Circuit Switching - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title: Circuit Switching
1
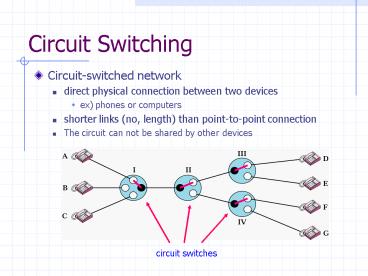
Circuit Switching
- Circuit-switched network
- direct physical connection between two devices
- ex) phones or computers
- shorter links (no, length) than point-to-point
connection - The circuit can not be shared by other devices
circuit switches
2
Packet Switching
- Datagram Approach
- each packet is treated independently from all
others - packet datagram
- datagrams may arrive at their destination out of
order - Transport layer reorders the datagrams
3
Packet Switching
- SVC(Switched Virtual Circuit)
- A virtual circuit is created whenever needed and
exists only for the duration of the specific
exchange - comparable conceptually to dial-up circuit
switching
4
Packet Switching
- Circuit switching vs. Virtual Circuit
- Path vs. Route
physical path
routing table
5
Packet Switching
- Circuit switching vs. Virtual Circuit (cont.)
- Dedicated vs. Shared
6
Frame Relay
- Higher data rate at lower cost
- the past WAN leased line or X.25 ? low data
rate - Solution T-lines, mesh network, Frame relay
- Data rate of Frame relay 1.544Mbps (T-1) /
44.376Mbps (T-3)
lower cost
Pure mesh T-line network vs. Frame Relay
7
Frame Relay
- Less overhead due to improved transmission media
- No need to have a WAN that spends time and
resources checking and double checking potential
errors - X.25 vs. Frame relay
- X.25
- extensive error checking and flow control at the
network layer - station-to-station frame checking at the data
link layer - overhead for reliability eats up bandwidth
- Frame Relay
- does not provide error checking or require
acknowledgment in the data link layer because
network become reliable and less error - All error checking is left to network and
transport layer protocols - Frame relay traffic simplified transmission
8
X.25 traffic
Frame Relay traffic
9
Frame Relay
- Frame Relay is normally used as a WAN to connect
LANs or mainframe computers.
Frame Relay network
10
Frame Relay
- Virtual Circuits
- Use a virtual circuit identifier (not physical
address) - Virtual circuit identifiers in Frame Relay
operate at the data link layer (cf. X.25 network
layer) - data link connection identifier (DLCI) local
number - Two type of connections in Frame Relay
- PVC(Permanent Virtual Circuit) Connection
- SVC(Switched Virtual Circuit) Connection
DLCIs
11
Frame Relay Layers
- Physical Layer
- No specific protocol
- Data Link Layer
- A simplified version of HDLC called core LAPF
- LAPF LAP for frame mode
- No extensive error and flow control fields
frame priority for discard in bottleneck (1high)
a switch informs that congestion has occurred
final(1)/more(0)
12
ISDN Services
Three categories
network may change or process the content of data
? layer 4-7 service
provides additional functionality to the bearer
services and Teleservices
provides the means to transfer information
(voice, data, video) between users without the
network manipulating the content of that
information
Layer 1-3 services
13
Subscriber Access to the ISDN
- User Interfaces
- BRI Basic Rate Interface for home or small
office - 2BD 192kbps
- PRI Primary rate Interface
- 23BD 1.544Mbps (North America) T1
- 30BD 2.048 Mbps (Europe) E1
TP local loop
T1
14
Broadband ISDN (B-ISDN)
- For the services beyond the capabilities of both
the BRI and PRI
15
ATM Architecture
- Virtual Connection
- Connection is accomplished through TP, VP, VC
- Transmission Paths (TPs)
- Physical connection (wire, cable, satellite and
so on) - Virtual Paths (VPs)
- A connection or a set of connection between
Switches - Virtual Circuits (VCs)
- All cells belonging to a single message follow
the same VC
TPs gt VPs gt VCs
16
ATM Architecture
TP
Example of VPs and VCs
17
ATM