Nursing Process 5 steps - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 34
Title:
Nursing Process 5 steps
Description:
effective activity exercise pattern. effective sleep rest pattern ... e.g. abdominal surgery. PC: Hemorrhage (hypovolemia) PC: urinary retention. 16. CASE STUDY ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:404
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Nursing Process 5 steps
1
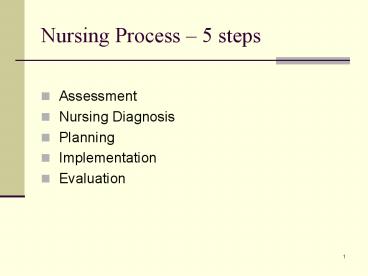
Nursing Process 5 steps
- Assessment
- Nursing Diagnosis
- Planning
- Implementation
- Evaluation
2
The Nursing Process
- is circular in nature
- is a process of constant change analysis
Assessment Evaluation Nursing
Diagnosis Implementation Planning
3
The Nurse
- Assesses the clients condition
- Determines an appropriate nursing diagnosis
- Plans care based upon the assessment and
diagnosis - Implements the plan of nursing actions
- Evaluates the results of care
- Assesses, diagnoses, plans, implements
4
During the Assessment Phase
- The nurse follows cues from client and uses all
five senses in this process - Collects
- Verifies
- Analyzes
- Communicates
Client Data
5
An Assessment Database includes information about
- The clients
- perceived needs
- health problems
- related life experiences
- health practices and lifestyle
- goals and values
- expectations of the health care system
6
Assessment Data
- Is obtained from the nurse-client relationship as
well as from a variety of other sources - Some other data sources include family members,
health practitioners, clients medical records,
and other records (e.g., childs school health
record)
7
The Nursing Diagnosis
- Is a statement that describes the clients actual
or potential response to a health problem that a
nurse is licensed and competent to treat - Is based upon a detailed analysis of the
assessment data - A wellness diagnosis describes a response to a
level of wellness that a client has a readiness
to change or enhance.
8
From Nursing Diagnosis To Outcome
Nursing Diagnosis
Goal Expected Outcome
Nursing Intervention
Client Choices Capabilities Resources
Creative Ideas Of The Nurse
Research Findings
Adapted from Fig. 12-6, p. 201 Potter Perry
9
A Nursing Diagnosis may pertain to any of the
following client dimensions
Physical Developmental Social Emotional Spiritu
al Intellectual
10
Types of Nursing Diagnostic Statements
(Carpenito-Moyet, 2004, p.15, Box 2-1)
- Three-part statement (Actual Nursing Diagnosis)
- e.g. Impaired Skin Integrity related to prolonged
immobility secondary to fractured pelvis as
evidenced by a 2 cm lesion on back. - Two-part Statement (Risk for Diagnosis)
- e.g. Risk for Injury related to lack of awareness
of hazards - One-part Statement (Wellness Diagnosis)
- e.g. Readiness for enhanced nutrition
11
Wellness Diagnoses11 Functional Health Patterns
Associated Positive Functioning Assessment
Statements
- positive health perception
- effective health management
- effective nutritional-metabolic pattern
- effective elimination pattern
- effective activity exercise pattern
- effective sleep rest pattern
- positive perceptual cognition pattern
- positive self perception pattern
- positive role relationship pattern
- positive sexuality reproductive pattern
- effective coping stress tolerance program
- positive value belief pattern
12
Wellness Diagnoses(Carpenito-Moyet, 2004, p.12)
- Clinical judgement about an individual, group or
community in transition from a specific level of
wellness to a higher level of wellness - 2 cues present
- Desire for increased wellness
- Effective present status or function
- Conclusion from assessment data which focuses on
patterns of wellness, healthy responses or
clients strengths
13
Collaborative Problems(Carpenito-Moyet, 2004,
p.19)
- Physiologic complications that nurses monitor to
detect onset or changes in status - Nurses manage collaborative problems using
physician-prescribed and nursing-prescribed
interventions to minimize the complications of
events
14
- Nurses can prevent
- Pressure ulcers
- Thrombophlebitis
- Complications of immobility
- Aspiration
- Nurses can treat
- Stage I or II pressure ulcers
- Swallowing problems
- Ineffective cough
- Nurses cannot prevent
- Seizures
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- Nursing Dx (Risk for)
- Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity
- Risk for ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion
- Disuse syndrome
- Risk for aspiration
- Nursing Dx (Actual)
- Impaired Skin Integrity
- Impaired swallowing
- Ineffective airway clearance
- (Nursing and Medicinal)
- Collaborative Problems
- PC Seizures
- PC GI Bleeding
15
- Nursing Diagnosis
- Both involves all steps of nursing process
- Assessment involves data collection to identify
signs and symptoms of nursing diagnosis or risk
factors for high risk nursing diagnosis
- Collaborative Problems
- Assessment focuses on determining physical
stability or risk for instability - Associated with specific pathology or treatment
- e.g. abdominal surgery
- PC Hemorrhage (hypovolemia)
- PC urinary retention
16
- CASE STUDY
- (Lunney, 2001, p.101)
17
Planning Nursing Care
- Planning is a phase of the nursing process in
which - Nursing diagnosis are identified and prioritized
- Client-centered goals and expected outcomes are
established, and - Nursing interventions are selected to achieve the
goals and expected outcomes established
18
OUTCOMES/GOALS
- An outcome is a measurable change of the clients
human response to nursing care. - Goals are designed to drive actions
- Goals are mutually agreed upon between nurse and
client.
19
GOALS
- Nursing Diagnosis
- Client centered
- Related to human response
- Client goals serve as criteria for measuring
effectiveness of care plan
- Collaborative Problems
- Nurse focused/ team focused
- Nurse will manage or minimize
- Nurse accountability includes
- Maintaining for physiologic instability
- Consulting standing orders and protocols and
physician to obtain new orders - Perform specific actions to manage reduce
severity of an event or situation - Evaluate client response
20
Goals are developed using the acronym SMART
- S Specific
- M Measurable
- A Achievable
- R Realistic
- T Time Oriented
21
Nursing Diagnosis Goal
- Nursing Diagnosis Anxiety related to altered
visual perceptions 2 to schizophrenia as
evidenced by pacing, crawling on floor down the
hall, increased respiratory rate, startle
response - Goal Client will verbalize a decrease in anxiety
from a 3 to a 1 and respiratory rate of 20 as
evidenced by decreased pacing, by the end of the
shift.
22
Wellness Diagnosis
- Dx Readiness for enhanced family processes
- Goals The family will eat breakfast together 5
days/ week for the next 6 months.
23
Collaborative Problem
- PC Fluid/ Electrolyte Imbalance
- Goal Fluid and electrolyte imbalance will be
managed and minimized.
24
- NOC
- NIC
- ICN
25
Goals can be
- Short term e.g. by end of shift
- Long term e.g. by discharge
26
Planning Specific Nursing Interventions
- Nursing Interventions are selected to assist the
client to move from his/her present level of
functioning (as stated in the nursing diagnosis)
to a level of functioning described in the
goal(s) and expected outcome statement(s)
27
Types of Nursing Interventions
- Nurse Initiated
- Nurses autonomous response to client needs
- Physician Initiated
- Nurse carries out written physician orders
- Collaborative Interventions
- Involves interventions by other (non-nurse)
specialized members of the care team
28
Each Nursing Care Plan
- Is unique to an individual client
- Constantly changes due to changes in client
status, and other variables - Varies in format from one clinical setting to
another - May be written or electronic
29
Nursing Care includes
- Supporting the person (conveying acceptance,
listening, etc.) - Sharing knowledge
- Facilitating learning personal development
- Helping the person build support networks
- Providing a supportive environment
- All nursing actions take place in the context of
the patient/ client relationships with health
professionals and the health care team members.
30
Nursing Implementation
- Any action taken by the nurse to help the client
reach the identified goals and expected outcomes - Pertains to nursing behaviours specific to the
initiation and completion of nursing care - Interactions are directed at managing the
etiology component of the nursing diagnosis
31
Implementation(Carpenito-Moyet, 2004, p.46)
- The skills and knowledge necessary for
implementation usually focus on - Performing the activity for or assisting client
(DO) - Performing nursing assessments to identify new
problems or monitor status of existing problems
(ASSESS) - Teaching to help clients gain new knowledge
(TEACH) - Assisting clients to make decisions about their
own healthcare - Conselling with referring to other health care
professionals - Provide specific treatment actions to remove,
reduce or resolve health problems - Assist clients to perform activities themselves
- Assist clients to identify risks or problems and
to explore options
32
Implementation actionsare varied and include
- Assessing/ Reassessing
- Performing or assisting
- Directing the performance of activities (such as
activities of daily living) - Counselling and teaching
- Providing direct care
- Recording and evaluating
33
After Implementation
- The nurse writes in the clients record a brief
description of - a nursing assessment,
- specific nursing actions carried out,
- and the clients response to nursing care
34
Critical Pathway
- This is a specific type of care plan that
- Is multidisciplinary in nature
- Predicts the client outcomes and nursing
interventions to be met for selected clients over
a projected length of stay (or a number of home
visits for clients with a specific case type) - Example critical pathway for post-natal recovery
of an uncomplicated delivery





![[PDF] Pharmacology and the Nursing Process 9th Edition Kindle PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10085907.th0.jpg?_=20240726122)
![[PDF] Fundamentals of Nursing 11th Edition Full PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10078430.th0.jpg?_=20240713108)
![[PDF] Foundations of Nursing 9th Edition Android PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10078635.th0.jpg?_=20240715017)
![[PDF] Quick guide for nursing in EP study and pacemaker implantation (Cath Lab nursing) Ipad PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10094241.th0.jpg?_=20240808117)

![[PDF] Foundations of Nursing 8th Edition Free PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10078622.th0.jpg?_=202407151211)


![[PDF] Mosby's Drug Guide for Nursing Students Free PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10081948.th0.jpg?_=202407190410)





![[PDF] Foundations and Adult Health Nursing 9th Edition Android PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10076360.th0.jpg?_=20240710094)










