Endothelial Dysfunction Hypercholesterolemia - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 5
Title:
Endothelial Dysfunction Hypercholesterolemia
Description:
23 patients undergoing PTCA assigned to lovastatin 40 mg/day vs placebo ... to acetylcholine was noted in the lovastatin group at 51/2 months (LDL reduced ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:90
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Endothelial Dysfunction Hypercholesterolemia
1
Endothelial Dysfunction - Hypercholesterolemia
Zeiher, A., et. al., Modulation of Coronary
Vasomotor Tone in Humans Progressive Endothelial
Dysfunction with Early Stages of Coronary
Atherosclerosis, Circulation, 1991 83 391-401
Pepine, C., et. al., Vascular Health as as
Therapeutic Target in Cardiovascular Disease,
Vascular Biology Working Group, University of
Florida, 1998.
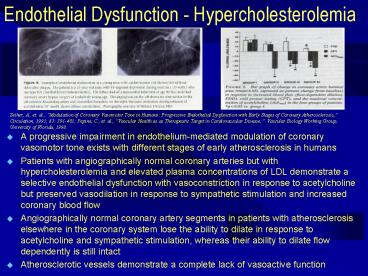
- A progressive impairment in endothelium-mediated
modulation of coronary vasomotor tone exists with
different stages of early atherosclerosis in
humans - Patients with angiographically normal coronary
arteries but with hypercholesterolemia and
elevated plasma concentrations of LDL demonstrate
a selective endothelial dysfunction with
vasoconstriction in response to acetylcholine but
preserved vasodilation in response to sympathetic
stimulation and increased coronary blood flow - Angiographically normal coronary artery segments
in patients with atherosclerosis elsewhere in the
coronary system lose the ability to dilate in
response to acetylcholine and sympathetic
stimulation, whereas their ability to dilate flow
dependently is still intact - Atherosclerotic vessels demonstrate a complete
lack of vasoactive function
2
Endothelial Dysfunction - Hypercholesterolemia
- Endothelium-dependent vasodilation is reduced in
hypercholesterolemic human epicardial coronary
and resistance vessels - There is a progressive impairment in
endothelium-mediated modulation of coronary
vasomotor tone with different stages of early
atherosclerosis in humans - These abnormalities likely contribute to angina
during exertion or emotional stress - Indeed, human coronary arteries exhibiting an
abnormal response to acetylcholine also
vasoconstrict with mental stress, exertion, or in
response to the cold pressor test, according to
previous studies
Pepine, C., et. al., Vascular Health as as
Therapeutic Target in Cardiovascular Disease,
Vascular Biology Working Group, University of
Florida, 1998.
3
Cholesterol-Lowering Endothelial Function
- Randomized, double-blind study to evaluate
HMGCoA-R rx. - 23 patients undergoing PTCA assigned to
lovastatin 40 mg/day vs placebo - Intracoronary infusion of acetylcholine at 12
days and 51/2 months - Significant improvement in response to
acetylcholine was noted in the lovastatin group
at 51/2 months (LDL reduced from 148/-7 to
110/-8)
Treasure, C., et. al., Beneficial Effects of
Cholesterol-Lowering Therapy on the Coronary
Endothelium in Patients with Coronary Artery
Disease, NEJM, vol. 332, no. 8, February 23,
1995, pp. 481-487.
4
eNOS Ischemic Stroke
- Few therapeutic options are available for
preventing or treating ischemic stroke
prophylactic treatment strategies are limited
mainly to agents that block platelet aggregation
or the coagulation cascade - Clinical trials have demonstrated the
effectiveness of anti-platelet agents in reducing
the incidence of ischemic stroke, but it is not
clear whether they impact on cerebral infarct
size - In mice, increased NO production achieved by
infusing L-arginine, the substrate for NO
synthesis, decreases cerebral ischemia and limits
cerebral infarct size
Liao, J., Nitric Oxide and Cardiovascular
Disease, Card.iology Rounds (Brigham Womens
Hospital), vol. 2, issue 5 (5/98).
5
eNOS Ischemic Stroke
Liao, J., Nitric Oxide and Cardiovascular
Disease, Card.iology Rounds (Brigham Womens
Hospital), vol. 2, issue 5 (5/98).
- In an experimental model using eNOS-deficient
mice, following middle cerebral artery occlusion,
larger strokes are noted as compared with
wild-type mice who are similarly treated - Recent studies have demonstrated that treatment
with statins upregulates eNOS mRNA expression and
enzyme activity even in mice who are
normocholesterolemic - This upregulation of eNOS by statins was
independent of serum cholesterol levels and
caused both increased cerebral blood flow and
smaller cerebral infarcts following experimental
middle cerebral artery occlusion