Simple%20Microscope - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Simple%20Microscope
Description:
Staining. Staining is a biochemical technique of adding a class-specific (DNA, proteins, ... Stains and dyes are frequently used in biology and medicine to highlight ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:174
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Simple%20Microscope
1
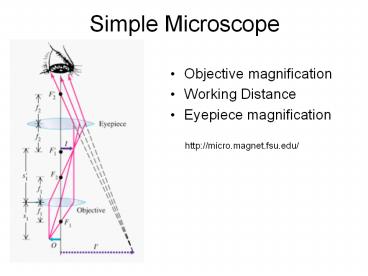
Simple Microscope
- Objective magnification
- Working Distance
- Eyepiece magnification
http//micro.magnet.fsu.edu/
2
Illumination (Bright Field)
Summary the field of view should be (reasonably)
evenly illuminated the illuminating train should
be able to fully illuminate the aperture of an
objective of NA 1.0 the light source should be
focused in the object in critical illumination,
the light bulb is the light source in Köhler
illumination, the light source is an iris
diaphragm attached to the illuminator (the field
stop) the condenser iris is adjusted for each
objective
- Simple mirror (historical microscope)
- Critical illumination
- Koehler Illumination
3
(No Transcript)
4
Staining
- Staining is a biochemical technique of adding a
class-specific (DNA, proteins, lipids,
carbohydrates) dye to a substrate to qualify or
quantify the presence of a specific compound. - Stains and dyes are frequently used in biology
and medicine to highlight structures in
biological tissues for viewing, often with the
aid of different microscopes.
5
Dark Field microscopy
Poor-mans dark field
bright
Dark
6
Dark Field
7
DIC (Differential Interference Contrast)
Wollaston Prism
Optical Path Length (OPL) n t
OPL difference 2pidelta/lambda
delta(n2 - n1) t
Nomarski
8
Phase Contrast
- Converts phase change to Amplitude change
http//micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/phas
econtrast/phaseindex.html
9
Phase Contrast
10
Phase Contrast
- Converts phase change to Amplitude change
11
- Converts phase change to Amplitude change
f(x,y) lt lt 1
Without PC optics
PSF(kx,ky) is the Point spread function (PSF)
With PC optics
12
Furhter Contrast Enhancement in Phase Contrast
Microscopy
- Select part of illumination
Reduce the size of the fat arrow
13
Proper Choice of the phase shift reverses contrast