Cell Cycle Control - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 20
Title:
Cell Cycle Control
Description:
Multiple cyclins direct kinase activity of Cdc28 during different cell-cycle phases ... of S phase and 2) prevents reformation of pre-RC once an origin has fired. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:50
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cell Cycle Control
1
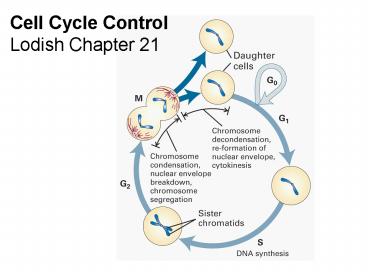
Cell Cycle Control Lodish Chapter 21
2
(No Transcript)
3
Cell in metaphase
DNA
Spindle pole
Mitotic spindle
4
(No Transcript)
5
The budding yeast S. cerevisiae
6
Multiple cyclins direct kinase activity of Cdc28
during different cell-cycle phases
Cdc28-Clb1/2
Cdc28-Clb3/4
Once a cell passes START, it is committed to
undergo division
Cdc28-Cln3
Cdc28-Cln1/2
Cdc28-Clb5/6
7
(No Transcript)
8
CDKs are highly conserved throughout evolution
9
Multiple cdks and cyclins regulate passage of
mammalian cells through the cell cycle
Cdc2/Cdk1-cyclin B Cdc2/Cdk1-cyclin A
Cdk4-cyclin D Cdk6-cyclin D
Restriction point is analogous to START
Cdk2-cyclin A
Cdk2-cyclin E
10
(No Transcript)
11
(No Transcript)
12
(No Transcript)
13
phosphorylation by Cdc25 kinase
14
Degradation of the S phase inhibitor p16 promotes
passage through the restriction point by
inhibiting Retinoblastoma (Rb)
p16
p16
Retinoblastoma is a tumor suppressor
15
Cdc28-Clb ensures that replication at each origin
is initiated only once during the cell cycle
16
Checkpoints in cell cycle regulation
mitosis
securin
Prophase
Anaphase
G1 phase
17
(No Transcript)
18
The mechanism of p53-induced cell-cycle arrest in
response to DNA damage
if DNA damage cannot be repaired
Direct inhibition of PCNA (replication clamp)
p53 is a tumor suppressor
APOPTOSIS
19
G1 and G2 arrest in cells with damaged DNA
depends on the p53 tumor suppressor
p53 mutations drive cells into S phase, they are
found in gt 50 of all cancers.
20
What you need to know Cell cycle is regulated by
cyclin-dependent kinases Passage through
START/restriction point is coupled to decision
to undergo cell division. Therefore, once cell
initiates DNA replication, it is committed to
divide (block replication initiation should
prevent proliferation). Rb inactivation triggers
S phase in humans S phase Cdk activity has dual
role 1) activates replication in beginning of S
phase and 2) prevents reformation of pre-RC once
an origin has fired. You need re-replication
control because you want exactly one and only one
copy of your DNA. p53 (active as a tetrameric
transcription factor) is an important
checkpoint signaling protein, induces p21, a CDK-
and PCNA inhibitor, which leads to cell cycle
arrest, such that DNA can be repaired before the
cell cycle progresses.