Sequence variation and sequence detection
1 / 23
Title:
Sequence variation and sequence detection
Description:
Identify the most important results and their significance ... Garnier et al. (2001) Mating system and reproductive skew in black rhinoceros. To do ... –
Number of Views:77
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Sequence variation and sequence detection
1
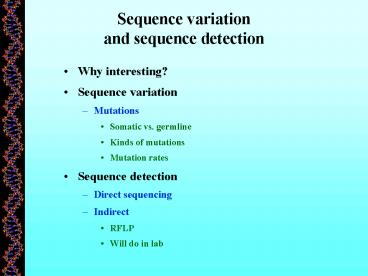
Sequence variation and sequence detection
- Why interesting?
- Sequence variation
- Mutations
- Somatic vs. germline
- Kinds of mutations
- Mutation rates
- Sequence detection
- Direct sequencing
- Indirect
- RFLP
- Will do in lab
2
Assignment
- 10 of course marks
- Due next Thursday before class
- Aims
- Identify the most important results and their
significance - Communicate the findings to a non-specialist
audience - Identify possible problems and their solutions
- Paper
- Garnier et al. (2001) Mating system and
reproductive skew in black rhinoceros - To do
- Write popular article (National Geographic)
- 1000 words
- Tell story, explain microsatellites
- Data evaluation
- Plug microsatellite data into spreadsheet
- H HO
- Use 6 most variable and 6 least variable loci
- Test assignment success and compare with paper
- Identify potential problems
- Have they dealt with them?
3
Direct and indirect sequence detection
- DNA sequence
- Ultimate code of life
- What we are after?
- Other methods used to detect it
- Allozymes
- Microsatellites
- Indirect methods detect only small part
- Question
- How do sequences mutate?
- How can we detect variation?
4
Mutations
- Somatic mutations
- Occur in soma (tissue)
- Not heritable
- May cause disease
- E.g. cancer
- Germline mutations
- Heritable
- Introduce genetic variability
- One of the main driving forcesof evolution
- Random process
- Blind watchmaker
5
Kinds of mutation
- Substitutions
- Synonymous / nonsynonymous
- Transitions / transversions
- Indels
- Insertions / Deletions
- Rearrangements
- Pieces of chromosomes switched around
- Transposable elements
- Move around in genome
- Gene duplications
- May free up genes from selection
- May acquire new function
- Ploidy changes
6
Mutation mechanism
- Base substitutions
- Wrong bases
- Wobble pairing
- G-T, A-C
- A-G, C-T
7
Substitution
8
Types and effects of substitutions
9
Types and effects of substitutions
10
Insertion - deletion
11
Mutation rates
- Depend on sequence and site
- DNA repair mechanisms
- Selection
- MtDNA gt nuclear
- Less efficient repair
- Coding gt non-coding
- Repair more efficient
- Selective removal of mutations
- Variation among coding genes
- Transversions gt transitions
- Less interuption to 3D structure
- Less likely to be repaired
- Codon position
- Related to amino acid change
- 3rd gt 1st gt 2nd
12
Mutation rates
A
- Some substitutions more likely than others
- Transitions gt Transversions (101)
- Transition (Ts) purine ? purine (A,G),
pyrimidine ? pyrimidine (C, T) - Transversion (Tv) purine ? pyrimidine
- But repeated mutations make apparent
transversions more common - Deep phylogenies only use transversions
C
T
G
13
Mutation rates
- Example
- Cichlid fishes
- Transversion / transition 0.1
- More divergent species
- Ratio approaches 0.5
14
Mutation rates - DNA sequences Substitution
saturation
- Coding sequences
- 3 nucleotides per amino acid (AA)
- Redundant code
- Change in 3rd position usually doesnt change the
AA - Synonymous mutation
- Relaxed selection higher mutation rates
- Sites with multiple hits
- Observed rate of substitution lower than real
- May have to discard from analysis
15
Substitution saturationribulose 1,5 biphosphate
carboxylase in algae
16
Sequencing
- PCR
- dNTP as ingredients
- Building blocks for DNA
- Sanger method
- ddNTP
- Stops DNA extension
- Bad nucleotide
- 4 reactions
- A,C,G,T ddA
- A,C,G,T ddC
- A,C,G,T ddG
- A,C,G,T ddT
Deoxynucleotide triphosphate (dNTP)
Dideoxynucleotide triphosphate (ddNTP)
17
Sequence Reaction
18
Sequencing
nucleotides
bad
good
G A G C T A G C G A T T C A G
G A G A G C T A G A G C T A G C G A G A G C T A
G C G A T T C A
G A G C G A G C T A G C G A G C T A G C G A T T C
G G A G G A G C T A G G A G C T A G C G G A G C
T A G C G A T T C A G
G A G C T G A G C T A G C G A T G A G C T A G C G
A T T
19
Electrophoresissort by size
A C G T
-
G A G C T A G C G A T T C A G G A G C T A G C G
A T T C A G A G C T A G C G A T T C G A G C T A
G C G A T T G A G C T A G C G A T G A G C T A G
C G A G A G C T A G C G G A G C T A G C G A G
C T A G G A G C T A G A G C T G A G C G A G
G A G
20
Sequencing
nucleotides
bad
good
G A G C T A G C G A T T C A G
G A G A G C T A G A G C T A G C G A G A G C T A
G C G A T T C A
G A G C G A G C T A G C G A G C T A G C G A T T C
G G A G G A G C T A G G A G C T A G C G G A G C
T A G C G A T T C A G
G A G C T G A G C T A G C G A T G A G C T A G C G
A T T
21
Electrophoresissort by size
-
G A G C T A G C G A T T C A G G A G C T A G C G
A T T C A G A G C T A G C G A T T C G A G C T A
G C G A T T G A G C T A G C G A T G A G C T A G
C G A G A G C T A G C G G A G C T A G C G A G
C T A G G A G C T A G A G C T G A G C G A G
G A G
22
Automated sequencing
Peaks instead of bands
23
Key Concepts
- Distinction of types of DNA
- Only some amenable to indirect detection
- Quest for sequence data
- Types of mutations
- Substitutions
- Synonymous / non-synonymous
- Codon position
- Transition / transversion
- Mutation rates
- Accumulation of mutations
- Multiple hits
- Transitions
- 3rd codon positions
- Direct sequencing