Nervous System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 37
Title:
Nervous System
Description:
Influenced by emotional states mediated by the amygdala. ... the amygdala. is involved in. recognizing. the emotional. content of. facial expression ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:77
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Nervous System
1
Nervous System
2
Introduction
- perform the three overlapping functions of
sensory input, integration, and motor output - 2 Main Divisions Central Nervous System include
the brain and spinal cord - Peripheral Nervous System made up of peripheral
nerves, cranial nerves, and spinal nerves - 2 Divisions of Peripheral
- Sensory Division picks up sensory information and
delivers it to the CNS - Motor Division carries information to muscles and
glands - Divisions of the Motor Somatic carries
information to skeletal muscle Autonomic
carries information to smooth muscle, cardiac
muscle, and glands
3
(No Transcript)
4
How it Works
5
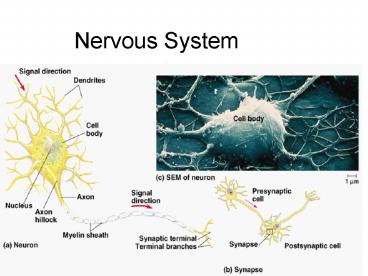
Nerves
- signals of the nervous system are conducted by
nerves. - neuron is the structural and functional unit of
the nervous system. Specialized to transmit
messages - impulses are conducted along a neuron.
- Dentrite ? cell body ? axon hillock ? axon
- Some axons are insulated by a myelin sheath
- Dendrites conduct impulses toward the cell body
- Axons conduct impulses away from the cell body
- Axonal terminals contain vesicles with
neurotransmitters - Axonal terminals are separated from by a gap
- Synaptic cleft gap between adjacent neurons
- Synapse junction between nerves
6
(No Transcript)
7
Types of Neurons
- Sensory Neurons are afferent carry impulse to
CNS - Interneurons link neurons in the CNS
- Motor Neurons carry impulses away from CNS to
effectors, muscle - SUPPORT CELLS Of Nervous System
- Schwann Cells peripheral nervous systemproduce
myelin sheath - Oligodendrocytes CNS myelinating cell
- Microglia CNS phagocytic cell
- Astrocytes CNS form scar tissue, mop up excess
ions, etc, induce synapse formation, connect
neurons to blood vessels - Ependymal CNS ciliated line central canal of
spinal cord line ventricles of brain
8
Simple Nerve Path
9
(No Transcript)
10
2 Main Paths Convergence and Divergence
11
Generating and Impulse
- polarized membrane inside is negative relative
to the outside under resting conditions due to
distribution of ions controlled by Na/K pump
that require ATP - Nerve impulse starts when the membrane of the
nerve depolarizes due to some stimulus, chemical,
temp. changes, mechanical ect. - Depolarization is caused by the influx of Na
which causes the membrane to become more
positive. This starts an action potential, or
nerve impulse. They follow the all or none law!!! - The membrane will repolarize when K leaves the
cell setting the membrane back to resting
potential or polarized - This de and repolarization continues down the
nerve until it reaches another nerve to pass on
the impulse or until it reaches an effector.
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
Saltatory Conduction
Appear the jump from node to node. Speed of
impulses is much faster on myelinated nerves then
unmyelinated ones. Speed also increases with
increase in diameter. Ex.) 120m/s skeletal muscle
.5m/s skin
15
Neuron Communication
16
2 Divisions
- Central nervous system (CNS)-Brain and spinal
cord. - contain fluid-filled spaces which contain
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). - The central canal of the spinal cord is
continuous with the ventricles of the brain. - White matter is composed of bundles of myelinated
axons - Gray matter consists of unmyelinated axons,
nuclei, and dendrites. - Peripheral nervous system.
- Everything outside the CNS.
17
PNS
- Helps to maintain homeostasis
- Made of cranial nerves that originate in the
brain and innervate the head and upper body
and----Paired spinal nerves that originate in the
spinal cord and innervate the entire body. - There are efferent and afferent nerves in the
PNS---efferent carry impulses to effectors like
muscles or glands these are also called motor
neurons. - Afferent carry impulses back to the CNS and are
called sensory neurons
18
(No Transcript)
19
Fight or Flight parasympathetic and sympathetic
are the 2 divisions of the Autonomic nervous
system which functions without conscious effort
controls visceral activities regulates smooth
muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
20
Classifying PNS Nerves
- General somatic efferent fiber- carry motor
impulses from CNS to skeletal muscles - General visceral efferent fibers- carry motor
impulses away from CNS to smooth muscles and
glands - General somatic afferent fibers- carry sensory
impulses to CNS from skin and skeletal muscles - General visceral afferent fibers- carry sensory
impulses to CNS from blood vessels and internal
organs - Special somatic efferent fibers- carry motor
impulses from brain to muscles used in chewing,
swallowing, speaking, and forming facial
expressions - Special visceral afferent fibers- carry sensory
impulses to brain from olfactory and taste
receptors - Special somatic afferent fibers- carry sensory
impulses to brain from receptors of sight,
hearing, and equilibrium
21
Cranial Nerves
22
Spinal Nerves31 pairs 8 cervical (C1 to C8) 12
thoracic (T1 to T12) 5 lumbar (L1 to L5) 5
sacral (S1 to S5) 1 coccygeal (Co)
23
CNSThe Brain and Spinal Cord
- Spinal Cord Carries impulses to and from the
brain as well as playing a major role in reflexes
both somatic and autonomic - extends foramen magnum to 2nd lumbar vertebra
- 31 segments each with a pair of nerves
- Central canal carries CSF
- CSF- Cerebrospinal fluid--Forms a watery cushion
to protect the brain, Similar to blood plasma
composition, Circulated in arachnoid space,
ventricles, and central canal of the spinal cord - Ventricles- interconnected cavities within
cerebral hemispheres and brain stem continuous
with central canal of spinal cord filled with
cerebrospinal fluid (csf)
24
Ventricles
25
(No Transcript)
26
Spinal Cord Reflex
27
The Brain
- Functions interprets sensations, determines
perception, stores memory, reasoning, makes
decisions, coordinates muscular movements,
regulates visceral activities, and determines
personality
28
Development
29
Structure and Function
- Brain stem--Consists of the medulla oblongata,
pons, and midbrain. - Functions in homeostasis, coordination of
movement, conduction of impulses to higher brain
centers - Medulla Oblongata- Breathing, heart and blood
vessel activity, swallowing, vomiting, digestion,
and Relays information to and from higher brain
centers - Pons- involved in the regulation of visceral
activities such as breathing and relays info. to
higher brain - Midbrain-integration of sensory information, in
the regulation of visual and auditory reflexes,
and relays as well
30
Cont
- Reticular Formation- network of nerve fibers
scattered throughout the brain stem connects to
centers of hypothalamus, basal nuclei,
cerebellum, and cerebrum - filters incoming sensory information
- arouses cerebral cortex into state of
wakefulness so controls sleep. Involved in motor
control of visceral organs - Cerebellum- develops from the metencephalon.
- Functions to error-check and coordinate motor
activities, and perceptual and cognitive factors.
Relays sensory information about joints, muscles,
sight, and sound to the cerebrum. Coordinates
motor commands issued by the cerebrum. Maintains
posture
31
Cont
- Epithalamus, thalamus, and hypothalamus are
derived from the embryonic diencephalon - Thalamus- gateway for sensory impulses heading to
cerebral cortex, receives all sensory impulses
(except smell), and channels impulses to
appropriate part of cerebral cortex for
interpretation - Hypothalamus- Regulates autonomic activity
involved in thermoregulation, hunger, thirst,
sexual and mating behavior, etc part of the
limbic system (emotions) - The pituitary gland is attached to the
hypothalamus - Epithalamus- contains the pineal gland which is
involved in hormone release
32
Cont
- Cerebrum is derived from the embryonic
telencephalon it is the most highly evolved
structure in the mammalian brain. - divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres.
- corpus callosum is the major connection between
the two hemispheres. - The left hemisphere is responsible for the right
side of the body. The right hemisphere is
responsible for the left side of the body. - Functions interpretation, initiating voluntary
movements, storing memory, retrieving memory,
reasoning, center for intelligence and
personality
33
(No Transcript)
34
Cont
- Frontal Lobe Association Areas concentrating,
planning, problem solving, judging - Parietal Lobe Association Areas understanding
speech, using words to express thought - Temporal Lobe Association Areas remember visual
scenes, remember music, remember complex patterns - Occipital Lobe Association Areas combine visual
images with other sensory experiences - Fact- 90 of population, left hemisphere is
dominant, some are right dominant, and others are
equal
35
Memory
- Short-term memory stored in the frontal lobes.
- The establishment of long-term memory involves
the hippocampus. changes structure and function
of neurons when you make a new connection. - 60 trillion possible connections so there is
plenty of free space. - The transfer of information from short-term to
long-term memory. - Is enhanced by repetition (remember that when you
are preparing for an exam). - Influenced by emotional states mediated by the
amygdala. - Influenced by association with previously stored
information.
36
Emotions
- limbic system is composed of the hippocampus,
olfactory cortex, inner portions of the cortexs
lobes, and parts of the thalamus and
hypothalamus. - Mediates basic emotions (fear, anger), involved
in emotional bonding, establishes emotional
memory - For example, the amygdala is involved in
recognizing the emotional content of facial
expression
37
References
- Jack Brown M.S. Biology
- Shier,David, Jackie Butler, Ricki Lewis Holes
Human Anatomy and Physiology 10th edition 2004
McGraw-Hill - Marieb, Elaine Essentials of Human Anatomy and
Physiology 7th edition. 2003 Pearson Education
Inc Benjamin Cummings pub. - Microsoft Encarta Encyclopedia 2004
- Starr and Taggart The Unity and Diversity of
Life 10th edition 2004 Thomson Brookes/Cole - Campbell and Reece Biology 6th edition 2002
Benjamin Cummings. - Raven and Johnson Holt Biology 2004 Holt,
Rinehart and Winston.