Lenses, Crescents, Bleeds in the Head - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
Lenses, Crescents, Bleeds in the Head
Description:
Onset usually in young adulthood. Women men. Affects neurons in white matter of brain ... Ataxia. Dysarthria. Dysphagia. Nystagmus, optic neuritis, diplopia ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:20
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Lenses, Crescents, Bleeds in the Head
1
(No Transcript)
2
(No Transcript)
3
(No Transcript)
4
Multiple Sclerosis
- Jaimie Lynn Maines, MS-IV
- SYB 3
- 5 March 2008
5
What is Multiple Sclerosis?
- Chronic, inflammatory, demyelinating disease that
affects the CNS - Onset usually in young adulthood
- Women gt men
- Affects neurons in white matter of brain and
spinal cord - Destroys oligodendrocytes ? loss of myelin sheath
6
Signs and Symptoms
- Changes in sensation (hypoesthesia)
- Muscle weakness
- Abnormal muscle spasms
- Difficulty with movement
- Ataxia
- Dysarthria
- Dysphagia
- Nystagmus, optic neuritis, diplopia
- Fatigue and acute or chronic pain syndromes
- Bladder and bowel difficulties
- Cognitive impairment, depression
- Lhermittes Sign
- Classic finding in MS
7
Disease Course and Clinical Subtypes
- Relapsing Form - new symptoms occur in discrete
attacks - Progressive Form - new symptoms slowly accumulate
over time - Relapse-Remitting Form - between attacks,
symptoms resolve completely, but permanent
neurological problems persist - May develop Secondary Progressive MS
8
Diagnosis
- Difficult to diagnose in early stages
- Definitive diagnosis cannot be made until other
possible causes for symptoms have been ruled out - In Relapsing-Remitting there must be evidence of
at least 2 anatomically separate demyelinating
events separated by at least 30 days - In Primary Progressive there must be slow
progression of si/sx over at least 6 months
9
McDonald Criteria
- Clinical data alone - 2 separate episodes of
neurologic symptoms characteristic of MS,
consistent PE - MRI - areas of demyelination appear as bright
spots (active plaques enhance with Gad) - CSF - evidence of chronic inflammation
- Oligoclonal bands combined with MRI and PE can
make definitive diagnosis - Visual or Somatosensory Evoked Potentials - brain
with MS responds less actively to stimulation
10
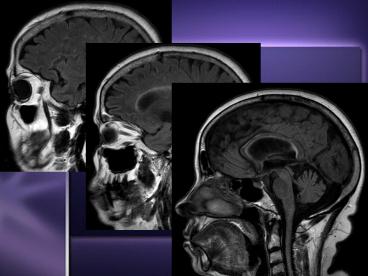
Imaging Studies
- MRI
- Test of choice to support clinical diagnosis
- Charactertistic lesion - cerebral or spinal
plaque periventricular region, corpus callosum,
centrum semiovale, deep white matter structures,
basal ganglia - Typically ovoid in appearance, arranged at right
angles to corpus callosum - Hyperintense on T2 MRI, hypointense on T1
- Diffusion imaging may identify plaques better
- Gad-enhancing plaques ? active lesions
- Discrete region of demyelination
11
(No Transcript)
12
Differential Diagnosis
- Neuromyelitis Optica
- Autoimmune disease - attack of optic nerves and
spinal cord - Stroke
- Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis
- Immune mediated disease of brain following viral
infection or vaccination multiple inflammatory
cell deposits found in white matter - Lyme Disease
- Tumors
- Lupus
13
Medical Treatment
- There is NO cure
- Treatments aimed at returning function following
an attack, preventing new attacks, and preventing
disability - IV steroids for acute attacks
- Interferon - disease modifying treatment
- Neurorehabilitation to ease burden of progressive
impairment