blue - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title: blue
1
Passive 3D imaging with rotating point spread
functions
Sri Rama Prasanna Pavani, Adam Greengard, and
Rafael Piestun Department of Electrical and
Computer Engineering, University of Colorado at
Boulder
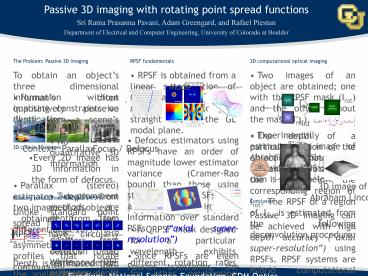
The Problem Passive 3D imaging To obtain an
objects three dimensional information without
imposing constraints on illumination 3D cues in
2D images
- RPSF fundamentals
- RPSF is obtained from a linear superposition of
Gauss-Laguerre (GL) modes lying along a straight
line in the GL modal plane.
- 3D computational optical imaging
- Two images of an object are obtained one with
the RPSF mask (Irot) and the other without the
mask (Iref). - The depth of a particular region of the object
is estimated from the angle of rotation of the
RPSF in the corresponding region of Irot. The
RPSF of a region of Irot is estimated from the
following deconvolution procedure
- Humans often qualitatively perceive depth from
a scenes context - No quantitative 3D information
- Parallax (stereo) estimates depth from two
images of an object - obtained from two different angles
- Suffers from occlusion and correspondence
problems
- Experimentally estimated 3D image of Abraham
Lincoln in the backside of a US one cent coin is
shown below.
- Defocus estimators using RPSFs have an order of
magnitude lower estimator variance (Cramer-Rao
bound) than those using standard PSFs. RPSFs
offer a 10 fold increase in Fisher Information
over standard PSFs (axial super-resolution) - Since RPSFs are eigen Fourier transforms, the
transfer function of a RPSF system is a scaled
version of the RPSF itself. - By simultaneously optimizing RPSFs in the GL
modal plane, Fourier domain, and spatial domain,
efficient phase-only transfer functions of quasi
RPSFs (QRPSFs) can be obtained. QRPSFs present
rotating features within a 3D domain of interest
and they form a cloud around a straight line in
the GL modal plane.
RPSF image
- Every 2D image has 3D information in the form of
defocus. - Two prominent methods are depth from focus (DFF)
and depth from defocus (DFD). While DFF estimates
depth by continuously refocusing until a focused
image is obtained, DFD uses a defocused image and
an image with extended depth. - Both DFF and DFD are largely based on geometric
optics models that do not optimize optics and
post processing together.
40 20 0 -20
(µm)
3D image of Abraham Lincoln
Standard image
Rotating point spread functions (RPSFs) Unlike
standard point spread functions (PSFs), RPSFs
have circularly asymmetric transverse profiles
that rotate continuously with defocus.
Conclusion Passive 3D imaging can be achieved
with high depth accuracy (axial
super-resolution) using RPSFs. RPSF systems are
hybrid computational optical imaging systems that
engineer the PSF of an imaging system to
optimally encode an objects 3D information.
References 1 A. Greengard, Y. Y. Schechner,
and R. Piestun, Depth from diffracted rotation,
Optics Letters 31, 183 (2006) 2 S.R.P. Pavani
and R. Piestun, High-efficiency rotating point
spread functions, Optics Express 16, 3484-3489
(2008) 3 R. Piestun, Y. Y. Schechner, and J.
Shamir, Propagation-invariant wave fields with
finite energy, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 17, 294 (2000)
- A QRPSF mask designed for a particular
wavelength exhibits different rotation rates for
other neighboring wavelengths. This phenomenon
can be used for simultaneous 3D measurements with
a broad band source. - QRPSF masks can be fabricated either as
continuous phase masks or more easily as masks
with quantized phase levels (with minimal
quantization effects). Alternatively, they can
also be implemented as computer generated
holograms (CGHs).
Depth is estimated from the angle of rotation of
RPSFs main lobes
Funding National Science Foundation, CDM Optics
fellowship, CU Technology Transfer Office,
Photonics Technology Access Program, and Honda