Multiple Mediator Models - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 38
Title:
Multiple Mediator Models
Description:
... X1 father's education, X2 father's occupation, X3 number of siblings in the ... Occupation. h2. B21. 4.3767 (.1202) g11 .0385 (.0025) X1 ?1 ?2. ?11 21 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:466
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Multiple Mediator Models
1
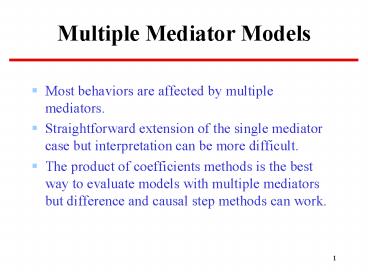
Multiple Mediator Models
- Most behaviors are affected by multiple
mediators. - Straightforward extension of the single mediator
case but interpretation can be more difficult. - The product of coefficients methods is the best
way to evaluate models with multiple mediators
but difference and causal step methods can work.
2
Step 1
MEDIATOR
M1
MEDIATOR
M2
INDEPENDENT VARIABLE
DEPENDENT VARIABLE
c
Y
X
MEDIATOR
M3
MEDIATOR
M4
- The independent variable causes the dependent
variable - Y cX e1
3
Step 2
MEDIATOR
M1
a1
a2
MEDIATOR
M2
INDEPENDENT VARIABLE
DEPENDENT VARIABLE
Y
X
a3
MEDIATOR
M3
a4
MEDIATOR
M4
2. The independent variable causes the potential
mediators M1 a1X e2, M2 a2X
e3, M3 a3X e4, M4 a4X e5
4
Step 3
MEDIATOR
M1
b1
a1
b2
a2
MEDIATOR
M2
DEPENDENT VARIABLE
INDEPENDENT VARIABLE
c
X
Y
a3
b3
MEDIATOR
M3
a4
b4
MEDIATOR
M4
- The mediators must cause the dependent variable
controlling for exposure to the independent
variable
Y cX b1M1 b2M2
b3M3 b4M4 e6
5
Measures of Mediation
Mediated effects a1b1, a2b2, a3b3, a4b4
Standard error Total mediated effect a1b1
a2b2 a3b3 a4b4 c - c Direct effect c
Total effect a1b1 a2b2 a3b3 a4b4 cc Test
for significant mediation z Compare to
empirical distribution of the mediated
effect
6
Measures of Relative Effect
- Proportion Mediated aibi/(c ?aibi) aibi/c
- Ratio of Mediated to Direct aibi/c
- Simulation studies suggest large samples are
necessary for these values to be accurate for the
single mediator model, e.g. 500 for the
proportion and 1000 for the ratio, MacKinnon et
al. (1995). - Absolute values do and squaring terms do not
improve the situation.
7
Expectancy effects on Achievement
- Harris and Rosenthal (1985) meta-analysis of
mediators of the relation between teacher
expectancy and student performance. - Here is a hypothetical study (N40) with two
mediators. (M1) social climate and (M2) material
covered. Y is a test of achievement and X is the
randomly assigned student ability value for each
student. It was hypothesized that the ability
score invokes an expectancy which affects warmth
and material covered which leads to greater
achievement.
8
SAS Program for Expectancy effects on Achievement
Model
- proc reg
- model yx
- model yx m1 m2/covb
- model m1x
- model m2x
9
SPSS Program for Expectancy effects on
Achievement Model
- Regression
- /variables x y m1 m2
- /dependenty
- /enterx.
- regression
- /variables x y m1 m2
- /dependenty
- /enterx m1 m2.
- regression
- /variables x y m1
- /dependentm1
- /enter x.
- regression
- /variables x y m2
- /dependentm2
- /enter x.
10
Two Mediator Model
MEDIATOR
.8401 (.1580)
.5690 (.1568)
M1
.1122 (.2073)
DEPENDENT VARIABLE
INDEPENDENT VARIABLE
Y
X
MEDIATOR
.5297 (.1696)
M2
.2219 (.1460)
11
Mediated Effect Measures
a1b1 (.8401) (.5690) .4781 for mediation
through social climate and a2b2 (.2219)
(.5297) .1175 for mediation through feedback.
The total mediated effect of a1b1 ( .4781) plus
a2b2 (.1175) equals .5956 which is equal to c-c
.7078-.1122 .5956. The a1b1 mediated effect
(sa1b1 .1499) was statistically significant
(ta1b1 3.183) and the a2b2 mediated effect
(sa2b2 .0838) was not (ta2b2 1.403). The
standard error of the total mediated effect is
equal to .1717 yielding a z statistic of
3.468.
12
Confidence Limits
Mediation through social climate, Asymmetric LCL
.2079 and UCL .8284. Using the delta standard
error, LCL .1654 and UCL .7906. Mediation
through feedback, Asymmetric LCL -.0261 and UCL
.3106. Using the delta standard error, LCL
-.0510 and UCL . 2861.
13
Special Topic Test of Equality of two Mediated
Effects
- Sa1b1-a2b2
- Add 2b1b2sa1a2 to the equation if there is a
covariance between a1 and a2, sa1a2 if
covariance structure modeling is used, for
example. There may also be other covariances
that are needed but these are typically very
small. - The difference between the two mediated effects
is equal to .3605 with a standard error of .1717
yielding a z statistic of 2.099. - Contrasts can be used to test pairs of mediated
effects in any model. - See MacKinnon (2000) Contrasts in Multiple
Mediator Models
14
Multiple Mediator Model of Intent to Use Anabolic
Steroids
Knowledge of the effects of AAS use
-.083 -.02 (.006)
.236 2.42 (.258)
Team as inform-ation source
-.079 -.08 (.006)
.217 .52 (.061)
.000 .001 (.056)
Group
Intentions
Perceived risks of AAS use
.168 .44 (.066)
-.265 -.25 (.024)
.149 .62 (.108)
.155 .09 (.014)
Reasons to use AAS
15
Mediated Effects
Effect Estimate Estimate/ LCL UCL (Std
Error) SE Knowledge -.046 -3.00 -.075 -.017
(.015) Team as -.041 -2.97 -.068 -.014 Infor
mation (.014) Perceived Severity -.108 -5.56 -
.145 -.071 (.013) Reasons to
use .056 4.29 .031 .081 Anabolic
Steroid (.031) Direct Effect of
.001 0.017 -.109 .111 Program on
Intentions (.056)
16
Contrasts of Mediated Effects
- Multiple mediator models introduce more than one
mediated effect for each dependent variable. - Contrasts may used to compare pairs of effects or
two groups of mediated effects. - The direct effect may be included in contrasts
also. - Any combination of effects may be compared as
long as all effects have the same dependent
variable makes scaling of all effects the same
and thus they may be directly compared to one
another.
17
Contrast Examples
a1b1-a2b2 2(a2b2) -(a3b3a4b4) a2b2c 2(a4b4)
18
Contrast Standard Errors
- Standard errors for contrasts are derived using
the multivariate delta method. This is a general
method for finding variances of functions (and is
the technique used by Sobel (1982) to find the
variance of the mediated effect). - The standard error formula will vary according to
the effects being compared. - For a simple contrast of two mediated effects
- Sa1b1-a2b2
- Add 2b1b2sa1a2 to the equation if there is a
covariance between a1 and a2, sa1a2 if
covariance structure modeling is used, for
example. There may also be other covariances
that are needed but these are typically very
small.
19
Pairwise Contrasts for the ATLAS program Effects
Model
Effect Estimate Estimate/ LCL UCL (Std
Error) SE Pairwise Contrast -.005 -0.22 -.046
.036 Of Knowledge vs. (.021) Team as
Information Pairwise Contrast -.066 2.67 -.11
5 -.017 Of Team as (.025) Information
vs. Perceived Severity From MacKinnon (2000)
Contrasts in Multiple Mediator Models.
20
Special Topic Inconsistent Mediation Models
- Inconsistent mediation models are models where at
least one of the mediated effects and direct
effects have different signs (see MacKinnon,
Krull, Lockwood 2000). - If the overall effect of X on Y is zero but there
is a significant mediated effect, then it is an
inconsistent mediation model. These effects are
sometimes called suppressor effects. In these
models the effect of X on Y actually increases
when the mediator is included in the model. - one may be equally misled in assuming that an
absence of relation between two variables is
real, whereas it may be due .. to the intrusion
of a third variable (Rosenberg, 1968, p. 84).
21
Inconsistent mediation in ATLAS Data
REASONS TO USE AAS
XM
.573 (.105)
.073 (.014)
PROGRAM
INTENTION TO USE AAS
-.181 (.056)
X
Y
Mediated effect .042 Standard error .011
22
Mediators of null effect of status on perceived
sexual harassment (Sheets Braver,1999)
Power Perceptions
M1
Harassment
0
Organizational Status
Y
X
Social Dominance
-
M2
23
Mediators of the null effect of age on typing
(Salthouse, 1984)
Reaction Time
-
M1
Typing Proficiency
0
Age
Y
X
Skill
M2
24
Mediation in Structural Equation Models
- Many models have multiple dependent variables,
multiple independent variables, and multiple
mediators. - With more than one dependent variable, a more
detailed modeling approach is required. The new
method is called path analysis or covariance
structure modeling. - Matrices are used to specify and estimate these
models because matrices organize all the
variables in the model. The number and type of
mediated effects are increased in these models.
Matrix equations are used to find mediated
effects and their standard errors.
25
Socioeconomic Status and Achievement
- Duncan et al. (1972) presented data on
achievement that have been used to illustrate
methodological developments in mediation. The
data are from 3214, 35-44 year old males measured
during the March of 1962 as part of a large
survey of the civilian labor force. - There are six variables X1 fathers education,
X2 fathers occupation, X3 number of siblings in
the respondents family, Y1 respondents
education, Y2 respondents occupational status,
and Y3 respondents income. - Many types of mediated effects
26
g11 .0385 (.0025)
B21 4.3767 (.1202)
B31 .1998 (.0364)
g21 .1352 (.0175)
g31 .0114 (.0045)
g12 .1707 (.0156)
g32 .0712 (.0275)
g22 .0490 (.1082)
g13 -.2281 (.0176)
g33 -.0373 (.0314)
B32 .0704 (.0045)
g23 -.4631 (.1231)
27
g11 .0385 (.0025)
B21 4.3767 (.1202)
- X1gt?1gt ?2
- ?11ß21
- (.0385) (4.3747) .1685
- s?11ß21 Square Root
- (.0385)2 (.1202)2 (4.3747)2 (.0025)2 .0118
28
Mediated Effects
- Effect Parameters Estimate SE
- FEDUC -gt REDUC -gt ROCC
- X1gt?1gt ?2 ?11ß21 .1685 .0118
- FEDUC -gt ROCC -gt RINC
- X1 gt ?2gt ?3 ?21ß32 .0095 .0014
- FEDUC -gt REDUC -gt RINC
- X1gt ?1gt ?3 ?11ß31 .0077 .0015
- FEDUC -gt REDUC -gtROCC -gt RINC
- X1gt ?1gt ?2 gt ?3 ?11ß21ß32 .0119 .0011
- FOCC -gt REDUC -gt ROCC
- X2gt ?1-gt ?2 ?12ß21 .7473 .0713
29
g11 .0385 (.0025)
B21 4.3767 (.1202)
B32 .0704 (.0045)
30
Three Path Mediated Effect
b4
b1
b2
b3
X
M1
M2
Y
Mediated effect b1b2b3 Var(b1b2b3) b12b22sb32
b12b32sb22 b22b32sb12 2 b1b2b32sb2b12 2
b1b22b3sb1b32 2 b12b2b3sb2b32 Standard
Error(b1b2b3)
31
g11 .0385 (.0025)
B21 4.3767 (.1202)
B31 .1998 (.0364)
g21 .1352 (.0175)
B32 .0704 (.0045)
32
LISREL and EQS Total Mediated Effects for the SES
Model
- The keyword EF command on the OUTPUT line in
LISREL requests output of total mediated effects
and their standard errors. The keyword
EFFECTSYES on the /PRINT line has EQS print out
total mediated effects and standard errors. - These programs print the total mediated effect of
X on Y. For example,with this model the total
mediated effect of X1 on ?2 is the same as the
specific mediated effect, X1 -gt ?1, -gt ?2,
.1683. The total mediated effect of X1 on ?3
equals X1 -gt ?2 -gt ?3 plus X1 -gt ?1 -gt ?3, plus
X1 -gt ?1 -gt ?2 -gt ?3 or the sum of three specific
indirect effects. - You will need to apply the formulas above to find
specific mediated effects and their standard
errors.
33
EQS Total Mediated effects for the SES Model
- DECOMPOSITION OF EFFECTS WITH NONSTANDARDIZED
VALUES - PARAMETER INDIRECT EFFECTS
- __________________________
- INC1961 V1 .308V3 .148V4
.029V5 .090V6 - .021
.014 .002 .012
- 14.403
10.286 13.186 7.413
- .070 E2
.508 E3 - .004
.031
- 15.682
16.601 - OCC1962 V2 .998V4 .168V5
.747V6 4.377 E3 - .082
.012 .071 .120
- 12.197
14.281 10.492 36.402
34
LISREL Total Mediated effects for the SES Model
- Indirect Effects of X on Y
- FATHOCC FATHEDUC NUMSIB
- ________ ________ ________
- EDUC _ _ _ _ _ _
- OCC1962 0.1683 0.7473 0.9982
- (0.0118) (0.0713) (0.0819)
- 14.2746 10.4868 12.1916
- INC1961 0.0291 0.0902 0.1485
- (0.0022) (0.0121) (0.0143)
- 13.3260 7.4621 10.3749
35
Mplus 3.0 (2004) Indirect Effect Capabilities
- Mplus 3.0 will compute bias-corrected bootstrap
confidence intervals. Specify the number of
bootstrap samples, BOOTSTRAP 500 and include
CINTERVAL on the OUTPUT line. - Mplus 3.0 now computes standard errors and
confidence intervals for tests of specific
indirect effects with the MODEL INDIRECT
statement! - MODEL INDIRECT
- INC1961 IND FATHOCC
- Requests the three indirect effects from fathers
occupation to income in 1961. - INC1961 IND EDUC FATHEDUC
- Requests specific indirect effect from fathers
education to 1961 income.
36
Latent Variable Mediation Model
M2
M3
M1
M
a
b
X
Y
c
X1
X2
X3
Y2
Y3
Y1
37
Latent Variable Mediation Models
- Equations for standard errors of mediated effects
are more complicated because they include the
measurement models for the variables in the
model. - Covariance between a and b may be nonzero so use
formula that includes covariance between a and b.
SEM programs compute the values of total mediated
effect and Mplus 3.0 will compute specific
mediated effects that include appropriate
covariances in the standard error calculations.
Resampling methods can also be used to obtain
confidence intervals such as in Mplus 3.0 by
specifying the number of bootstrap samples,
BOOTSTRAP 500 and CINTERVAL on the OUTPUT line.
38
Summary of Multiple Mediators
- There are methods to incorporate multiple
mediators and latent variables in mediator
models. These models require a covariance
structure analysis program to estimate the
models. Standard errors of mediated effects can
contrasts among mediated effects can be
evaluated. - However, remember the assumptions of the single
mediator model apply to the multiple mediator
model. The additional variables address the
omitted variable assumption. But other
assumptions still apply. Specificity of
significant mediation paths improve
interpretation. - The results from a multiple mediator model may
shed light on the true underlying mechanisms but
there are alternative explanations of results.
Remember that the path relating the mediators to
Y is correlation.