Chem 108 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 35
Title:
Chem 108
Description:
Based on the use of outer shell electrons, what is a reasonable ... Protection against sunburn is needed. Reduce time in the sun between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:41
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chem 108
1
Chem 108
- Environmental chem
2
- 1 A diatomic molecule has the structure shown.
Based on the use of outer shell electrons, what
is a reasonable identity for "X" in the
structure? - A)X Ne B)X F C)X O D)X N
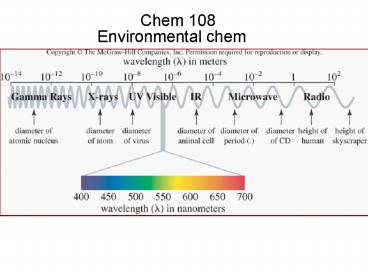
- 2 For these three parts of the electromagnetic
spectrum, which is the correct order of
increasing wavelength? - A) visible, ultraviolet, infrared
- B) infrared, visible, ultraviolet
- C) ultraviolet, visible, infrared
- D) ultraviolet, infrared, visible
3
Light
- Electromagnetic spectrum The entire range of
radiant energy - Visible spectrum that which we see with our eyes
- Wavelength The distance between successive
peaks of a wave l - Frequency the number of waves passing a point in
unit time n - C ln
4
Light
- For Electromagnetic radiation
- Speed of Light 3x108 m/s(in a vacuum)
- Its not just a good Idea its the law its the
fastest speed there is - From this
- Frequencync/l wavelength lc/n
- Red light has a wavelength of 650 nm what is its
frequency - blue light has a frequency of 7.5 x10 14 What is
its wavelength
5
Light
- The shorter the wavelength the higher the
frequency the more energy light has - Order the following in order of highest to lowest
energy - Infrared microwave visible ultraviolet
- (These are not in order)
- Order them in from longest to shortest wavelength
6
Light
- Light is quantized that is to say the smallest
step you can have is one wavelength - no half steps.
- We express this using Plancks constant
- Ehn
- We view light as packets of waves containing a
specific amount of energy. - The effect of this is that it interacts with
matter in stepwise fashion
7
Light
- When light interacts with matter it interacts in
a quantized way - First recognized by Einstein as the photoelectric
effect (why he actually won the Nobel prize) - its not the intensity of a light source that
causes interaction its the wavelength. - you will never tan under visible or IR light
only under uv light
8
IR
UV
Vis
9
What does UV do
- Breaks bonds
10
Biological Effects of Ultraviolet Radiation
- The consequences depend primarily on
- The energy associated with the radiation, and
- The sensitivity of the organism to that radiation.
2.7
11
What does UV do to the body
- Breaks bonds
- broken bonds typically break so that each atom is
electron deficient so they go around looking for
a way to resolve that. - dimerization of DNA is a common solution
- DNA is electron rich
- DNA has to be able to be copied dimers interfere
with copying - mistakes in copying lead to cancer
12
How ozone helps us
13
- UV-A 320 -400
- least energetic most prevalent
- UV-B 280-320
- More damaging than UV-A most absorbed by Ozone
- UV-C 200-280
- Most damaging lowest presence as we are screened
by O2 and O3 in stratosphere
14
The UV index
- http//www.epa.gov/sunwise/uviscale.html
15
The UV index
- 2 or less Low
- A UV Index reading of 2 or less means low danger
from the sun's UV rays for the average person - Wear sunglasses on bright days. In winter,
reflection off snow can nearly double UV
strength. - If you burn easily, cover up and use sunscreen.
- Look Out Below
- Snow and water can reflect the sun's rays. Skiers
and swimmers should take special care. Wear
sunglasses or goggles, and apply sunscreen with
an SPF of at least 15. Remember to protect areas
that could be exposed to UV rays by the sun's
reflection, including under the chin and nose. - 3 - 5 Moderate
- A UV Index reading of 3 to 5 means moderate risk
of harm from unprotected sun exposure. - Take precautions, such as covering up, if you
will be outside. - Stay in shade near midday when the sun is
strongest. - Me and My Shadow
- An easy way to tell how much UV exposure you are
getting is to look for your shadow - If your shadow is taller than you are (in the
early morning and late afternoon), your UV
exposure is likely to be low. - If your shadow is shorter than you are (around
midday), you are being exposed to high levels of
UV radiation. Seek shade and protect your skin
and eyes.
16
The UV index
- 6 - 7 High
- A UV Index reading of 6 to 7 means high risk of
harm from unprotected sun exposure. Apply a
sunscreen with a SPF of at least 15. Wear a
wide-brim hat and sunglasses to protect your
eyes. - Protection against sunburn is needed.
- Reduce time in the sun between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Cover up, wear a hat and sunglasses, and use
sunscreen. - Made in the Shades
- Wearing sunglasses protects the lids of your eyes
as well as the lens. - 8 - 10 Very High
- A UV Index reading of 8 to 10 means very high
risk of harm from unprotected sun exposure.
Minimize sun exposure during midday hours, from
10 a.m. to 4 p.m. Protect yourself by liberally
applying a sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15.
Wear protective clothing and sunglasses to
protect the eyes. - Take extra precautions. Unprotected skin will be
damaged and can burn quickly. - Minimize sun exposure between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
Otherwise, seek shade, cover up, wear a hat and
sunglasses, and use sunscreen. - Stay in the Game
- Be careful during routine outdoor activities such
as gardening or playing sports. Remember that UV
exposure is especially strong if you are working
or playing between the peak hours of 10 a.m. and
4 p.m. Don't forget that spectators, as well as
participants, need to wear sunscreen and eye
protection to avoid too much sun.
17
The UV index
- 11
- A UV Index reading of 11 or higher means extreme
risk of harm from unprotected sun exposure. Try
to avoid sun exposure during midday hours, from
10 a.m. to 4 p.m. Apply sunscreen with an SPF of
at least 15 liberally every 2 hours. - Take all precautions. Unprotected skin can burn
in minutes. Beachgoers should know that white
sand and other bright surfaces reflect UV and
will increase UV exposure. - Try to avoid sun exposure between 10 a.m. and 4
p.m. - Seek shade, cover up, wear a hat and sunglasses,
and use sunscreen. - Beat the Heat
- It is possible to go outside when the UV Index is
11 or higher. Make sure you always seek shade,
wear a hat, cover up, wear 99-100 UV-blocking
sunglasses, and use sunscreen. Or you can opt to
stay indoors and take the opportunity to relax
with a good book rather than risk dangerous
levels of sun exposure.
18
How ozone helps us
- For every 6 decrease in Ozone we expect to see a
12 increase in skin cancer - Fortunately is mostly non melanoma type
- From 1973 ozone measured about Arosa Switzerland
has decreased Approximately 6. (Fig 2.17)
19
(No Transcript)
20
?????
?240-320
21
How is Ozone Made
- The Chapman Cycle
- Step 1
- O2 ????? ? 2O
- Step 2
- O O2? O3
- UV absorbtion by Ozone
- O3 ?240-320 ? O O2
Step 3 O O3? 2O2
22
Where ozone is found
23
How much is there
- Not much
- 1018 to 1019 Molecules m3 in the stratosphere
- thats 183 ppb (0.2 ppm)
- If you brought it together as a isolated band at
1 ATM it would be 1/8th inch thick - A lot
- 3 x 108 Tons Formed and consumed daily
24
What governs the amount of stratospheric ozone
- The amount of UV radiation
- more at the poles than at the equator.
- the incident angle of radiation is higher at the
poles - Seasonal variation Summer levels are Higer than
winter levels - 22 year Solar cycle
- Distribution by upper atmospheric winds
- Both natural and man made chemicals that degrade
ozone.
25
The Antarctic Ozone hole
From the NASA Web Site
26
What do we think is causing the Hole.
- Presence of Chlorofluorocarbons in the
stratosphere
27
The Evidence
As ClO. concentrations increase, ozone
concentration decreases. We will see that ClO.
is a product of CFC degradation.
2.9
28
l ? Cl . .CCl2F
2Cl . ? Cl2
29
(No Transcript)
30
Catalytic Cycles For Ozone Loss General Idea
O3 X ? XO O2 O XO ? X O2 Net O3
O ? 2 O2 X is a catalyst
The catalyst is neither created nor destroyedbut
the rate for the catalytic cycle Ox removal in
this case depends on catalyst concentrations
31
(No Transcript)
32
Chlorofluorocarbons
- Great refrigerants
- Previous chemicals where amonia and H2S
- Great propellants
- Aerosol cans
- Non-toxic Non-flammable Inert
- Used for asthma inhalers
33
Additional compound that affect Ozone
- Other Haloforms
- Non toxic fire suppressants
- Halon 1211 (bromochlorodifluoromethane, CF2ClBr)
- Halon 1301 (bromotrifluoromethane, CBrF3)
- Not so benign
- Carbon tetrachloride CCl4
- Formerly Used both as fire suppressant and dry
cleaning fluid
34
Next Up
- What to do What to Do?
35
Where we are
- Completed 2.8
- some bits of 2.9-11 covered today next lecture
will focus on sections 2.9-2.13 - Work problems 1-18 25-36 41-43