BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF OXYGEN - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 11
Title:
BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF OXYGEN
Description:
BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF OXYGEN. Carbohydrate metabolism for ATP ... Hydroxyl radical (OH.) Hypochlorite (HOCl) O2 H2O. NADPH oxidase. Superoxide dismutase ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:119
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF OXYGEN
1
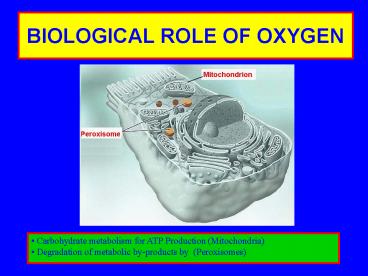
BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF OXYGEN
- Carbohydrate metabolism for ATP Production
(Mitochondria) - Degradation of metabolic by-products by
(Peroxisomes)
2
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Production of Reactive Oxygen Species
3
REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES (ROS)
NADPH O2
NADPH oxidase
Superoxide (O2-.)
Superoxide dismutase
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
Myeloperoxidase
Hypochlorite (HOCl)
Fe2
Catalase
Hydroxyl radical (OH.)
O2 H2O
4
GENERATION OF REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES
5
GENERATION OF ROS AS METABOLIC BY-PRODUCTS
6
GENERATION OF ROS IN IMMUNE DEFENSES
7
OXIDATIVE DAMAGES
8
OXIDATIVE DAMAGE TO LIPIDS
- Increase membrane rigidity
- Reduce activity of membrane-bound enzyme
- Alter activity of membrane receptors
- Alter cell permeability
9
OXIDATIVE DAMAGE TO PROTEINS
- Site-specific amino acid modifications
- Fragmentation of peptide chain
- Aggregation of cross-linked reaction products
- Increased susceptibility to proteolysis
- Degradation of enzymes
10
OXIDATIVE DAMAGE TO NUCLEIC ACIDS
- Mutation
- Single strand breakage
- Nucleotide degradation
- Cross-linking to protein
11
ANTIOXIDANTS
Enzymatic Antioxidants
Superoxide dismutase Catalysis the dismutation of superoxide to hydrogen peroxide.
Catalase Catalysis the dismutation of superoxide to water and oxygen.
Glutathione peroxidase Degradation of hydrogen peroxide
Non-Enzymatic Antioxidants
Vitamin E Trap peroxy radicals in cellular membranes.
Vitamin C Reduce radicals from a variety of sources. Recycling of Vitamin E radicals.
Glutathione Defense against reactive oxygen species.