Deep vein Thrombosis (DVT) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Deep vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Description:
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a vein located deep inside your body. A blood clot is a clump of blood that is in a gelatinous, solid state. Deep vein blood clots typically form in your thigh or lower leg, but they can also develop in other areas of your body. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1021
Updated: 15 July 2017
Slides: 9
Provided by:
lazoithelife
Category:
Medicine, Science & Technology
Tags:
Title: Deep vein Thrombosis (DVT)
1
Deep vein Thrombosis (DVT)
2
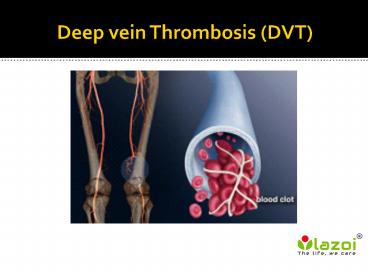
Deep vein Thrombosis (DVT)
- Deep vein thrombosis occurs when a blood clot
forms deep inside a part of the body. Deep vein
thrombosis can typically form in the thigh and
lower leg, but sometimes it can form in the arm
and pelvis area. Deep vein thrombosis itself is
not dangerous, but it can be life-threatening
when the piece of the blood clot breaks of and
travel through the circulating system known as
embolism reaching to the heart and pulmonary
artery and getting lodged there. - This can prevent blood from flowing properly
through the lung and decreasing the amount of
oxygen absorbed and distributed back to the body
which is known as pulmonary embolism. - Embolism can travel and get lodged in any part of
the body in heart, lungs, brain or any other
area.
3
Symptoms of DVT
- Swelling of foot, ankle, or leg, usually on one
side - Cramping pain in the affected leg
- Severe, unexplained pain in your foot and ankle
- An area of skin that feels warmer than the skin
on the surrounding areas - Skin over the affected area turning pale or a
reddish or bluish color
4
Causes of deep vein thrombosis
- Prolonged travel or sitting, such as of long
airplane, car or train travel. - Thrombophilia-An abnormality in blood
coagulation that increases the risk of blood
thrombosis. - Venous statis-An condition of slow blood flow in
the vein, usually in the legs, which can cause
thrombosis in legs. - Surgery can lead to high risk of deep vein
thrombosis and mainly surgery in the lower
extremist such as that of knee replacement
surgery. - Pregnancy-Change in the level of the hormones,
and slower blood flow as the uterus expands
increase the risk of DVT.
5
Risk factors of DVT
- Adults above the age of 60 are mostly at the
highest risk of having DVT. - Having an injury that damages the veins
- Being overweight, which puts more pressure on the
veins of the legs and pelvis - Having a family history of DVT
- Having a catheter placed in a vein
- Taking birth control pills or undergoing hormone
therapy - smoking (especially heavy usage)
6
Treatments of DVT
- Medication-Anticoagulants prevent further
formation of blood clot and can stop an embolus
to reach to lungs or other part of the body. - Heparin-It is an anticoagulant and it may be
given depending on the history and severity of
the patient. - Warfarin-A blood thinning drug is given with
heparin, which blocks blood clotting factors. - Pressure stocking- A pressure stocking improves
blood flow in your legs and reduces your risk for
complications from blood clots. - Filters-If any patient is not able to take blood
thinners, the filters can be placed inside the
vena cava, this prevents pulmonary embolism by
preventing the blood from entering into the
lungs. This is often placed after surgery.
7
Diagnosis of DVT
- The primary test for the diagnosis is done by a
physical test. - The two foremost technique needed for the
diagnosis of DVT are - D-dimer blood test-D-dimer is a blood test that
may be used as a screening test to determine if a
blood clot exists. A positive test may not mean a
DVT is present. Any blood clot will give positive
results. - Ultrasonography-It is the standard method to
determine DVT.USG would be able to show different
DVT in any part of the body. But clot in chest or
pelvis may not be identified by Ultrasound. - There are other certain blood tests which can
show an increase chance in blood clot. They are- - Activated protein C resistance (checks for the
Factor V Leiden mutation) - Antithrombin levels
- Antiphospholipid antibodies
- Complete blood count (CBC
- Genetic testing to look for mutations that make
you more likely to develop blood clots, such as
the prothrombin G20210A mutation - Lupus anticoagulant
- Protein C and protein S levels
8
CONNECT WITH US
- Logon to
- www.lazoi.com
- Like us on Facebook
- https//www.facebook.com/LazoiTheLife
- Follow us on Twitter
- https//www.twitter.com/lazoithelife
- Follow us on Pinterest
- https//www.in.pinterest.com/lazoithelife