General Biology 2Class 17 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title:
General Biology 2Class 17
Description:
The Anatomy of the Mammalian Respiratory System. Alveoli ... The Human Heart in a Radiograph. Courtesy Yale Medical School. The Human Heart. Martini (2003) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:80
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: General Biology 2Class 17
1
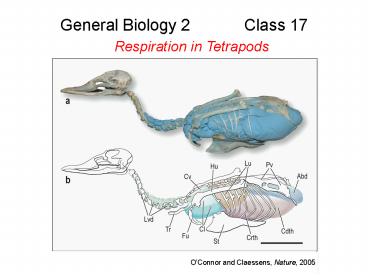
General Biology 2 Class 17
Respiration in Tetrapods
OConnor and Claessens, Nature, 2005
2
The Anatomy of the Mammalian Respiratory System
3
Alveoli
The "Dead" Space and "Alveolar (Exchange)" Space
concepts.
4
Breathing Musculature
- All breathing muscles are skeletal ("Voluntary")
muscles. - 1. Diaphragm (inspiration)
- 2. Intercostals
- external (forced inspiration) and
- internal (forced expiration)
- 3. Abdominals (forced expiration)
5
The Mammalian Diaphragm
Courtesy NIH
6
The Respiratory System as a Mechanical System
Elasticity of the "Chest wall" (thorax) and Lungs
The Pleural Space
Pneumothorax?
7
Quiet Breathing
Inspiration is controlled by the
diaphragm. Expiration is elastic (i.e. energy
came during inspiration).
8
Breathing in Exercise
Additional muscles used in inspiration --
diaphragm Expiration is a combination of forcing
by muscles and elastic rebound.
9
Graphs of Breathing in Rest and Exercise
Initially f increases more than VE (hard to see
on graph -- proportionately more)
10
Various Respiratory Volumes
(Functional Reserve Capacity -- the minimum air
that at rest always remains in your lungs)
11
A Comparison of Airflow and Bloodflow Strategies
Between Fish, Birds, and Mammals
12
The Circulatory System
Volume rendered CT scan showing stenosis of the
right internal carotid artery, courtesy of
Philips Medical
13
Where is your heart located?
14
The Human Heart in a Radiograph
Courtesy Yale Medical School
15
The Human Heart
Martini (2003)
16
The Circulation
The circulation is an internal convective system.
Exchange between the circulation, tissues and
environment is by diffusion.
Functional Components of the Circulation Pumps
Vascular System Lymphatic System Types of
circulations Open vs. closed
17
Schematic of the Mammalian Blood
Circulation(lymphatic circulation not shown)
Pumps Vasculature Circulating tissues -- blood
and lymph