Define: - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title: Define:
1
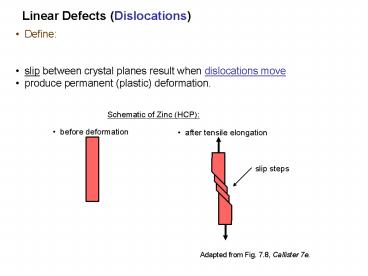
Linear Defects (Dislocations)
- Define
- slip between crystal planes result when
dislocations move - produce permanent (plastic) deformation.
Schematic of Zinc (HCP)
before deformation
after tensile elongation
slip steps
Adapted from Fig. 7.8, Callister 7e.
2
Type of Linear Defects (Dislocations)
- Edge dislocation (?) -- occurs when an
_________________________________ inserted in a
crystal structure - a linear defect that centers around the line
that is defined by extra half-plane of atoms - Dislocation line the line that extends along the
end of the extra half-plane of atoms is
perpendicular to plane of page (for an edge
dislocation) - Leads to lattice distortion
- Burgers vector, b measure of magnitude and
direction of lattice distortion associated with a
dislocation - b is perpendicular to dislocation line (for an
edge dislocation)
Above dislocation line, atoms __________________
Below dislocation line, atoms _________________
Less lattice distortion as distance from
dislocation line increases
3
Edge dislocation (?)
Lattice planes
Edge dislocation line
4
Type of Linear Defects (Dislocations)
- Screw dislocation C
- A crystal is cut along a plane only ½ the way
through and ½ of crystal is twisted - Formed by shear stress
- __________________________________________________
___________ - b is parallel to dislocation line
Lattice planes
- Burgers vector, b measure of magnitude and
direction of lattice distortion associated with a
dislocation
5
Type of Linear Defects (Dislocations)
- Mixed Dislocation
- Most solids exhibit mixed dislocations exhibit
components of edge and screw dislocations.
6
Edge, Screw, and Mixed Dislocations
Adapted from Fig. 4.5, Callister 7e.
7
- Dislocations are visible by electron microscopy
- Dislocations are introduced via
- Dislocation density increases with plastic
(permanent) deformation - Due to dislocations, metals possess high
plasticity characteristics ductility and
malleability.
Titanium Alloy TEM image
Adapted from Fig. 4.6, Callister 7e.
8
f12_20_pg434
Magnification limit
1 nm
10,000,000X
1,000,000X
50,000X
2000X
9
Interfacial Defects
- Interfacial Defects
- Boundaries with 2 dimensions
- typically separate regions with
__________________________________________________
_______________ - two types
1. External Surface - crystal structure
terminates - surface atoms not bonded to
max nearest neighbors higher surface energy
10
- 2. Grain Boundaries
- Separates two small grains or crystals having
different crystallographic orientations in
polycrystalline materials (p. 64, next slide) - the interface separating two adjoining grains
having two _______________________________________
_____________
High degree of crystallographic misalignment
Low degree of crystallographic misalignment
Adapted from Fig. 4.7, Callister 7e.
- Features
- Different degrees of atom misalignment
(depicted) - Atoms bonded less regularly along grain boundary
- Higher energy
- Higher chemical reactivity
- Impurity atoms tend to segregate along grain
boundaries
11
Polycrystalline refers to crystalline materials
that are composed of more than one crystal or
grains (collection of small crystals) see pp
64-65. Two grains meet along a grain boundary
(d).
12
- Grain Boundaries
- disrupt the motion of dislocations through a
material improve strength - - a dislocation passing into grain B will have
to _______________________________________________
_________ (p. 189)
Fig. 7.14
13
- Grain Boundaries Formation via Solidification
- Solidification- result of casting (cooling) of
molten material - 2 steps
- Nuclei form
- Nuclei grow to form crystals grain structure
- Start with a molten material all liquid
- Crystals grow until they meet each other
- See also Fig. 3.17 (polycrystalline materials)
14
Ceramic Defects (Sec. 12.5)
Point Defects in Ceramics a. Vacancy
Pair Schottky Defect - in an ionic solid, a
defect consisting of a ___________________________
____________________________ - maintains
charge neutrality b. Vacancy Interstitial
Frenkel Defect - in an ionic solid, a
______________ __________________________ cation
leaves normal position and goes to interstitial
site -maintains charge neutrality