Bioinformatics for Genome data - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 31
Title:
Bioinformatics for Genome data
Description:
Bioinformatics is the field of science in which biology, computer science, and ... Mouse: MGD, http://www.informatics.jax.org ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:56
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Bioinformatics for Genome data
1
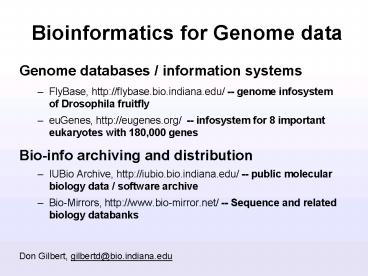
Bioinformatics for Genome data
- Genome databases / information systems
- FlyBase, http//flybase.bio.indiana.edu/ --
genome infosystem of Drosophila fruitfly - euGenes, http//eugenes.org/ -- infosystem for 8
important eukaryotes with 180,000 genes - Bio-info archiving and distribution
- IUBio Archive, http//iubio.bio.indiana.edu/ --
public molecular biology data / software archive - Bio-Mirrors, http//www.bio-mirror.net/ --
Sequence and related biology databanks
Don Gilbert, gilbertd_at_bio.indiana.edu
2
What is bioinformatics?
- Bioinformatics is the field of science in which
biology, computer science, and information
technology merge into a single discipline. The
ultimate goal of the field is to enable the
discovery of new biological insights as well as
to create a global perspective from which
unifying principles in biology can be discerned. - There are three important sub-disciplines within
bioinformatics - development of new algorithms and statistics with
which to assess relationships among members of
large data sets - analysis and interpretation of various types of
data including nucleotide sequences and proteins
gene and genome features and functions,
expression in cells and through development and
other biology data. - development and implementation of tools that
enable efficient access and management of
different types of information. - http//www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Education/index.html
w/ dgg edits
3
BioData
- BioData size, contents, dispersion, uses
- Genome data
- very important, highly complex, harder to find,
long lived - Literature (abstracted and curated), Sequence and
feature analyses, maps, controlled
vocabulary/ontologies, people, biologics,
contacts, etc. - BioData access
- Need to find and use best data
- New data kinds and sources - bio-information is
very fluid - Need current data update monthly, weekly, daily
- Distributed widely in world among 1000s of
national, regional centers labs
4
Bio Databanks, EBI, Sept. 2002
5
Constellation of Bio-Data (SRS - Lion Bioscience)
6
Genome Data Objects
Drosophila genome, FlyBase, Sept. 2002
8 eukaryote genomes, euGenes, July 2002
7
Genome Databases
- Drosophila FlyBase, http//flybase.net/ (Indiana
Univ.) - C. elegans WormBase, http//www.wormbase.org/
- Mouse MGD, http//www.informatics.jax.org/
- Saccaromyces SGD, http//genome-www.stanford.edu/
Saccharomyces/ - Human LocusLink, http//www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Locu
sLink/ - Human GeneCards http//bioinfo.weizmann.ac.il/car
ds/ - Various eukaryotes Ensembl http//www.ensembl.org
/ - Various eukaryotes euGenes http//eugenes.org/
(Indiana Univ.) - Many new organism genome systems for Daphnia,
insects, vertebrates, others with complete genome
data
8
FlyBase and euGenes
9
FlyBase.net
- Distributed project (4 sites, 6 PIs, 15
curators, 15 informaticians) 10 years old - Multiple databases project data flow and
exchange critical - Curated and computed data, from expt. literature,
genome sequence - Integrated database modules (for generic use w/
GMOD) - Genetics, Sequences, Maps, Expression
- Controlled vocabularies Ontologies
- Computational analyses
- Organism, taxonomy, phylogenetic/comparative
- Publications, General
10
euGenes.org
- Automated genome summaries for Human, Fruitfly,
Mouse, Mosquito, Arabidopsis, C. elegans,
Saccharomyces, Zebrafish - 3 year, computational DB project, 1 part-time
informatician (dgg ?) - genome maps, sequences, gene reports, external
database links - cross-species comparisons similar genes, genome
features, gene function
11
(No Transcript)
12
Anatomy of genome database info system
13
Anatomy of genome database
- Data components
- biosequences, literature, external data,
expression info, pathways, maps, anatomy,
populations, species, ecology, stocks, people - Metadata about primary data (ID, dates, sources,
evidence) - Architecture
- Relational database for management
- Search and retrieval software for flat file data
- Backend (database, analyses piplelines) Frontend
(public views and access web, ftp) Middleware
('glue' back and front) - Flexible data schema changes common
- Performance constraints
- Internet-shared, standards-based, open-source
preferred
14
Anatomy of genome database, cont.
- Analysis software
- Project uses sequence analyses, external
database comparisons - Pipeline for automated analyses, rerun as needed
- Public uses (e.g. BLAST search)
- Editing / data management interface
- Interactive document editing
- Batch data updates
15
Anatomy of genome database, cont.
- Publication interface
- Detailed biological object views (sequences,
genes, etc.) - Queries simple and frequent, ad-hoc and general
- Graphic viewers
- Data exchange
- Data definitions schema (XML)
- Controlled vocabularies of science terms,
ontologies - Minimal information for collaboration, sharing
16
Compute parts of system
- Web server (Apache) and modules
- FTP server for bulk data exchange
- Relational DBMS PostgreSQL.org, MySQL.com,
Oracle.. - Analysis programs BLAST, various bioinformatics
tools - Perl, Java middleware for data access analysis,
search and report - Limited, secure access for project data
management - Public access for released data (web, ftp)
17
FlyBase/euGenes Query System
18
FlyBase Query Results
FlyBase Genes query results Query (
libsFBgn PFgn-allwing or libs-synwing )
and libs-orgDmel, No. matches 1437 Bookmark
FBquery ( libsFBgn PFgn-allwing
libs-synwing ) libs-orgDmel
Symbol Name Map Alleles Stocks Refs DNA Date
1 18w 18 wheeler 56F11 16 2 56 13 31 May
02 2 2R-F - - 2 1 3 - 31 May 02 ...
19 Act42A Actin 42A 42A2 2 - 73 23 31 May
02 20 Act5C Actin 5C 5C7 14 1 129 43 31 May
02 ------------------- Page and Sort results
------------------ Batch Download Fetch items x
All Items Format Spreadsheet
Report content Summary Report only Select
fields Field list Refine query or find
items in related data Refine query ( libsFBgn
PFgn-allwing or libs-synwing ) and
libs-orgDmel and other fields matches
.. Search Genes , retrieve Related Data
Classes (alleles, aberrations, transcripts,
insertions, sequences )
19
Efficiency of SRS versus RDB
Drosophila Genome Annotations SRS or Gadfly DB
relational database Web search time (shorter is
better two computers - O,F)
20
Current System Dataflow
Master Genes File (rw)
People DB
Stock Center DB
Image Curation
Supplemental nightly update
Mol5 (rw)
Public (ro) /SRS
Web Browser
Dumper
Gene Loader
Gene -Seen applet
GenBank
Sequence Analysis Pipeline
gadfly (rw)
Apollo
gadfly scripts
gadfly x xml
From Stan Letovsky, FlyBase
21
Ultimate System Dataflow?
Master Genes File (rw)
People DB
Stock Center DB
Image Curation
Public (ro) /SRS
IDB proto (rw)
Web Browser
XML Dumper
XML Loader
Error cleanup
XML?
Gene -Seen applet
Apollo
GenBank
Sequence Analysis Pipeline
From Stan Letovsky, FlyBase
22
Single DB vs. Federated Info. S/R
23
GMOD - Generic Model Organism Database
Construction Set, http//www.gmod.org/
- Database schemas
- Literature curation tools
- Gene ontology management tools
- Visualization tools
- Data processing pipelines
24
From Shawn Hoon, Fugu Informatics Group
25
From Shawn Hoon, Fugu Informatics Group
26
From Shawn Hoon, Fugu Informatics Group
27
From Shawn Hoon, Fugu Informatics Group
28
Bio-Grids
29
Bio-Grids - what are they?
- transparent use of available workstations
commodity grid resources (commercial, academic) - find biodata, computing resources easily and
automatically via directories - personal/project resources and peer-peer sharing
- less reliance, less cost for centralized services
or building local IT centers - Power grid - plug in your toaster, ignore the
power sources and grid. Bio grid - plug in
workstation, ignore where data and compute power
comes from -- eventually!
30
BioGrid Schematic
- Grid-aware client software
- Data and software resource directories
- Grid of processing computers
31
From Shawn Hoon, Fugu Informatics Group