Effect of Drug A on BP - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 10
Title:
Effect of Drug A on BP
Description:
Vagal stimulation delivered in the neck region, indicated by red bar. ... Atropine. Cocaine. Dexamphetamine. Dopamine. Edrophonium. Ephedrine. Epinephrine ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:18
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Effect of Drug A on BP
1
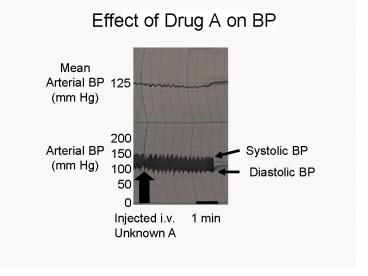
Effect of Drug A on BP
MeanArterial BP(mm Hg)
125
200
Systolic BP
Arterial BP(mm Hg)
150
100
Diastolic BP
50
0
Injected i.v.Unknown A
1 min
2
Vagal Stimulation Before After
Q1 How does vagal stimulation reduce BP?
(A1) Q2 List two mechanisms by which vagal
responses could be blocked (A2)
Vagal stimulation delivered in the neck region,
indicated by red bar.
3
ACh (i.v.) Before After
Q3 List two mechanisms by which a high dose of
ACh could cause a decrease in mean
arterial BP (A3) Q4 What mechanism would
predominate at low doses of ACh? (A4) Q5 What
kind of drug could block the effects of ACh as
shown?(A5)
4
Carotid Occlusion Before After
Q6 How could a carotid occlusion (on both sides)
produce a pressor response? (A6) Q7 Name
two different classes of drugs that could block
such a pressor response (although it was not
blocked here). (A7)
5
Epinephrine
Q8 Name 4 receptor subtypes stimulated by
epinephrine. (A8) Q9 Which receptors are
responsible for the rise in diastolic BP?
(A9) Q10 Which receptors produce the increase in
pulse pressure? (A10) Q11 What is the primary
mechanism for the decline in Epinephrines
effect with time? (A11)
This initial hypotensive transient was an
atypical volume effect observed with saline
injections as well. Not every experiment is
perfect!
6
Norepinephrine
Q12 Compare contrast the effects produced by
norepinephrine epinephrine. Do they
stimulate the same identical receptor
subclasses? (A12)
7
Isoproterenol
Q13 What receptors does isoproterenol stimulate?
(A13) Q14 Which receptor subtype produces the
fall in diastolic BP which produces
the increase in pulse pressure? (A14)
8
High Dose ACh
1x Dose
3x Dose
1x Dose
Q15 How do you explain the response produced by
3x Ach vs. 1x ACh after Unknown A was
given? (A15) Q16 What mechanism could account
for the presser response seen after a
delay when the 3x dose of ACh was given? (A16)
3x 3 times higher dose
9
Summary
Q17. What drug class does Unknown A belong to?
(see next slide for a list of possibilities)
10
Drug Unknown Options
- Acetylcholine
- Angiotensin II
- Atropine
- Cocaine
- Dexamphetamine
- Dopamine
- Edrophonium
- Ephedrine
- Epinephrine
- Hexamethonium or trimethaphan
- Isoproterenol
- Neostigmine
- Nicotine
- Norepinephrine
- Phentolamine
- Prazosin
- Propranolol
- Reserpine
- Sarin
- Tyramine