolean expected true
- boolean actual servlet.isAuthenticated(
theRequest ) - Assert.assertEquals( expected, actual )
37
Running the test case
- All the previous test case needs to run is to
ensure the EasyMock class library is available. - Tests are run without using an application
server, and are run directly by JUnit. - Advantages
- Test is easy to set up and will run quickly
- Disadvantages
- The test is not running in the actual servlet
container, and we dont know if the container
will provide the correct request or not.
38
In-container Strategy (1)
Container
Servlet
JUnit Test Case
Request
Response
Application server
Test DB
39
In-container Strategy (2)
Container
Servlet
JUnit Test Case
Request
JUnit Test Proxy
Response
Application server
Test DB
40
In-container testing with Cactus
- Cactus part of the Apache Jakarta project
- jakarta.apache.org/cactus
- Cactus is a framework to install a test component
inside an application server, and to communicate
with that test component. - Extension of the JUnit framework
- Result You can run JUnit tests from outside the
container, but have the tests executed inside the
container.
41
How Cactus Works
- Cactus uses a proxy mechanism to run test cases
at the client, and redirect the requests to a
copy of the test case inside the server
container.
42
In-container testing with Cactus
- What is required
- Include the JUnit and Cactus libraries as part of
the deployment to the application server
container. - Implement a client redirector that takes a JUnit
test case run outside the container, and
duplicate it within the container. - Implement a server redirector that lets Cactus
intercept incoming requests during test case
execution and provide them as objects to the test
case. - Provide a mechanism to get the test case results
back from the container to the test runner.
43
Cactus JUnit test cases
- Test class must inherit from one of the following
classes - org.apache.cactus.ServletTestCase, to test a
servlet - org.apache.cactus.FilterTestCase, to test a
filter - org.apache.cactus.JspTestCase, to test a Java
server page
44
Cactus JUnit test cases
- For a servlet test case, the JUnit test case will
have access to the following objects - request
- response
- config
- session
- The servlet context can also be accessed
indirectly.
45
Structure of a Cactus test
- begin(), end() executed on the client side
before and after each test case - setUp(), tearDown() executed on the server side
before and after each test case - testXXX() a test method, to be executed within
the server container - beginXXX(WebRequest request) a method to be
executed on the client immediately before
testXXX(). - The parameter is used to set up the request to be
passed to the server. - endXXX(WebResponse theResponse ) a method to be
executed at the client immediately after
testXXX(). This is used to verify the HTTP
response from the user.
46
How Cactus Works
- Here is the order of execution of the various
methods
47
First In-Container Test Project
- Goal Execute a servlet test case on an Apache
Tomcat application server. - Create an Eclipse dynamic web project
- The target server is defined at project creation
time. - Eclipse will create the web.xml deployment
descriptor for the project. - Using the servlet wizard to create the servlet
will add the servlet to the deployment descriptor
48
Additions to Deployment Descriptor
- Cactus redirectors must be added to the web.xml
file, so that they can be part of the project
deployment. - ltservletgt
- ltservlet-namegtServletRedirectorlt/servlet-namegt
- ltservlet-classgt
- org.apache.cactus.server.ServletTestRedirect
or - lt/servlet-classgt
- lt/servletgt
- ltservlet-mappinggt
- ltservlet-namegtServletRedirectorlt/servlet-namegt
- lturl-patterngt/ServletRedirectorlt/url-patterngt
- lt/servlet-mappinggt
49
Test class, part 1
- public class TomcatCactusTest extends
ServletTestCase - private SampleServlet servlet
- _at_Before
- public void setUp( ) throws Exception
- servlet new SampleServlet( )
- _at_Test
- public void testIsAuthenticatedTrue( )
- session.setAttribute( "authenticated", "true"
) - boolean actual servlet.isAuthenticated(
request ) - boolean expected true
- assertEquals( expected, actual )
50
Test class, part 2
- _at_Test
- public void testIsAuthenticatedFalse( )
- boolean actual servlet.isAuthenticated(
request ) - boolean expected false
- assertEquals( expected, actual )
- public void beginIsAuthenticatedNoSession(
- WebRequest theRequest )
- theRequest.setAutomaticSession( false )
- _at_Test
- public void testIsAuthenticatedNoSession( )
- boolean actual servlet.isAuthenticated(
request ) - boolean expected false
51
Eclipse view of projectwith Cactus deployment
descriptor
52
Libraries needed
- For the client
- junit.jar from JUnit
- servlet-api.jar from target Application Server
- cactus.jar
- aspectjrt.jar
- commons-httpclient.jar
- commons-logging.jar
- For the server
- junit.jar from JUnit
- Application server libraries
- cactus.jar
- aspectjrt.jar
- commons-logging.jar
53
Libraries added to Eclipse projectfor Cactus
54
Test run on Tomcat Server
55
Cactus Jetty
- Cactus is used to run test cases inside the
container provided by Jetty. - Jetty can run the previous servlet test case that
was run on the Tomcat server. - Since Jetty is embedded, the server will be
started by the test case. - Cactus provides a wrapper to set up tests within
Jetty by doing a combined server start-up and
test case deployment.
56
Cactus test wrapped for Jetty
- // The _at_RunWith line is needed for JUnit 4 to run
test suite - _at_RunWith( AllTests.class )
- public class JettyCactusTest
- public static Test suite( )
- // The next line adapts a JUnit 4 test for
a JUnit 3 runner - Test suite3 new JUnit4TestAdapter(
TomcatCactusTest.class ) - System.setProperty( "cactus.contextURL",
- "http//localhost8080
/test" ) - TestSuite suite new TestSuite( "All
tests with Jetty" ) - suite.addTest( suite3 )
- return new JettyTestSetup( suite )
57
Test run on embedded Jetty server