Center for Computational Visualization - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title:
Center for Computational Visualization
Description:
The free energy of an ion of charge : Center ... Generalized Born (GB) equation: calculates the free energy ... and are the weights for the radial and angular ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:29
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Center for Computational Visualization
1
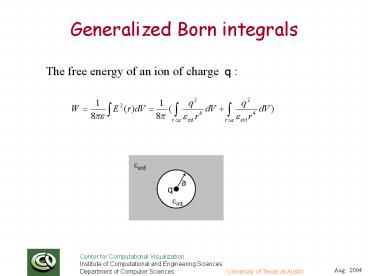
Generalized Born integrals
The free energy of an ion of charge
2
Born Energy the energy required to transfer a
nonpolarizable ion of charge and radius
from a phase (solute) into another Phase
(solvent).
(cgs units)
(Kcal/mol)
3
Generalized Born (GB) equation calculates the
free energy of solvent polarization for an
arbitrary charge distribution of n Charges.
where
distance between atom i and j
Born radius of atom i
4
How to calculate Born Radii efficiently? Feig
and Brooks, 2004 Method 1 Need to evaluate
the self polarization energy of a unit charge
at the atom center. In Lee et al (2003),
is the molecular volume density at point
and are empirical cofficients
5
Method 2 approximate the electric displacement
of a set of charges as the Coulomb field
Bashford and Case, 2000
Where is the van der Waals radius. Both
method 1 and 2 need to compute the 3D integral.
6
How to define the volume function in method 1?
Function 1 Preprocess Where , and
are parameters. Drawback even choosing
optimal parameter
- gap regions (space inside a cluster of atoms)
- will be unfilled
- open regions (space outside a cluster of atoms)
- bulge
7
Function 2 Preprocess
- The sum of is a means to identify gap and open
regions. - When is in a gap region, will usually
add destructively, - while if is in an open region, will
usually add - constructively.
- Vectors are weighted by the atomic function
so that only - the relevant vectors contribute to the
result. - The criteria for choosing
- Value inside the vdw sphere should greater than
or equal - to 1.
- The tail of the function decay monotonically from
1 at the - vdw surface to approximately 0 at about 2.8 A
from the - surface.
- The tail has a similar decay length regardless of
the size - of the atom.
8
Atomic functions that are usually
used where , , and are empirical
parameters. So, the volume density function is
9
Function 3
Where
is the distance between the spatial point and
atom , is half of the smoothing length
which is less than 1 A, is the van der Waals
radius.
10
How to compute the integrals? Integrate the
radial component and the angular
component independently
and are the weights for the radial and
angular components, is the distance between
the integration point and the origin. The
integration points and the weights for the radial
component are generated by the Gauss-Legendre
quadrature. Those for the angular component are
generated by the Lebedev quadrature.
11
Another way to compute the integral
Decompose as , where
is the weight function assigned to each atom.
Then
12
In spherical coordinate system,
- Integration on the surface of the shell
- Lebedevs quadrture
- Konyaevs quadrature (icisahedral symmetric
distribution) - Radial integration
- Gauss-Chebyshev quadrature (simple formula)
- Gauss-Legendre quadrature
13
Weight function
Let , where denotes the distance
between the point in the space and atom , is
the distance Between atom and atom . Define
the step function
The Voronoi polyhedron can be defined by the cell
function
14
Continuous cell function We want to smoothen the
discontinuity at . Need to find a proper
cutoff function , which satisfies The
simplest possible function is where
15
Let , then is another
possible cutoff funcion. The appropriate choice
of k is 3. Finally, define the weight function
as where the summation includes all atoms in
the molecule.