Transition - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 11
Title:
Transition
Description:
none. none. total. total. The economic transition of formally centrally planned economies has ... none. none. total. total. No country in the world fits in ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:48
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Transition
1
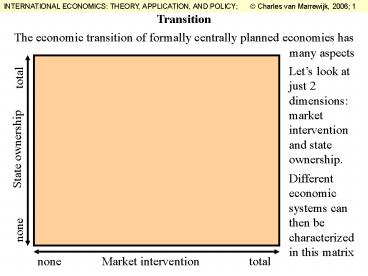
Transition
Lets look at just 2 dimensions market
intervention and state ownership.
total
State ownership
Different economic systems can then be
characterized in this matrix
none
Market intervention
none
total
2
Transition
total
At the other extreme communism with total state
ownership and total government control.
State ownership
none
Market intervention
none
total
3
Transition
No country in the world fits in either extreme
description.
Even the USA has a public sector spending 30 of
GDP
total
State ownership
Even North Korea and Cuba have private production
and incentives.
none
Market intervention
none
total
4
Transition
Note that other hypothetical extremes are also
possible.
A country in transition is changing the mix of
state ownership and market intervention in the
medium run.
total
State ownership
From the same initial position many different
paths are possible.
none
Market intervention
none
total
5
Transition
total
If we would place Holland in this figure and
characterize its path over the last 15 years it
would look somewhat like this
State ownership
Holland
Holland
Holland
Holland
Holland
Holland
none
Market intervention
none
total
6
Transition, a second J-curve
The multidimensional character of transition, the
differences in initial positions, the differences
in transition mix and speed of privatization and
deregulation make it easy to understand why
different countries have widely varying
transition experiences.
Transition involves a series of steps at the
institutional, micro-economic and macroeconomic
level. Inevitably, adjustment requires a
reallocation of capital, services and labour
between sectors of the economy, leading to an
initial phase of decline in production.
- There are two strategies of reform
- the big bang approach, achieving necessary
steps of transition in a short period of time,
leading to large initial declines of production
(Poland is the prime example) - the gradual approach, trying to systematically
sequence the steps to be taken and minimize
transition pain and output loss (successor states
of the former Soviet Union).
7
Transition, a second J-curve
Poland used the big bang strategy. It started
to recover quite quickly this strategy seems to
have worked better than the gradual approach.
8
Transition, the costs
The transition process is estimated to lead to
huge costs.
Lets look at these costs using a neoclassical
framework and our knowledge of the construction
of statistics.
We draw a ppf for a transition country.
On the axes we put market goods versus planned
good.
The economy produces a lot of planned goods at P0
P0
9
Transition, the costs
The transition process brings the economy from
production point P0 to P2.
market goods
How long it takes, and how it evolves we cannot
say here we have drawn a possibility.
P2
Production point P1 is reached after some time.
P1
P0
planned goods
10
Transition, the costs
How do we measure the loss in output resulting
from the transition?
Statisticians use the prices at P0 to estimate
the fall in production.
market goods
Clearly, the estimated production loss at P1
compared to P0 is substantial.
P2
P1
P0
planned goods
11
Transition, the costs
Remember that the initial production point P0 was
not optimal.
After the transition process is complete the
production point P2 should represent true
preferences.
market goods
P2
Using P2 prices there is no production loss at P1
relative to P0.
Using preferences there is actually a welfare
gain.
P1
P0
The estimated loss is exaggerated.
planned goods