Optical Burst Switching - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
Optical Burst Switching
Description:
Optical Burst Switching ... The data burst is launched after a small offset delay. Bursts remain in the optical plane end-to-end, and are typically not buffered as ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1747
Avg rating:1.0/5.0
Title: Optical Burst Switching
1
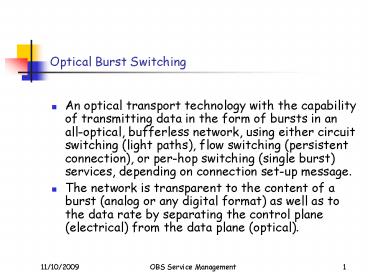
Optical Burst Switching
- An optical transport technology with the
capability of transmitting data in the form of
bursts in an all-optical, bufferless network,
using either circuit switching (light paths),
flow switching (persistent connection), or
per-hop switching (single burst) services,
depending on connection set-up message. - The network is transparent to the content of a
burst (analog or any digital format) as well as
to the data rate by separating the control plane
(electrical) from the data plane (optical).
2
Burst definition
- A burst can be defined as a contiguous set of
data bytes or packets. It can be as short as a
few microseconds or as long as several hours.
3
Control plane vs. data plane
- The fundamental premise of OBS is the separation
of the control and data planes, and the
segregation of functionality within the
appropriate domain (electronic or optical). - a set-up message (control message) to an OBS
ingress switch. The control processor forwards
the message along the data transmission path
toward the destination. - Control messages are processed at each node
(requiring OEO conversions) they inform each
node of the impending data burst, and initiate
switch configurations to accommodate the data
burst. - The data burst is launched after a small offset
delay. Bursts remain in the optical plane
end-to-end, and are typically not buffered as
they transit the network core.
4
OBS features
- OBS has the potential of meeting several
important objectives - high bandwidth, low latency, deterministic (very
little if any network elasticity no buffers)
transport required for high demand (grid)
applications - all-optical data transmission with ultra-fast
user/application-initiated light path setup - implementable with cost effective COTS optical
devices.
5
E2E burst transmission
Application/user initiated Control message
OEO
OEO
- -
X
Control signal created Cross connection, awaiting
burst
Control signal has not been processed yet, but
will arrive ahead off burst by time offset delay
6
When will carriers have it?
- Many in the networking research community believe
that optical burst switching (OBS) can meet the
needs of the scientific community in the near
term (2-3 years). - Research test beds in several Labs globally
- ATDnet MAN testbed
- The opportunity work on a networking technology
during pre-standardization development for the
purpose of meeting service management needs and
requirements (not an after thought!).
7
Optical Packet Switching (OPS)
- OPS is the ultimate optical switching technology
- requires optical buffering (beyond todays coarse
fiber delay lines) - also, requires line-rate header parsing.
- Many experts do not expect OPS to be commercially
feasible for at least a decade.
8
OBS Network Architectures
- Most OBS research has focused on edge-core,
overlay architectures. - Few (myself included), are looking at e2e
user/application initiated connections. - Working on OBS NICs
- User/application initiated optical network
connections. - Use Just In Time (JIT) protocol for connection
signaling.
9
OBS and QoS
- 1) Application layer QoS (latency, jitter,
datarate) - Handled at edges during burstification (similar
to SAR in ATM) and scheduling not in
cut-through optical network (no buffering) - 2) Physical layer QoS (BER)
- Function of optical components, optical fiber,
length of transmission controlled and monitored
at the optical layer - 3) QoS and priority
- Pre-emption during congestion
10
OBS Service Requirements
- Network feedback mechanisms to user
- Status
- Alarms
- Availability and reach
11
OBS Service Requirements
- Policy based routing algorithms user or
carriers decide on how forwarding tables are
created. - Integrating security concerns at both the
protocol level as well as control and management
plane. - Incorporating necessary inter-domain information
exchange in protocol definitions. - Providing necessary flexibility in architectures
to meet both carrier-owned and user-owned
networks.
12
OBS Service Requirements
- Understanding the requirements for both physical
layer QoS and application layer QoS and
incorporating them into protocol definitions. - Determine how users will get billed for the
network service. - Determine what is meant by SLAs and how the
network can provide them.