Bone Fracture Treatment – Dr. Kunal Aneja - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Bone Fracture Treatment – Dr. Kunal Aneja
Description:
Bone fractures are breaks in a bone’s continuity, often due to high-force impact. If you need the best orthopedic surgeon for Bone Fracture Treatment in Delhi, then contact Dr. Kunal Aneja. Orthopaedics is a medical science department that requires specialists. Despite the rising number of orthopedic doctors in our country, it is becoming increasingly challenging. You can always rely on Dr. Kunal Aneja for Bone Fracture and orthopedic treatments. Visit For More Information : 9811211503 info@drkunalaneja.com(email) Naveda Healthcare Centre 57 & 61, Pocket D-15, Sector-7, Rohini, Delhi – 110085 – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:0
Title: Bone Fracture Treatment – Dr. Kunal Aneja
1
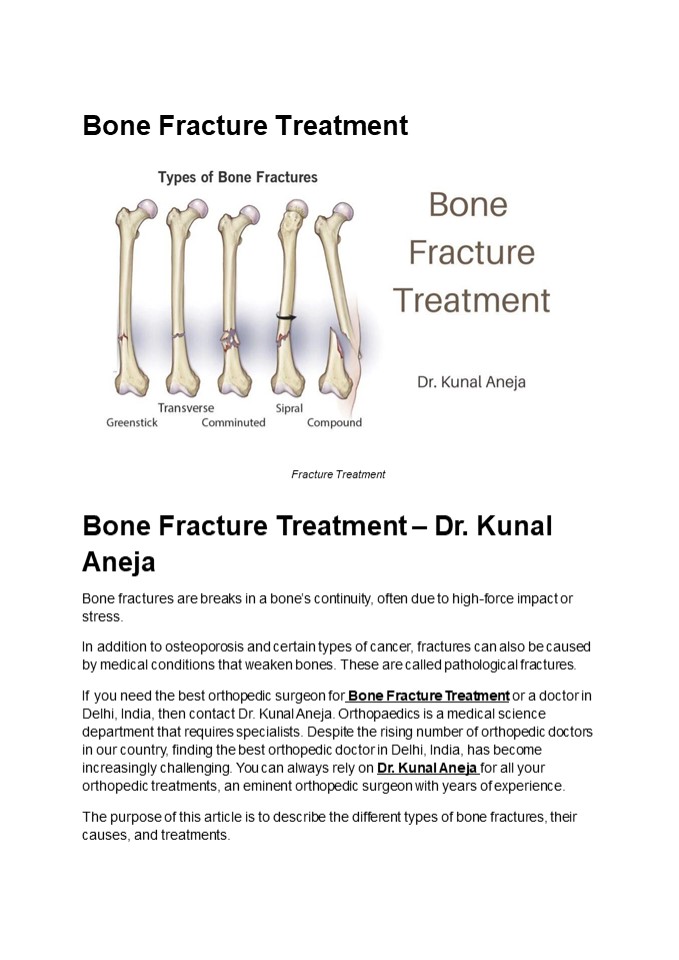
Bone Fracture Treatment
Fracture Treatment
Bone Fracture Treatment Dr. Kunal Aneja Bone
fractures are breaks in a bones continuity,
often due to high-force impact or stress. In
addition to osteoporosis and certain types of
cancer, fractures can also be caused by medical
conditions that weaken bones. These are called
pathological fractures. If you need the best
orthopedic surgeon for Bone Fracture Treatment or
a doctor in Delhi, India, then contact Dr. Kunal
Aneja. Orthopaedics is a medical science
department that requires specialists. Despite the
rising number of orthopedic doctors in our
country, finding the best orthopedic doctor in
Delhi, India, has become increasingly
challenging. You can always rely on Dr. Kunal
Aneja for all your orthopedic treatments, an
eminent orthopedic surgeon with years of
experience. The purpose of this article is to
describe the different types of bone fractures,
their causes, and treatments.
2
What is a bone fracture treatment?
bone fracture
A bone fracture occurs when a force is applied to
a bone stronger than it can bear. This results
in pain, loss of function, bleeding, and injury
to surrounding tissues. Our skeleton is made up
of bones. Bones are a type of connective tissue
reinforced with calcium and bone cells. Bones
have a softer center, called bone marrow, where
blood cells are made. Our skeleton supports us,
enables us to move, and protects our internal
organs. A bone fracture can be mild or severe,
depending on the strength and direction of the
force, the type of bone involved, and the
persons age and general health. Common bone
fractures include
3
- Hands and wrists
- Ankle tendon
- hip hip fractures occur most often in older
people. - In general, broken bones will heal within 4 to 8
weeks, depending on the persons age and health. - Bone Fracture Treatment includes immobilizing the
bone with a plaster cast or surgically inserting
metal rods or plates to hold the bone pieces
together. Some complicated fractures may need
surgery and surgical traction.
What are the different types of bone fractures?
4
- different types of bone fractures
- There are several types of fractures, including
- Closed (simple) fracture The broken bone does
not penetrate the skin. - Open (compound) fracture Fractures where the
bone is exposed through the skin or where a
wound leads to the fracture site are more likely
to cause infection and external bleeding. - Greenstick fracture A small, thin crack in the
bone. Childrens bones are more flexible than
adults bones, so this can occur. - Hairline fracture Stress fractures are most
commonly caused by repetitive stress from
activities like jogging or running. - Complicated fracture During a fracture, the
surrounding structures are injured. Veins,
arteries, nerves, and the periosteum (bone
lining) may be damaged. - Comminuted fracture As the bone breaks into
small pieces, it heals more slowly than other
fractures. - Avulsion fracture Muscles are attached to bone
by tendons and connective tissue. Muscular
muscle contractions can pull out pieces of bone,
usually at the knees and shoulders. - Compression fracture When two bones hit each
other, it can cause a fracture. Vertebrae in the
spine are most likely to suffer these kinds of
fractures. Those with osteoporosis are most
likely to suffer these types of fractures.
5
- In addition to fractures of the legs and arms,
skulls and ribs can be broken due to trauma to
the head, chest, spine, or pelvis. These
fractures are compounded by the underlying body
structure the bone is supposed to protect. - When this type of fracture occurs, it may present
a life-threatening injury, so always seek
emergency help if you suspect it may be
life-threatening. - How are bone fractures caused?
- Many factors can lead to bone fractures,
including - Trauma or injury, such as a fall or direct blow
to the head - Osteoporosis is a condition that weakens bones
and makes them more likely to fracture. - Overuse can lead to minor fractures or cracks in
the bones due to repetitive stress. - Certain medical conditions include cancer or
osteogenesis imperfecta (a genetic disorder
affecting bone growth). - It is possible for specific medications, such as
glucocorticoids, to weaken bones and make them
more susceptible to fractures. - Various factors, including type, location, and
severity, can cause bone fractures. - How is a bone fracture diagnosed?
- The following tests can be used to diagnose bone
fractures - 1. X-ray
6
- The most common and widely used test for
detecting bone fractures. The test uses
radiation to create images of the bones, which
can reveal any breaks or cracks. - CT Scan
- Using X-rays and a computer, this test creates
three-dimensional images of bones. It is helpful
in detecting fractures that might not show up on
a standard X-ray and planning surgery. - MRI
- Magnetic fields and radio waves create detailed
images of bone and surrounding soft tissues.
This test is beneficial for diagnosing fractures
that are hard to see on X-rays, such as those in
the spine or pelvis. - Ultrasound
- For detecting fractures in wrists, ankles, and
feet, this test uses high-frequency sound waves
to create images of the bones and soft tissues
around them.
5. Bone Scan In this test, a small amount of
radioactive material is injected into the
bloodstream, and then photographs are taken to
detect areas of increased uptake. This can help
detect stress fractures that are not visible on
X-rays. The type and location of the fracture
will likely determine which of these tests your
doctor orders.
7
- What should you know about bone fracture
treatment? - In general, bone fractures are treated by
immobilizing the affected bone so that it can
heal. Some of the most common treatments are - Cast or splint
- The affected bone is immobilized for six to eight
weeks, and most fractures can be treated with
this. - Surgery
- When the bone is displaced or open, surgery may
be necessary. This involves realigning the bone
and securing it with screws, plates, or pins. - Physical therapy
- This practice often recommends strengthening and
regaining the range of motion in the affected
area. - Medications
- Ibuprofen or acetaminophen may be prescribed as
pain relievers.
- Bracing
- Some fractures, such as those of the wrist and
ankle, can benefit from this treatment to help
support and protect the bone. - Weight-bearing restrictions
- Depending on the location and type of fracture,
you may be advised not to place weight on the
affected limb until the bone has healed.
8
- Follow-up
- As your doctor monitors your progress, you may
need additional imaging tests to check on the
healing process. To ensure the best outcome for
your bone fracture treatment, you should follow
your doctors instructions and attend all
follow-up appointments.