Normal liver - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 60
Title:
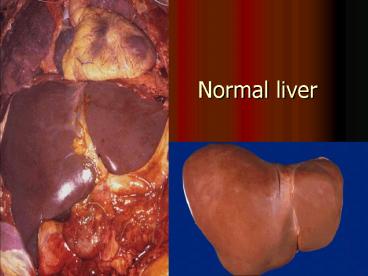
Normal liver
Description:
Cirrhosis is a diffuse process characterized by fibrosis ... Aflatoxin. exposure. Mutant. Hepatic. enzymes. HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA. Hepatocellular carcinoma: ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:131
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Normal liver
1
Normal liver
2
(No Transcript)
3
Fatty Liver
4
Fatty Liver
5
alcoholism. Diabetes mellitus, obesity, and
severe gastrointestinal malabsorption
Fatty Liver
6
(No Transcript)
7
- Cirrhosis is a diffuse
process characterized by fibrosis and the
conversion of the normal liver architecture
in to structurally abnormal nodules. - Cell death,
- Progressive fibrosis,
- Regeneration
8
CLASSIFICATION MORPHOLOGICAL
MICRONODULAR --- lt 3 mms.,
MACRONODULAR --- gt 3 mms., MIXED
AETIOLOGICAL A. Established etiological
associations 1. Alcoholism --- 60 - 70
2. Viral hepatitis (B, C D) 10 - 20
9
3. Metabolic diseases, Haemochromatosis
--- 5 Wilson's disease,
Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, Glycogen
storage diseases - III IV, Cystic
fibrosis, Galactosemia, Hereditary
fructose intolerance, Amino acid
disorders, Abetalipoproteinaemia,
10
4. Biliary --- 5 - 10 Primary,
Secondary,
5. Venous outflow obstruction, Budd -
chiari syndrome, Veno - occlusive
disease, 6. Drugs toxins, 7. Intestinal
bypass for obesity, 8. Others
Sarcoidosis, Carcinomatous fibrosis,
11
PATHOGENESIS OF FIBROSIS
Chronic Inflammation TNF - alpha, TGF -
beta, Interleukin - 1
TOXINS
Ito cell
Hepatic stellate cell
Disruption of extracellular Matrix
FIBROSIS
12
- CLINICAL FEATURES
- Asymptomatic,
- Anorexia,
- Weight loss,
- Weakness --- debilitation,
- Palmar erythema ,
- Spiderangiomas,
- Gynecomastia,
- Gonadal atrophy,
- Amenorrhea,
- Bleeding tendencies
13
Macronodular cirrhosis.
14
Macronodular cirrhosis.
15
Macronodular cirrhosis.
16
Micronodular cirrhosis
17
Micronodular Cirrhosis with Fatty Liver
18
Micronodular Cirrhosis with Fatty Liver
Alcoholism, Wilson's disease, primary biliary
cirrhosis, hemochromatosis.
19
Regenerative nodules are surrounded by fibrous
connective tissue
20
Regenerative nodules Fatty Change
21
Mallory's hyaline, also known as "alcoholic"
hyaline
22
caput medusae
23
Portal hypertension Pathogenesis in
cirrhosis Increased resistance in
sinusoids, Compression of central
veins, Anastomoses of arterial and portal
vessels
- Clinical consequences
- Ascites,
- Porto systemic venous shunts,
- Congestive splenomegaly,
- Hepatic encephalopathy,
24
esophageal varices
25
portal hypertension with splenomegaly
26
Hemosiderosis/ pigment cirrhosis
27
Prussian blue iron stain demonstrates the blue
granules of hemosiderin in hepatocytes and
Kupffer cells.
28
PROGNOSIS DEATH PROGRESSIVE LIVER
FAILURE, PORTAL HYPERTENSION
BLEEDING EPISODES
( esophageal varices )
HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA
29
NORMAL
Exposure
Exposure
Abstinence
Abstinence
STEATOSIS
HEPATITIS
Abstinence
Severe exposure
Continued Exposure
Repeated attacks
CIRRHOSIS
ALCOHOLIC LIVER DISEASE
30
(No Transcript)
31
(No Transcript)
32
TUMOURS OF THE LIVER
BENIGN --Adenomas,
MALIGNANT ( Primary ) --
Hepatoblastoma, -- Angiosarcoma,
-- Hepatocellular carcinoma, --
Cholangiocarcinoma
33
LIVER CELL ADENOMAS
- Young women using oral contraceptives,
- Regress after discontinuance,
- Can be mistaken for hepatocellular ca.,
- Have tendency to rupture
- Severe intraperitoneal hemorrhage,
- Rarely may harbor hepatocellular ca.
34
Hepatic adenoma
35
Hepatic adenoma
36
(No Transcript)
37
HAEMANGIOMA, LIVER
38
Angiosarcoma
- Exposure to ---
- Vinyl chloride,
- Arsenic,
- Thorotrast
- Metastasise widely,
- Kills within a year.
39
PRIMARY CARCINOMAS OF THE LIVER
- Hepatocellular carcinoma,
- ( Hepatoma, Hepatocyte origin ),
- Cholangiocarcinoma
- ( Origin Bile duct epithelium )
40
Hepatocellular carcinoma Epidemiology
- Low incidence areas
- 2 - 4 cases/ yr. / 100,000 popn.,
- - North south America, Europe,
- High incidence areas
- 150 / yr. / 100,000 popn.,
- - Korea, Taiwan, Mozambique,
- Southeast China
41
Hepatocellular carcinoma Epidemiology
- Blacks predominate,
- M F 8 1 in high incidence areas,
- High incidence areas
- Global incidence linked to HBV infection,
- High carrier state --- 200 fold risk,
- Cirrhosis may be absent,
- Seen around 20 40 years of age,
42
Hepatocellular carcinoma Pathogenesis
- Molecular origins -- unclear,
- Cell turn-over ( cirrhosis, HBV, HCV )
- Mutations
- Viral integration ( HBV )
43
HBV infection
Mutant Hepatic enzymes
Aflatoxin exposure
HEPATOCYTE
HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA
44
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- NO HBV INFECTION(Low incidence)
- HCV infection,
- Chronic alcoholism
- Haemochromatosis
- Hereditary Tyrosenemia
- ( 40 )
CIRRHOSIS
HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA
45
Morphology
- Macroscopic-
- Unifocal
- Multifocal
- Diffusely infiltrative
46
Hepatocellular carcinomaClinical features
- Often marked by background cirrhosis and
chronic hepatitis, - Upper abdominal pain,
- Malaise, fatigue, weight loss, mass,
- Jaundice, fever, bleeding /-
47
Hepatocellular carcinomaLaboratory findings
- Alpha fetoprotein -- 60 75 ,
- False positive
- Yolk-sac tumors,
- Cirrhosis,
- Massive liver necrosis,
- Normal pregnancy,
- Fetal distress
- Fetal defects -- spina bifida,
- Small lesions NOT detected
48
Hepatocellular carcinoma
49
Hepatocellular carcinoma
50
Hepatocellular carcinoma
51
Hepatocellular carcinoma
52
Hepatocellular carcinoma
53
HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA- Trabecular pattern
54
Metastases to the liver
55
Metastases to the liver
56
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- DEATH
- With in 10 months,
- Cachexia,
- G.I. Bleeding,
- Hepatic coma,
- Rupture of the tumor
- Hemorrhage
57
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- FIBROLAMELLAR TYPE
- Affects young adults ( 20 40 yrs. ),
- No association with cirrhosis or HBV,
- Better prognosis
- --- 5 yr. Survival - 60
58
Cholangiocarcinoma, liver
59
CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA
60
THANK YOU













![[PPT] Five Crucial Tips for a Healthy Liver PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/9403150.th0.jpg?_=20200222059)
















