Drug elimination 2: Liver - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 26
Title:
Drug elimination 2: Liver
Description:
(e.g. heparan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate), sulfated ... FAD. FMN. Heme (Fe) NADPH H NADP 2H 2 e- 2 e- 2 e- O2. R-H. O2- R-OH. Cytochrome P450 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:647
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Drug elimination 2: Liver
1
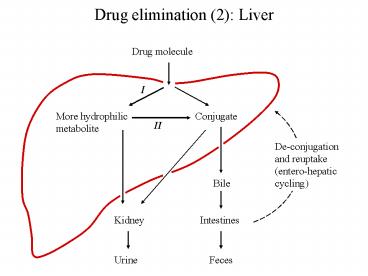
Drug elimination (2) Liver
Drug molecule
I
More hydrophilic metabolite
Conjugate
II
De-conjugation and reuptake (entero-hepatic
cycling)
Bile
Kidney
Intestines
Urine
Feces
2
Hepatic metabolism of morphine
Morphine UDP-glucuronide
Morphine-glucuronide UDP
Urine, bile
Morphine
Glucuronate
3
Hepatic metabolism of phenobarbital
4
Blood flow and bile flow in the liver tissue
to right heart
to bile bladder intestine
from intestine
5
UDP glucuronide
Glucose-6P Glucose-1P UDP-Glucose UDP-Glucur
onide Drug conjugates
Glycogen
Polysaccharides, proteoglycans
6
3-Phospho-adenosine-5-phosphosulfate (PAPS)
ATP
Sulfate
ATP
Pyrophosphate
ADP
PAPS
Sulfated polysaccharides and proteoglycans (e.g.
heparan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate), sulfated
sphingolipids (sulfatides)
Drug conjugates
7
Drug biotransformation reactions
- Oxidative reactions
- N- and O-dealkylation
- Aliphatic and aromatic hydroxylation
- N-Oxidation and N-Hydroxylation
- Sulfoxide formation
- Deamination
- Desulfuration
- Conjugation reactions (with)
- Glucuronidation (UDP-Glucuronic acid)
- Acetylation (Acetyl-CoA)
- Conjugation with glycine
- Sulfate (PAPS)
- O-, N-, S-Methylation (S-Adenosylmethionine)
- Hydrolysis (Esters and amides)
- Reduction Azo reduction, nitro reduction
8
S-Adenosylmethionine (SAM)
ATP
Methionine
PP P
SAM
Methylation of DNA, Lipids,
Drug conjugates
9
Metabolism of Isoniazid (isonicotinic acid
hydrazide)
Acetyl-CoA
CoA
H2O
Acetylation of proteins
Isonicotinic acid
Acetylhydrazine
Liver toxicity
10
Genetic variability in INH acetylation
fast acetylators
slow acetylators
11
Cytochrome P450
12
Endoplasmic reticulum in the liver
13
The microsomal cytochrome P450 system
- Cytochrome P450 enzymes
- Catalyze oxidation / hydroxylation of hydrophobic
substrates, transferring a single oxygen atom
from O2 to the substrate - Use molecular oxygen as substrate and NADPH as a
cosubstrate, to dispose of the second oxygen not
transferred to the substrate - Large gene superfamily, present in both
prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms - In mammalian cells, present in both the ER and
(with some variations) the mitochondrion - Several dozen isoforms in humans, several of
these involved in drug metabolism
14
The microsomal cytochrome P450 system (2)
- Effects on drugs / poisons can be beneficial
(inactivation, accelerated excretion) and harmful
(conferment of toxic activity to inert compound) - A single isoform CYP3A4 is responsible for
the metabolism of gt 50 of the clinically
prescribed drugs that do get metabolized in the
liver - CYP3A4 and several other isoforms are inducible
prolonged drug application enhances expression
and activity of enzyme in liver - Induction may lead to accelerated metabolism of
multiple drugs (not just the inducer itself).
Example Rifampicin or phenytoin ? accelerated
inactivation of contraceptive agents
15
a)
b)
c)
16
Propranolol as an example of drug transformation
in the liver
Propranolol
17
Mechanism of drug-mediated cytochrome P450
induction
D
hnf4
hnf4
mRNA
CYP 3A4
18
Benzopyrene as an example of harmful drug
metabolism
Mutation, carcinogenesis
CYP 1A1
19
Glutathione conjugation A detoxifying pathway
Glutathione-S-
Glutathione-S- Transferase
Urine
20
Metabolism of acetaminophen
21
Reductive drug metabolism
- NADPH- and NADH-dependent reductases
- CYP450 reductases, CYP450 itself
- Thioredoxin
Prontosil rubrum
22
Vicia faba (broad bean)
23
Favism Catalytic depletion of glutathione by
isouramil
Glutathione peroxidase
spontaneous
spontaneous
24
Uses of NADPH (4) Scavenging reactive oxygen
species
H2O2
G-SH HS-G
NADP
Glutathione reductase
Glutathione peroxidase
2 H2O
G-SS-G
NADPHH
25
Glucose-6P-dehydrogenase deficiency is one of the
most common enzyme defects
- Most patients healthy most of the time
hemolytic crisis occurs upon exposure to drugs or
diet components that cause enhanced formation of
ROS - Manifestation in the red cells because these
cells lack protein synthesis no replacement of
deficient protein molecules - Affords partial protection against malaria
similar to sickle cell anemia and other
hemoglobinopathias
26
Primaquine and G6PDH deficiency