Human information processing: Chapters 49 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 40
Title:
Human information processing: Chapters 49
Description:
Description of bias and heuristics that reflect human limits. Analytical. Slow ... Action selected without comparison with alternates ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:359
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Human information processing: Chapters 49
1
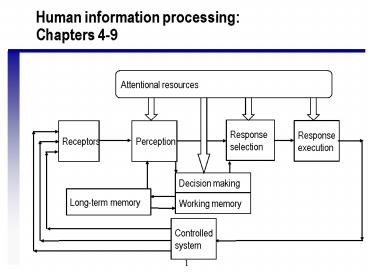
Human information processingChapters 4-9
Attentional resources
Response selection
Response execution
Receptors
Perception
Decision making
Long-term memory
Working memory
Controlled system
2
Objectives
- Different types of decision making descriptions
and the implications for design - Heuristics and biases affecting decisions
- Levels of cognitive control describe
qualitatively different types of human
performance - Levels of cognitive control span many theories of
DM and can identify training and cognitive
support strategies - Skill-based processing and affect are key
elements of decision making
3
Decision making defined
- Decision making defined as
- Select one choice from many
- Some information available regarding choices
- Time frame is relatively long (gt 1 sec)
- Uncertainty regarding best or acceptable choice
- Builds upon basic cognitive mechanisms of
perception, working memory, attention and LTM
4
Decision making types
- Intuitive
- Quick
- Automatic
- Classical Decision Theory
- Optimal, rational decision determined through use
of expected values - Description of bias and heuristics that reflect
human limits
- Analytical
- Slow
- Deliberate, controlled
- Naturalistic DM
- Experienced people
- Complex, dynamic environments
- Based on experiences and mental simulations
5
Expected utility calculations example
Expected value of choice v equals the sum of
the probabilities and values E(v) ?p(i)v(i)
For the most simple case of the
lottery Purchase ticket p(winning)1x10-7 v(wi
nning) 1x106 E(ticket value-ticket
cost)0.10-1.0 Save money p(bank
surviving)1-1x10-7 v(with interest)
1.02 E(money saved)1.019999
6
Types of classical decision theory
- Normative models
- What people SHOULD do
- Basis of computer aids
- Basis for understanding when people make rational
decisions - Basis for training
- Descriptive models
- What people ACTUALLY do
- Heuristics used/ Biases that undermine
performance - Information processing model as a descriptive
model of DM
7
Elements of decision process
- Obtain and combine cues (selective attention)
- Generate hypotheses (LTM)
- Hypothesis evaluation and selection (working
memory) - Action selection (working memory, LTM)
8
Information processing model of DM
Working memory
Uncertainty
Choice
Diagnosis
Cues
Selective attention
C1
H
H
A
A
C2
C3
C4
LTM
A
A
H
H
A
A
H
A
H
H
A
A
A
H
H
H
9
Factors influencing heuristics and biases
- Selective attention
- Limited capacity of working memory
- Time available
- Limited attentional resources
- Limited knowledge (LTM)
- Ability to retrieve appropriate information
(inert knowledge)
10
Which penny Precise decisions with imprecise
knowledge
11
Heuristics and biases Obtaining and selecting
cues
- Attention to limited number of cues (landing gear
light fixation) - Cue primacy (first cues get greater weight)
- Inattention to later cues (ignore later cues)
- Cue salience
- Inappropriate weight to unreliable cues
12
Heuristics and biases Hypothesis generation
- Limited number of hypotheses generated
- Availability heuristic (frequent, recent)
- Representative heuristic (take as typical of
category) - Overconfidence
13
Heuristics and biases Hypothesis evaluation and
selection
- Cognitive fixation (continue along path, ignoring
contrary information) - Confirmation bias
- Seek only evidence to confirm NOT to disconfirm
- Fail to use absence of important cues
14
Heuristics and biases Action selection
- Retrieve small number of actions
- Availability heuristic for actions
- Availability heuristic for possible outcome
- Subjective probability does not equal actual
15
Decision making types
- Classical Decision Theory
- Heuristics and biases associated information
processing limits
- Naturalistic DM
- Levels of cognitive performance/control for
experienced people in complex, dynamic
environments
16
Characteristics of naturalistic decision making
situations
- Ill-structured problems
- Uncertain high-risk environments
- Cognitive processing as an iterative
action/feedback loop - Time constraints and time stress
- Multiple persons involved in decision
- People with extreme domain expertise
17
The strange case of Phineas Gage
http//www.mc.maricopa.edu/academic/ cult_sci/anth
ro/origins/phineas.html
Left intellectual abilities intact, but greatly
impaired decision making
18
Elements of naturalistic decision making
- Implications of levels of cognitive control
- Types of information
- Level of expertise
- Error tendencies
- Situation awareness
- Implications for decision aids
19
(No Transcript)
20
Levels of cognitive control
21
(No Transcript)
22
Types of information
23
Amount of experience
Novice
Expert
24
Error tendencies
Failure to consider consequence
Misclassification of situation
Perform task out of habit Motor control error
25
Situation awareness
- The perception of the elements in the
environment with a volume of time and space, the
comprehension of their meaning and the projection
of their status in the near future - Level 1 Perceiving status
- Level 2 Comprehending information in light of
goals - Level 3 Projecting the activity to the future
26
Situation awareness
Level 3 SA
Level 2 SA
Level 1 SA
27
Cognitive continuum theory
Analytic
Intuitive
28
Cognitive continuum theory
- Factors inducing Intuition
- Large number of cues
- Brief display of cues
- Complex relationship between cues
- Short DM time
- Analog display
- Factors inducing Analysis
- Few cues
- Long availability of cues
- High consequence
- Digital display
29
Recognition-primed decision making
- Pattern matching used to recognize situation
- Recognition primes the selection of a plausible
solution - Action selected without comparison with
alternates - Action evaluated through simulation using a
mental model - Particularly effective in time-constrained
situations - 40-80 based on condition-action rules
30
Recognition-primed decision making
Simulation-based evaluation with mental model
Application of condition-action rules
31
Improving decision making
- Redesign to support decision making and
performance - Decision aids
- Training
32
Redesign
- Accentuate relevant cues
- Warning devices to guide attention to critical
events - Restructure situation and overall system
- Analysis of system dynamics
33
Training
- Train analytic methods, has proven marginally
successful - Train better metacognition (e.g., manage time
pressure), has proven marginally successful - Focus on job-relevant knowledge and procedures
- Train skill-based with actual cues
- Cognitive feedback rather than performance
feedback
34
Decision aids
- Fallacy of expert systems
- No basis for evaluation of the input
- Output mistrusted
- Joint cognitive breakdowns due to unanticipated
complexity - Cognitive support
- Interactive system that improves DM by extending
users capabilities - Tool rather than prosthesis
35
Types of cognitive support
Display and call attention to important
cues Present reliability/value of cues Allow
operators to specify alarms according to
circumstances
36
Types of cognitive support
Use spatial organization to state
information Present condition-action rules and
discrepancies Indicate variable levels that
require responses (e.g., level associated with
normal operations)
37
Types of cognitive support
Support what if analysis Provide an
externalized mental model in the display Provide
critiques of hypotheses generated
38
Problem solving
Requires Knowledge Mental model for
simulation Working memory capacity
39
Critiquing systemhttp//freney.sys.virginia.edu/
sag3c/ProblemBasedLearning.html
40
Key concepts
- Different types of decision making descriptions
and the implications for design - Heuristics and biases affecting decisions
- Levels of cognitive control describe
qualitatively different types of human
performance - Levels of cognitive control span many theories of
DM and can identify training and cognitive
support strategies - Skill-based processing and affect are key
elements of decision making