Upper and Lower Bounds - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 8
Title:
Upper and Lower Bounds
Description:
She used 23.7 litres of petrol correct to the nearest tenth of a litre. Workout the upper bounds for the petrol consumption for Kathy's journey. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:951
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Upper and Lower Bounds
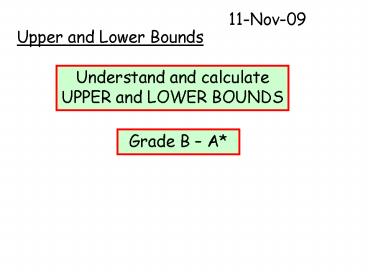
1
11-Nov-09
Upper and Lower Bounds
Understand and calculate UPPER and LOWER BOUNDS
Grade B A
2
Its 11 cm long
Its 11 cm long
Often, size is rounded off to the units that we
wish to use. We would say , for example, that
both of the fish are 11 cm long. So a fish 11 cm
long could be 10.5 cm to 11.5 cm long.
3
Its 11 cm long
Bounds are always half the units being used
10.5 cm is the LOWER BOUND
Its 11 cm long
11.5 cm is the UPPER BOUND
4
Here are some more examples of upper and lower
bounds
5
10 cm
What are the upper and lower bound areas?
4 cm
Lower Bound Area ? 9.5 x 3.5 33.25 cm2 Upper
Bound Area ? 10.5 x 4.5 47.25 cm2
6
What are the upper and lower bound volumes?
8 cm
6 cm
20 cm
Lower Bound Vol ? 19.5 x 5.5 x 7.5 804.4
cm3 Upper Bound Vol ? 20.5 x 6.5 x 8.5 1132.6
cm3
7
Calculate the area upper and lower bounds
LB 51 UB 88
1.
9 cm
2.
LB 16.6 UB 23.6
LB 74.8 UB 93.8
3.
7 cm
4 cm
12 cm
12 cm
10 cm
4.
5.
LB 167.8 UB 171.3
4 cm
5.4 cm
2.3 cm
7.7 cm
LB 89.9 UB 93.3
6. A car travels at 50 mph for 4 hours and 15
minutes. What distance has it travelled? 7. An
train travels a distance of 15 miles in 12
minutes. What is the trains speed?
LB 210 UB 215
LB 69.6 mph UB 80.9 mph
8
Kathy drove 238 miles correct to the nearest
mile. She used 23.7 litres of petrol correct to
the nearest tenth of a litre. Workout the upper
bounds for the petrol consumption for Kathys
journey. Give your answer to 2 d.p.
Petrol consumption Number of miles travelled
Number of litres of petrol used
Upper Bound Petrol consumption 238.5
23.65
10.08 miles/litre