Diffusion Weighted Imaging - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
Diffusion Weighted Imaging
Description:
Stejskal and Tanner technique: ... Surgical planning & post-surgical monitoring ... DTI as a still evolving technology is a powerful tool for white matter tracts ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:472
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Diffusion Weighted Imaging
1
Diffusion Weighted Imaging Diffusion Tensor
Imaging
Dilek GOKSEL Bogazici University, Biomedical
Engineering Institute, Turkey
- Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI)
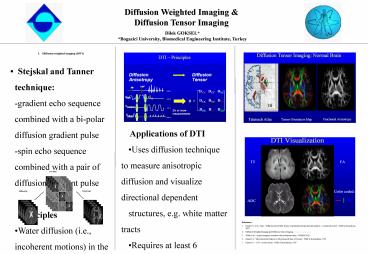
- Stejskal and Tanner technique
- -gradient echo sequence combined with a bi-polar
diffusion gradient pulse - -spin echo sequence combined with a pair of
diffusion gradient pulse - Principles
- Water diffusion (i.e., incoherent motions) in
the presence a magnetic field will dephase MR
signal, or causing signal attenuation. - Signal is attenuated exponentially by the
apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC). - Low ADC appears hyper-intense, brighter
- Higher ADC appears hypo-intense, or darker
- Different level of diffusion weighting can be
achieved by changing b-value, which is a function
of gradient amplitude and duration. - Summary of DWI
- DWI is very powerful technique for a
noninvasive in vivo study of diffusion process in
human tissue. - It requires fast imaging technique, such as
EPI. - DTI is a sensitive and specific tool for the
diagnosis of acute infarction in stroke patient,
and it can be used to improve stroke management
and treatment.
Applications of DTI Uses diffusion
technique to measure anisotropic diffusion and
visualize directional dependent structures, e.g.
white matter tracts Requires at least 6
diffusion encoding directions, plus one
T2. Diffusion Anisotropy can be represented
by Fractional Anisotropy (FA) map most
frequently used, Tensor orientation map RGB
color coded. Other quantitative info.
Potential Applications of Diffusion Tensor
Imaging White matter tracts visualization
tract tracking Neurological pathway and
connectivity White matter integrity in various
white matter related diseases Surgical planning
post-surgical monitoring Comprehensive brain
exam in conjunction with fMRI, MR perfusion, and
MRA etc. Summary of DTI DTI as a
still evolving technology is a powerful tool for
white matter tracts visualization
non- invasively. DTI can be used for study and
better understanding of neurological pathways and
connectivity. The areas of the technical
improvements include High-resolution
DTI, Correction for the artifacts caused by
motions, eddy-current induced distortions, and
susceptibility differences, DSI (q-space
imaging) for differentiating fibers
crossing, Better model (multi-component) for
diffusion in tissue.
- References
- Basser P.J., D.K. Jones, Diffusion-tensor MRI
theory, experimental design and data analysis a
technical review, NMR in Biomedicine, 2002. - Diffusion Weighted Imaging and Diffusion Tensor
Imaging, www.bme.emory.edu - Welsh et al, 'q-space imaging correlates with
mechanical strain, ISMRM 2002. - Basser P.J., Microstructural Features
Physiological State of Tissues, NMR in
Biomedicine, 1995. - Basser P.J., DTI - review article, NMR in
Biomedicine, 1995