Flow of Genetic Information - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 27
Title:
Flow of Genetic Information
Description:
DNA chains are synthesized 5'- 3' DNA replication is semidiscontinuous ... have to take a detour to make a 0.13 mile Okazaki fragment. and then rejoin the truck ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:49
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Flow of Genetic Information
1
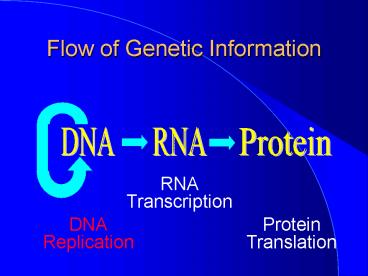
Flow of Genetic Information
DNA
RNA
Protein
RNA Transcription
DNA Replication
Protein Translation
2
What were going to talk about
- DNA replication is semiconservative
- DNA chains are synthesized 5- 3
- DNA replication is semidiscontinuous
- Components necessary to replicate a DNA helix.
- Other relevant polymerases and polymerase factoids
3
Possible Mechanisms of DNA Replication
Semiconservative
Conservative
Dispersive
4
DNA Replication is Semiconservative
- In 1958 Messelson and Stahl carried out
experiments that demonstrated that DNA
replication is semiconservative
Semiconservative means that each template strand
directs the synthesis of a new strand. Thus each
new molecule of double-stranded DNA consists of a
new strand and an old strand
We have a winner
5
What were going to talk about
- DNA replication is semiconservative
- DNA chains are synthesized 5- 3
- DNA replication is semidiscontinuous
- Components necessary to replicate a DNA helix.
- Other relevant polymerases and polymerase factoids
6
Elongation of DNA Chains
- DNA chains elongate by the addition of a dNTP
molecule to the 3-OH group at the end of an
existing chain of DNA or RNA
A
G
3
7
Polymerization Reaction
G
..G3-OH dATP
3
A
.GA3-OH PPi
3
8
DNA Polymerases
- DNA polymerases catalyze the addition of a
deoxyribonucleotide to the 3-OH of the chain - They only work in the 5-3 direction
- This means they have a 5-3 polymerase activity
- Specificity of the polymerases is directed by the
template - i.e. the polymerase can bind any of the dNTPs but
only the one that pairs correctly with the
template strand will be added to the chain
9
Polymerase Mediated Strand Elongation
10
Reality Check!!!!!!!
- What did Anita just spend an hour telling you
yesterday? - DNA is double-stranded
- DNA is also supercoiled and highly packaged
- So how is double-stranded supercoiled DNA
replicated in the cell?
11
DNA Replication in vivo Occurs at Replication
Forks
Origin
12
Replication is Bidirectional
- Both strands are replicated at the same time and
two forks proceed in opposite directions from one
another with both strands being replicated on each
13
What were going to talk about
- DNA replication is semiconservative
- DNA chains are synthesized 5- 3
- DNA replication is semidiscontinuous
- Components necessary to replicate a DNA helix.
- Other relevant polymerases
- e.g. Reverse transcriptase
14
Strand Synthesis at a Replication Fork
5
3
Pol
Pol
3
5
15
Semidiscontinuous DNA Replication
- One strand (leading strand) is made in a
continuous manner and the other (lagging strand)
is made in a discontinuous manner - i.e. its made in a series of small fragments
(called Okazaki fragments) that are synthesized
5-3
3
5
5
3
Pol
3
3
3
5
5
5
3
5
16
What were going to talk about
- DNA replication is semiconservative
- DNA chains are synthesized 5- 3
- DNA replication is semidiscontinuous
- Components necessary to replicate a DNA helix.
- Other relevant polymerases
- e.g. Reverse transcriptase
17
Additional Proteins Required to Replicate a DNA
Helix
- A lot of energy is required to pull the DNA helix
apart (helicases) - Once it is pulled apart it wants to go back
together (single-stranded binding protein) - Proteins are also needed to prime DNA synthesis
(primases) - DNA polymerases will only add dNTPs to the
existing 3-OH of nucleic acid chains
18
Replication Proteins
- Helicases pull the two DNA strands apart in a
manner that is energy dependent - Once the strands are separated the SSB protein
coats them and keeps them from reannealing
Single Stranded DNA Binding Protein (SSB)
Helicase
Pol
5
Ligase
Topoisomerases
5
19
Replication Proteins (contd)
- Topoisomerases act in front of the fork to
relieve the supercoils that accumulate - DNA ligase seals the nicks that are left between
the Okazaki fragments even after other repair
polymerases fill in the gaps
3
20
Other Polymerases Help Out
- The primase works by laying down a ribonucleotide
primer (an RNA primer) - Other polymerases come along and fill the gaps
that are left in the Okazaki fragments on the
lagging strand - These polymerases take advantage of other
activities besides their 5-3 polymerase activity
5
3
3
5
21
Polymerases are Versatile
- 5-3 polymerase activity
- The DNA polymerization activity that weve
discussed ad nauseum - 3-5 exonuclease activity
- This is a proofreading function that allows the
polymerase to say Oops! I goofed- I need to take
out that last base and fix it!! - Some also have a 5-3 exonuclease activity
- Used for DNA repair and to excise the RNA primers
laid down to make Okazaki fragments
22
Replication Systems
- Prokarotes
- DNA polymerases
- I, II, and III
- Helicases (DnaB)
- Single-stranded Binding Protein (SSB)
- Primase (DnaG)
- Sliding Clamp (b subunit)
- Eukaryotes
- DNA polymerases
- a, b, d, g, e
- Helicases (MCM?)
- Single-stranded Binding Protein (RP-A)
- Primase (pola)
- Sliding Clamp (PCNA)
23
Polymerases are actually Clamped to their DNA
substrate
Either a subunit of the polymerase
(prokaryotic) or an accessory protein
(eukaryotic) actually form a ring around the DNA
and clamp the polymerase
24
What were going to talk about
- DNA replication is semiconservative
- DNA chains are synthesized 5- 3
- DNA replication is semidiscontinuous
- Components necessary to replicate a DNA helix.
- Other relevant polymerase factoids and other
relevant polymerases
25
Polymerases are Very Efficient Enzymes
- Polymerases that replicate the DNA are very
processive and very precise (due in part to the
clamp) - If the DNA helix was 1 M in diameter
-The replication fork would move at 375 mph
-The replication machinery would be about the
size of a FedEx truck
-An error would occur only once every 106 miles
-Once every second one deliveryman from the truck
would have to take a detour to make a 0.13 mile
Okazaki fragment and then rejoin the truck
Baker and Bell, Cell 92, 295 (1998)
26
Other polymerases of Interest
- RNA polymerase (soon to be appearing in an
upcoming lecture) - Reverse transcriptase
- Uses the RNA genome of the HIV virus as a
template to create a DNA copy and thus replicate
the virus- inhibited by AZT - Thermostable polymerases
- Can be used to carry out the polymerase chain
reaction (PCR) to amplify DNA samples
27
What do I need to Know for the TEST????
- DNA replication is semiconservative (what does
that mean?) - Polymerases replicate DNA and can only do so by
adding a nucleotide to the 3-OH of an existing
DNA chain- Specificity?? - DNA synthesis is semidiscontinuous
- Accessory proteins are required to duplicate the
double-stranded DNA helix - Polymerases have multiple enzymatic activities
and are very efficient enzymes