Chapter 2: An Overview of the Financial System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 8
Title:
Chapter 2: An Overview of the Financial System
Description:
Short term (maturity 1 year), Intermediate term (1 maturity 10 years) Long ... Money Market market for short-term debt instruments ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:785
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chapter 2: An Overview of the Financial System
1
Chapter 2 An Overview of the Financial System
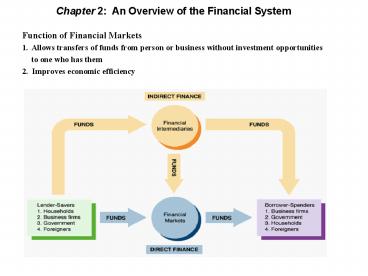
- Function of Financial Markets
- 1. Allows transfers of funds from person or
business without investment opportunities - to one who has them
- 2. Improves economic efficiency
2
Financial Markets
- Classifications A firm or an individual can
obtain funds in a financial market in two ways - 1. Debt Markets
- Short term (maturity lt 1 year), Intermediate
term (1ltmaturity lt 10 years) Long-term (maturity
gt 10 year) - Money Market market for short-term debt
instruments - Capital Market market for intermediate- and
long-term debt instruments - No ownership for debt holders.
- 2. Equity Markets
- Common stocks
- Confer ownership rights on the equity
holders. - The equity holders benefit directly from any
increases in the corporations profitability or
asset value. - The corporation must pay all its debt holders
before it pays its equity holders.
3
Another Classifications of Financial Markets
- 1. Primary Market
- New security issues sold to initial buyers
(investment banks underwriting securities). - 2. Secondary Market
- Securities previously issued are bought and sold
(e.g., NYSE/AMEX, NASDAQ) - Secondary markets do not help the corporations to
acquire funds, but do increase the liquidity of
the securities, which makes the securities in the
primary markets more attractive. - Secondary markets also determine the prices of
the securities issued in the primary market. - Secondary market can be organized in two ways
- 1) Exchanges
- Trades conducted in central locations (e.g., New
York Stock Exchange) - 2) Over-the-Counter Markets
- Dealers at different locations buy and sell
(e.g., NASDAQ)
4
Internationalization of Financial Markets
- International Bond Market
- 1. Foreign bonds (sold in a foreign country,
denominated in that countrys currency). - 2. Eurobonds (sold in a country but denominated
in a currency other than that of the country).
Now larger than U.S. corporate bond market. - a variant Eurocurrencies foreign currencies
deposited in banks outside the home country.
(e.g., Eurodollars) - nothing to do with euros.
- World Stock Markets
- U.S. stock markets are no longer always the
largest Japan sometimes larger
5
Indirect Finance Financial Intermediaries
- Financial Intermediaries
- More important source of finance than
securities markets - Needed because of transactions costs and
asymmetric information - Functions of Financial Intermediaries
- Financial intermediaries make profits by reducing
transactions costs. Reduce transactions costs by
developing expertise and taking advantage of
economies of scale. - Risk Sharing Create and sell assets with low
risk characteristics and then use the funds to
buy assets with more risk (also called asset
transformation). - Also lower risk by helping people to diversify
portfolios - Financial intermediaries reduce adverse selection
and moral hazard problems, enabling them to make
profits.
6
Asymmetric Information Adverse Selection and
Moral Hazard
- Adverse Selection
- 1. Before transaction occurs
- 2. Potential borrowers most likely to produce
adverse outcomes are ones most likely to seek
loans and be selected - Moral Hazard
- 1. After transaction occurs
- 2. Hazard that borrower has incentives to engage
in undesirable (immoral) activities making it
more likely that wont pay loan back
7
Financial Intermediaries
8
Regulation of Financial Markets
- Three Main Reasons for Regulation
- 1. Increase information to investors
- A. Decreases adverse selection and moral hazard
problems - B. SEC forces corporations to disclose
information - 2. Ensuring the soundness of financial
intermediaries - A. Prevents financial panics
- B. Chartering, reporting requirements,
restrictions on assets and activities, deposit
insurance, and anti-competitive measures - 3. Improving monetary control
- A. Reserve requirements
- B. Deposit insurance to prevent bank panics