Health The Great Market - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 65
Title: Health The Great Market
1
Health The Great Market
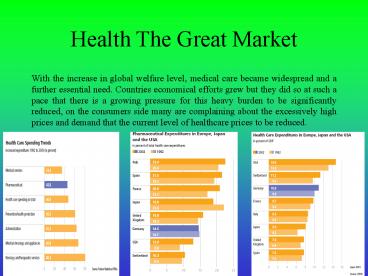
- With the increase in global welfare level,
medical care became widespread and a further
essential need. Countries economical efforts grew
but they did so at such a pace that there is a
growing pressure for this heavy burden to be
significantly reduced, on the consumers side many
are complaining about the excessively high prices
and demand that the current level of healthcare
prices to be reduced.
2
Current Situation
- As marketing exclusivity periods for first
in-class drugs decline, drug developers are
facing incresing pressure to improve productivity
in their drug development activities to help
bolster return on investment. - RD strategies that strive to attain a best
in-class status for new drugs or, at the least,
clear advantages over existing therapies with
patient subgroups or particular indications will
dominate. - They are also suffering growing pressures to
contain costs from managed care organizations and
pricing and reimbursement. - Authorities are increasing pressure on firms to
get new drugs to market sooner, preferably with
clear advantages in safety, efficacy, or economic
value.
3
Market Size
- The health market makes millions and many more as
expected as more and more people have access to
medical care. Also the population aging in
developed countries, with the many health
implications it has, causes that a new set of
needs arise. As more elderly people demand for
attention and preventive care the market will
continue to grow. The world goes on with its
globalization trend and diseases stop being local
or regional to become wide spreading at a world
level. The transmission of diseases also becomes
more and more quickly. - Despite the economic downturn, the pharmaceutical
industry has grown 7 globally with an estimated
value of 390 billion. The US market alone is
valued at 189 billion. Several factors have
contributed to this growth and the increased
revenues. The price of drugs has increased 4. A
growing baby boomer population has led to an
increased demand for medicines, and the number of
medications being prescribed for treating a
disease has also increased in recent years.
4
Market Evolution
- There have been significant changes in the
pharmaceutical business environment with several
mergers and acquisitions in the past few years,
which has resulted in a consolidated, fiercely
competitive market with fewer players. The
biggest change to come over the next 4 years is
that the industry in the US alone stands to lose
more than 36 billion in sales when several
branded drugs come off patent. This is a
formidable challenge for the pharmaceutical
industry and boosts the opportunities for
manufacturers of generics. - Another factor that has changed the business
environment is the patent life (years that offer
a market exclusivity to the manufacturer sell the
drug) for drugs, which has been decreasing. The
patent life, which symbolizes the period when
companies usually recover their RD costs and
generate profits is currently about 12 years and
is expected to drop to 10 years within the next
decade. Hence, with the shrinking patent life,
the companies are under more pressure to curtail
costs and increase RD efficiencies. With the
entry of me-too drugs, companies also have to
increase their marketing budgets to better
differentiate their products.
5
Market Changes
- Companies looking for synergies and for
developing healthy pipelines account for several
mergers that have occurred in recent years.
Several factors can be attributed to this
scenario. The drug development time has increased
from 8 years during the 1960s to about 14 years.
The obvious opportunities in well-characterized
disease areas have already been exploited and
scientists now have to explore diseases that are
not so well understood to come up with superior
and innovative drugs. The RD involved in this
process is very challenging and time-intensive.
Hence, RD costs have gone up about 213 in the
last decade. It is estimated that it now costs
almost 800 million to bring a new drug to
market. The payoffs generated by the genomics
revolution have been slow and have not met
expectations.
6
Market Future Trends
- The profiles of the diseases being targeted have
evolved over the years along with the changing
population dynamics. A decade ago, infectious
diseases and development of antibiotics were a
large RD focus. Today with the aging population,
the fastest growing and highest selling market is
the one for statins - the cholesterol lowering
drugs. What was once considered a niche and small
disease market is now offering a large
undiagnosed patient population with a large unmet
medical need and a huge commercial opportunity.
Although this changing disease profile has not
been sudden, it still presents a formidable
challenge because not all companies have aligned
their business model to address this issue.
Statins for lowering cholesterol, glitazones for
diabetes, monoclonal antibodies for cancer, and
COX-2 inhibitors for pain management are
targeting some of these new markets. - Companies are investing billions in developing
immunotherapy drugs, designed to selectively and
optimally use the bodys own immune system to
prevent or fight disease. Among these
immunotherapies are monoclonal antibodies and
therapeutic vaccines. The development of
therapeutic vaccines for the treatment of
HIV/AIDS, cancer, and other major diseases holds
tremendous promise as adjunctive therapies to
conventional treatments.
7
Drugs Prices
- The increasing healthcare expenditure, shrinking
healthcare funding and the growing consumer
outcry has resulted in mounting pressure on drug
companies to lower drug prices. The rising
healthcare expenditure on prescription drugs can
be attributed to the pharmaceutical companies
endeavor to shift the patients to newer, more
expensive products, as older products mature and
give way to generic competition. The increase in
the use of drugs in chronic diseases, such as
cardiovascular, diabetes, gastrointestinal, and
CNS has also contributed to this increase. Due to
the presence of multiple products within the same
class, there is a pressure to lower costs. The
industry is also under fire for the high drug
inflation rate, which over the past five years
has far exceeded the average rate of inflation.
The average cost of prescription drugs has
increased by 4 every year during the past
several years. Escalating product development
costs and a shorter market exclusivity period on
one hand, and the increasing pressure to curtail
costs on the other, puts the pharmaceutical
manufacturers in a tight spot. In addition, the
consistent pressure from the managed-care
organizations also counteracts the premium
pricing strategies employed in the marketplace.
8
Life Expectancy
9
Life Expectancy
The longest documented human life span is 122
years. Though a life span that long is rare,
improvements in medicine, science and technology
over the last century have helped more people
live longer, healthier lives. If you were born in
the early 1900s in the United States, your life
expectancy was only about 50 years. Today it's
around 77. The aging boom is upon us. Since 1900,
the number of Americans age 65 and older has
increased 10-fold. The oldest-old, people age 85
and older, constitute the fastest growing segment
of the U.S. population. By 2050, this population,
currently about 4 million people, could top 19
million. Living to 100 likely will become more
commonplace. In 1950, only about 3,000 Americans
were centenarians by 2050, there could be nearly
one million. This remarkable burst of longevity,
unprecedented in human history, has been possible
because of equally remarkable improvements in
sanitation, health care, and lifestyle. Some
gerontologists suspect an average life expectancy
of 85 years or more may be possible in the near
future.
10
Life Expectancy
- Worldwide population ageing is a public health
challenge affecting many aspects of human life
and societies in developed and developing nations
alike. Population ageing has a great impact on
individuals health and social needs, family
structures, health systems and overall
socioeconomic development. The birth rate has
been decreasing compared to the elders increase
so that we face a future society of fewer
children and more elderly persons. In the very
near future this will give way to a super-aged
society. As a result, in looking at health on
a national basis, the health of the elderly
persons, their medical treatment, welfare, and
care, are among the most pressing issues the
world faces. - The percentage of the population who are in the
older age groups (gt65 years) will increase in all
countries in the next few decades. This process
of population ageing will take place more rapidly
in developing countries than it did in developed
countries. Ageing of the population will present
two major challenges. First, health care systems
must reorient themselves to preventing and
treating the conditions, such as increased
chronic diseases and functional impairments that
characterize an older population and second,
countries must mobilize the additional resources
that will be required to meet the increase in
needs.
11
Consequences of Higher Life Span
- As Europes population grows older and demands
for healthcare provision increase, the developed
world is facing a nightmare scenario of rapidly
increasing healthcare costs. - According to studies from the EU Economic Policy
Committee, on the Budgetary challenges posed by
ageing populations, due to the growing number of
elderly people amongst Europes population, the
number of working age citizens contributing to
social service funds is rapidly diminishing,
while conversely, the number of elderly citizens
is rising. It is estimated that by 2050 there
will be only two working age citizens for each
elderly person in the EU, instead of the current
four. - One readily available solution to these problems
is to be found, in part, in increasing the use of
generic medicines. These competitively priced
therapeutic equivalents to patent expired
originator pharmaceuticals have demonstrated they
possess the same quality, safety, and efficacy as
their originator products, and they go through
the same regulatory procedures. The only
difference is their price, which is typically 20
to 80 below that of brand-name originator
pharmaceuticals.
12
Death Causes
13
Problems For Old People
- Cardiovascular system High blood pressure
(hypertension) - Bones, muscles and joints Osteoporosis
- Digestive system Healthy digestion
- Constipation
- Kidneys, bladder and urinary tract
Urinary incontinence - Prostate gland enlargement
- Brain and nervous system How to keep your
mind sharp - Eyes Dry eyes
- Cataracts
- Glaucoma
- Macular degeneration
- Presbyopia
- Ears Hearing loss
14
Problems For Old People
- Teeth Dry mouth
- Oral and throat cancer
- Dentures
- Dental implants
- Skin, nails and hair Skin cancer
- Hair loss
- Gray hair
- Nail ridging
- Skin tags
- Sleep Sleep and seniors
- Weight Menopause and weight gain
- Sexuality Medecines
- Food Exercise Exercise regularly
- Eat nutritious food
15
Cardiovascular
- Over time, the heart muscle becomes a less
efficient pump, working harder to pump the same
amount of blood through the body. In addition,
blood vessels become less elastic. Hardened fatty
deposits may form on the walls of the arteries
(atherosclerosis), narrowing the passageway
through the vessels. The natural loss of
elasticity, in combination with atherosclerosis,
makes arteries stiffer, causing the heart to work
even harder to pump blood through them. This can
lead to high blood pressure (hypertension). - High blood pressure (hypertension) is often
called a silent killer because people can have it
for years without knowing it. Blood pressure is
determined by the amount of blood the heart pumps
and the amount of resistance to blood flow in the
arteries. Blood pressure normally varies during
the day. It can even vary slightly with each beat
of the heart. It increases during activity and
decreases with rest. Many people may not view
high blood pressure as life-threatening. But
uncontrolled high blood pressure can increase the
risk of serious health problems.
16
Bones, Muscels and Joints
- Bones reach their maximum mass between ages 25
and 35. As people age, their bones shrink in size
and density. One consequence is that they might
become shorter. Gradual loss of density weakens
the bones and makes them more susceptible to
fracture. Muscles, tendons and joints generally
lose some strength and flexibility as people age. - Osteoporosis, which means "porous bones," causes
bones to become weak and brittle - so brittle
that even mild stresses like bending over,
lifting a vacuum cleaner or coughing can cause a
fracture. In most cases, bones weaken when people
have low levels of calcium, phosphorus and other
minerals in their bones. Osteoporosis can also
accompany endocrine disorders or result from
excessive use of drugs such as corticosteroids. - Although it is often thought of as a women's
disease, osteoporosis affects many men as well.
Even children are not immune.
17
Digestive Sistem
- Swallowing and the motions that automatically
move digested food through the intestines slow
down as people get older. The amount of surface
area within the intestines diminishes slightly.
The flow of secretions from the stomach, liver,
pancreas and small intestine may decrease. These
changes generally do not disrupt the digestive
process but constipation conditions are more
frequent. - The digestive system can adjust to a wide variety
of foods, tolerate an astonishing amount of
emotional stress and put up with hurried meals of
questionable nutritional value. But over time a
poor diet, bad eating habits and other unsavory
lifestyle habits can take their toll. The
possible results? Distressing bouts of heartburn,
nausea, cramps, diarrhea or constipation.
18
Kidneys, Bladder and Urinary Trackt
- With age, kidneys become less efficient in
removing waste from the bloodstream. Chronic
conditions, such as diabetes or high blood
pressure, and some medications can damage kidneys
further. - About 30 percent of people age 65 and older
experience urinary incontinence. Incontinence can
be caused by a number of health problems, such as
obesity, frequent constipation and chronic cough.
Women are more likely than men to have
incontinence. Women who have been through
menopause might experience stress incontinence as
the muscles around the opening of the bladder
lose strength and bladder reflexes change. Pelvic
muscles become weaker, reducing bladder support.
In older men, incontinence is sometimes caused by
an enlarged prostate, which can block the
urethra. This makes it difficult to empty the
bladder and can cause small amounts of urine to
leak. Urinary incontinence is an all too common,
often embarrassing and frustrating problem for
millions of people. - Prostate enlargement affects about half of men in
their 60s and up to 90 percent of men in their
70s and 80s.
19
Brain and Nervous Sistem
- The number of cells (neurons) in brain decreases
with age, and memory becomes less efficient.
However, in some areas of the brain, the number
of connections between the cells increases,
perhaps helping to compensate for the aging
neurons and maintain brain function. Reflexes
tend to become slower. There is also a tendency
to become less coordinated. To try to slow down
or even revert this process occupational
therapies are advised so as to stimulate their
intelect to remain active.
20
Eyes
- With age, eyes are less able to produce tears,
your retinas thin and lenses gradually turn
yellow and become less clear. During the 40s,
focusing on objects that are close up may become
more difficult. Later, the irises stiffen, making
pupils less responsive. This can make it more
difficult to adapt to different levels of light.
Other changes to lenses can make people sensitive
to glare, which presents a problem when driving
at night. Cataracts, glaucoma and macular
degeneration are the most common problems of
aging eyes. - Healthy eyes are continuously covered by a tear
film - a constant layer of fluid designed to
remain stable between blinks. A stable tear film
prevents irritation of the nerves of the cornea,
the clear front surface of eyes, and allows the
eye to maintain clear, comfortable vision. The
tear film protects the eyes and lubricates them.
It also reduces the risk of eye infection and,
with each blink of the eyelids, helps clear eyes
of any debris. When the eyes become irritated
from dust or are bothered by wind, smoke or
fumes, extra tears form to help wash away the
foreign material. Decreased production of fluids
from tear glands can destabilize the tear film,
allowing it to break down rapidly and creating
dry spots on the cornea that cause irritation and
diminished vision. An imbalance in the substances
that make up the tear film also can make eyes
become dry. For most people who have dry eyes,
it's a chronic condition.
21
Eyes
- A cataract is a clouding of the normally clear
lens of eyes. Clouded vision can make it more
difficult to read, drive a car or see the
expression on a friend's face. Cataracts commonly
affect distance vision and cause problems with
glare. They generally do not cause pain, double
vision with both eyes open or abnormal tearing.
Clouding of the lens is a normal part of getting
older. About half of people older than 65 have
some degree of clouding of the lens. After age
75, as many as 70 percent have cataracts that are
significant enough to impair their vision. Most
cataracts develop slowly and do not disturb
eyesight early on. But as the clouding
progresses, the cataract eventually interferes
with vision. In the early stages, stronger
lighting and eyeglasses can help to deal with the
vision problems. But at some point, if impaired
vision jeopardizes normal lifestyle, it might
need surgery. - Glaucoma is sometimes called the silent thief
because it can slowly steal your sight before
people realize anything's wrong. The most common
form of glaucoma, primary open-angle glaucoma,
develops gradually, giving no warning signs. Many
people are not even aware they have an eye
problem until their vision is extensively
compromised. Glaucoma is the second most common
cause of vision loss in the United States as it
affects approximately 3 million Americans.
Glaucoma is not just one disease, but a group of
them. The common feature of these diseases is
damage to the optic nerve that usually is
accompanied by an abnormally high pressure inside
the eyeball. If left untreated, glaucoma may lead
to blindness in both eyes.
22
Eyes
- Age-related macular degeneration is a chronic eye
disease that occurs when tissue in the macula,
deteriorates. Degeneration of the macula causes
blurred central vision or a blind spot in the
center of your visual field. The first sign of
macular degeneration may be a need for more light
when doing close-up work. Fine newsprint may
become harder to read and street signs more
difficult to recognize. Eventually people may
notice that when they are looking at a grid, some
of the straight lines appear distorted or
crooked. Gray or blank spots may mask the center
of the visual field. The condition usually
develops gradually, but may sometimes progress
rapidly, leading to severe vision loss in one or
both eyes. Macular degeneration is the leading
cause of severe vision loss in people age 60 and
older. - Presbyopia is the gradual loss of the eye's
ability to focus actively on nearby objects. It
is a natural part of aging that usually begins to
affect people after age 40. For most people,
presbyopia becomes apparent when they need to
hold print at arm's length in order to read it.
23
Ears
- Hearing loss is one of the most common conditions
affecting adults who are middle-aged and older.
One in three people older than 60 and half of all
people older than 85 have significant hearing
loss. Over the years, sounds and noise can damage
the hair cells of the inner ears. In addition,
the walls of the auditory canals thin, and
eardrums thicken. People may have difficulty
hearing high frequencies. Some people find it
difficult to follow a conversation in a crowded
room. Changes in the inner ear or in the nerves
attached to it, earwax buildup and various
diseases can all impact hearing. - The gradual hearing loss that occurs as people
age (presbycusis) is a common condition. An
estimated one-third of the peolple older than age
60 and one-half of those older than age 85 have
some degree of hearing loss. Over time, the wear
and tear on ears from noise contributes to
hearing loss by damaging the cochlea, a part of
your inner ear. It is believed that heredity and
chronic exposure to loud noises are the main
factors that contribute to hearing loss. Other
factors, such as earwax blockage, can prevent
ears from conducting sounds as well as they
should.
24
Teeth
- How teeth and gums respond to age depends on how
well people cared for them over the years. But
even if they were meticulous about brushing and
flossing, may notice that their mouth feels drier
and gums have receded. Teeth may darken slightly
and become more brittle and easier to break. Most
adults can keep their natural teeth all of their
lives. But with less saliva to wash away
bacteria, teeth and gums become slightly more
vulnerable to decay and infection. - Some older adults experience dry mouth
(xerostomia), which can lead to tooth decay and
infection. Dry mouth can also make speaking,
swallowing and tasting difficult. Oral cancer is
more common among older adults. Lack of saliva is
a common problem that may seem little more than a
nuisance, but it can affect both enjoyment of
food and the health of teeth. - Missing teeth can make it difficult to eat and
can cause discomfort in social situations.
Implants or dentures may help people once again
to chew, talk and smile with teeth that look and
feel like their own. - The American Cancer Society estimates more than
28,000 new cases of oral and throat
(oropharyngeal) cancer occur annually in the
United States an estimated more than 7,000
Americans die of these cancers annually. The
worldwide market for implant-based dental
reconstruction products will approach nearly 3.5
billion by 2010.
25
Skin, Nails and Hair
- With age, skin thins and becomes less elastic and
more fragile. It is also likely to bruise more
easily. Decreased production of natural oils may
make skin drier and more wrinkled. Age spots can
occur, and skin tags are more common. Nails grow
at about half the pace they once did. Hair may
gray and thin. In addition, older people are
likely to perspire less, making it harder to stay
cool in high temperatures and putting them at
increased risk of heat exhaustion and heat
stroke. Skin cancer is also a concern as people
age. There is a 40 to 50 chance of getting
skin cancer at least once by the time people
reach 65. - Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer
diagnosed. Doctors diagnose skin cancer in
approximately 1 million Americans each year, and
about 9,800 Americans die annually of skin
cancer. Fair-skinned people who live in areas
that get a lot of sunshine are at greatest risk.
But anyone can develop skin cancer, which is most
commonly caused by overexposure to ultraviolet
(UV) radiation from the sun. - Baldness typically refers to excessive hair loss
from your scalp and can be the result of
heredity, certain medications or an underlying
medical condition. Anyone - men, women and
children - can experience hair loss. The most
common type is pattern baldness (androgenetic
alopecia). It accounts for about 95 percent of
hair loss from the scalp. It's typically
permanent and can be attributed to heredity.
Another type of alopecia, alopecia areata, can be
temporary.
26
Skin, Nails and Hair
- Hair typically turns gray as a result of aging.
Pigment in the hair shaft comes from special
cells at the root (base) of the hair. These cells
are genetically programmed to make a certain
amount of pigment (melanin) at specific ages. At
some point in the aging process, these cells make
less and less pigment until the hair has very
little pigment. White hair has no pigment, and
gray hair has some but not as much as a red,
black or brown hair. - Vertical nail ridges, which run from the cuticle
to the tip of the nail, are fairly common. They
do not indicate serious illness and typically
increase with age. - Skin tags are small, soft, flesh-colored growths
that protrude from your skin. They most often
occur in fold areas of the body, such as on the
sides of the neck, armpit or groin. Skin tags
typically appear in middle age.
27
Sleep
- Sleep needs change little throughout adulthood.
However, as people age, they will likely find
that they sleep less soundly, meaning they will
need to spend more time in bed to get the same
amount of sleep. By age 75, some people find that
they are waking up several times each night.
Having difficulty getting to sleep and staying
asleep is common as people age. But that does not
mean insomnia cannot be avoided. Some medicines
and therapies can help reduce or even eliminate
these conditions.
28
Weight
- As people age, maintaining a healthy weight - or
losing weight if they are overweight - may be
more difficult. This because metabolism generally
slows, meaning that their body burns fewer
calories. Calories that were once used to meet
the daily energy needs instead are stored as fat.
Also the level of activity may decrease,
resulting in unwanted weight gain. There is also
the tendency that the weight gain tends to
accumulate around the stomach, rather than hips
and thighs.
29
Sexuality
- With age, sexual needs, patterns and performance
may change. Impotence becomes more common in men
as they age. By the time they are 65, up to 25
percent of men have difficulty getting or keeping
an erection about one in every four times they
have sex. In others, it may take longer to get an
erection, and it may not be as firm as it used to
be.
30
Opportunities
- The demand for medical products related to
cardiovascular, bones, muscles, joints, digestive
system, kidneys, brain, eyes, teeth, skin, nails,
hair sleeping disorders, overweight or sexual
problems are meant to rise as the population
requiring them is meant to increase. The previous
conditions that we saw before are just some of
the new opportunities that derive from the
population ageing. These conditions will
represent a greater share of the diseases
affecting mankind. They have, therefore, a great
potential for the health industry and should be
regarded with special attention as they represent
a potential market of million consumers.
Therefore the development or generic production
of medicines related to these conditions
represent a very important niche that should be
regarded as a strategically one.
31
Stem Cells
- Stem cells can be derived from an embryo or an
adult. Unlike most cells in the body, such as
skin or heart cells, which are dedicated to
perform a specific function, stem cells are not
specialists. But under certain circumstances,
they can differentiate into specialized cells.
Another unique characteristic of stem cells is
their ability to replicate for indefinite periods
without becoming senescent. It is not clear,
however, if adult stem cells can fully match
embryonic stem cells capacity to differentiate
into vast arrays of replacement cells and
tissues. In animal studies, certain adult stem
cells have shown some potential to develop into
multiple cell types, suggesting that both
embryonic and adult stem cells could have
therapeutic applications. Still, the discovery of
human stem cells is an important scientific
breakthrough that clearly has the potential to
improve the quality and length of life.
32
Geriatric Care
- As the senior will be a significant part of the
population and they demand specific treatment,
geriatric care will be a area of greater
importance and with a growing demand.
Additionally this segment of the population will
posses a considerable income, due to the social
welfare, to spend in this kind of care. Therefore
geriatric care services will meet a great
expansion and some of the retirees will move to
countries where the cost of living is lesser than
in their own to enjoy their retirement.
33
Generics Vs Brand Name
- There are basically two forms of drug -
proprietary (or 'brand-named') drugs that are
developed and produced by large multinational
pharmaceutical companies, and generic drugs that
are either copies, or the basic form of a
proprietary drug. Paracetamol for example is the
generic form of Panadol or Tylenol. The companies
that make these brand-names may spend thousands
on marketing and inventing new formulations, but
the basic active ingredient in their tablets is
just standard paracetamol which can be bought
without the label for far less money. Paracetamol
can be made generically because there is no
longer a patent on it. However, drugs that are in
patent can also be copied under certain
conditions, and are also known as generics. - A generic medicine is an equivalent of an
originator pharmaceutical product. It contains
the same active substance as, is essentially
similar to, and is therefore interchangeable
with, the originator product. - A generic medicine is marketed in compliance with
international patent law. It is identified either
by its internationally approved non-proprietary
scientific name (INN) or by its own brand name.
Generic medicines are widely used in many EU
countries in cost-effective treatment programmes,
and are increasingly prescribed by doctors as
effective alternatives to higher-priced
originator pharmaceuticals.
34
Generics
- Also governments, as the number of retired people
starts to get too close to the number of workers,
will try to find cheaper ways to supply the
surging medical with the minimum possible costs.
This effort will lead them to incentive the
increase usage of such type of medicines as they
are significantly cheaper and provide the same
results.
35
Generics
- Increasing patient access to generic medicines
generates four main public health benefits. It - Reduces Prices.
- Generic medicines are themselves more
economically priced than originator products
selling at 20-80 less than original prices - Competition from these generic rivals forces
originators to reduce their own prices after, or
even before patent expiry. - 2. Stimulates Competition
- A permanent monopoly on pharmaceutical products
would provide little incentive to originator
companies to discover new medicines. As in all
sectors, competition is a major stimulation to
innovation. - 3. Creates Budget Headroom for Innovation.
- The billion dollars saved annually in the world
by buying equivalent generic medicines allows
healthcare budgets and personal budgets the
capacity to buy the newer, more expensive
treatments when required. - 4. Encourages new pharmaceutical companies.
- This ensures less dependency on large
multinational firms for the provision of
medicines worldwide.
36
Generics
- In the end of 2004, 35 of top selling
pharmaceuticals were patent expired, creating a
major opportunity over the next few years for
increasing the purchase of generic medicines,
both in community prescription and in hospital
sectors. This poses good perspectives for the
generics industry as the increasing trend is
supposed to continue with more and more
applications for generic patents being made.
37
Global Warming
- Areas like the North America and Europe are
reconsidering their previous position on tropical
diseases as their range is moving up north and
south and are threatening to hit those areas.
They are doing so by filling their stocks with
supplies of available medicines to fight those
diseases to prevent possible epidemics. Global
warming will cause a significant increase in
human mortality due to extreme weather and
infectious disease. No country, even
industrialized nations will escape these impacts.
Scientists project that as warmer temperatures
spread north and south from the tropics, and to
higher elevations, malaria-carrying mosquitoes
will spread with them. They conclude that global
warming will likely put as much as 65 of the
world's population at risk of infection and that
means an increase of 20. Spreading infectious
disease, longer and hotter heat waves, and
extreme weather will all claim thousands of
additional lives nationwide each year. Doctors
and scientists around the world are becoming
increasingly alarmed over global warnings impact
on human health. Abnormal and extreme weather,
which scientists have long predicted would be an
early effect of global warming, have claimed
hundreds of lives across the world in recent
years. Our warming climate is also creating the
ideal conditions for the spread of infectious
disease, putting millions of people at risk.
38
Global Warming
- Malaria, generally does not afflict regions with
annual average temperatures below 16C, because
lower temperatures inhibit the parasite. As
minimum temperatures climb, the disease could
spread into previously malaria free regions. Yet
the predicted consequences of global warming
would fall most heavily on tropical regions,
where malaria could spread in both latitude and
altitude. A relatively small increase in winter
(minimum) temperature would likely facilitate the
spread of malaria into large urban highland
populations that are currently malaria free and
immunologically naive, such as Nairobi, Kenya,
and Harare, Zimbabwe. - Future trouble will also come from the seas as
the global warming should make the oceans a more
hospitable home for cholera and harmful algal
blooms.
39
New Diseases
- New diseases will show up in areas previously
safe not only because of the global warming
effects but also as new strains of virus and
bacterias will emerge. With the growing
population density of cities and villages and the
sometimes poor sanitation conditions, diseases
thrive and evolve. Also the irresponsible usage
of current drugs is helping mutations in the
antibiotics situation the scenario is alarming as
many are ceasing to be effective and stronger
ones are being put to general use. This creates
many problems as current available drugs, unlike
diseases, are ceasing to be effective and deaths
are more frequent. Also previous deaths whose
causes were unexplained may on the future have
their causes met what will enable new research
fields. - This presents itself as an opportunity for
pharmaceuticals, as diseases that were under
control will no longer be and drugs that
previously were controlling the market will cease
to, as they will need to be replaced by new, more
effective ones.
40
Human Genome Project
- All diseases have a genetic component, whether
inherited or resulting from the body's response
to environmental stresses like viruses or toxins.
The successes of the human genome project have
even enabled researchers to pinpoint errors in
genes - the smallest units of heredity - that
cause or contribute to disease. - The ultimate goal is to use this information to
develop new ways to treat, cure, or even prevent
the thousands of diseases that afflict humankind.
But the road from gene identification to
effective treatments is long and fraught with
challenges. In the meantime, biotechnology
companies are racing ahead with commercialization
by designing diagnostic tests to detect errant
genes in people suspected of having particular
diseases or of being at risk for developing
them. - An increasing number of gene tests are becoming
available commercially, although the scientific
community continues to debate the best way to
deliver them to the public and medical
communities that are often unaware of their
scientific and social implications. While some of
these tests have greatly improved and even saved
lives, scientists remain unsure of how to
interpret many of them.
41
Human Genome Project
- Explorations into the function of each human gene
- a major challenge extending far into the 21st
century - will shed light on how faulty genes
play a role in disease causation. With this
knowledge, commercial efforts are shifting away
from diagnostics and toward developing a new
generation of therapeutics based on genes. Drug
design is being revolutionized as researchers
create new classes of medicines based on a
reasoned approach to the use of information on
gene sequence and protein structure function
rather than the traditional trial-and-error
method. Drugs targeted to specific sites in the
body promise to have fewer side effects than many
of today's medicines. - The potential for using genes themselves to treat
disease - gene therapy - is the most exciting
application of DNA science. This rapidly
developing field holds great potential for
treating or even curing genetic and acquired
diseases, using normal genes to replace or
supplement a defective gene or to bolster
immunity to disease.
42
The Genome
- Rapid progress in genome science and a glimpse
into its potential applications have spurred
observers to predict that biology will be the
foremost science of the 21st century. Technology
and resources generated by the Human Genome
Project and other genomics research are already
having a major impact on research across the life
sciences. The potential for commercial
development of genomics research presents the
health industry with a wealth of opportunities,
and sales of DNA-based products and technologies
in the biotechnology industry are projected to
exceed 45 billion by 2009. Those opportunities
can derive from - Molecular Medicine
- Improved diagnosis of disease
- Earlier detection of genetic
- predispositions to disease
- Rational drug design
- Gene therapy and control
- systems for drugs
- Pharmacogenomics "custom
- drugs"
- DNA Forensics (Identification)
- Identify potential suspects whose DNA may match
evidence left at crime scenes - Identify crime and catastrophe victims
- Establish paternity and other family
relationships - Identify endangered and protected species as an
aid to wildlife officials (could be used for
prosecuting poachers) - Detect bacteria and other organisms that may
pollute air, water, soil, and food - Match organ donors with recipients in transplant
programs - Determine pedigree for seed or livestock breeds
43
Anti-Aging Products
- Demand for anti-aging products is expected to
reach 30 billion in 2009, propelled by a stream
of new and improved products offering health
maintenance and appearance enhancing benefits to
a largely untapped customer base of middle-aged
and elderly consumers. The value of chemicals
used to manufacture these products will reach
3.8 billion. New product introductions and the
passage of the relatively affluent baby boomer
generation through middle age (when age related
changes become more apparent) will stimulate
demand for formulated appearance anti-aging
products. Strong growth will arise from various
products that reduce the visibility of wrinkles
and age spots, such as wrinkle removal injections
and age-defying lotions. However, gains will be
limited by fierce price competition among the
large number of over-the counter brands
continuing to emerge. Hair growth stimulants will
also record robust gains. - Chemicals expected to benefit from rapid gains in
anti-aging products include memory-enhancing
neurological and ophthalmic agents botulinum
toxin for wrinkle-reducing applications and a
host of small volume herbal extracts, including
lutein, lycopene and black cohosh, used in both
dietary supplements and cosmeceuticals.
44
Tobacco Addiction
- Tobacco addiction is widespread and its prejudice
is also widely known. As governments from the
developed countries start to tax at a higher rate
these products the incentives for a change of
habits are bigger. The economical and health
advantages of quitting to smoke will be greater
and people will be willing to spend a greater
amount of money in recovering from their
condition. - Cigarette smoking is a major preventable cause of
disease worldwide, and it is the major cause of
premature death in North America. The important
causes of mortality are atherosclerotic vascular
disease, cancer, and chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease (COPD). Smoking also can
contribute to other diseases, eg, histiocytosis
X, respiratory bronchiolitis, obstructive sleep
apnea, idiopathic pneumothorax, low birth weight,
and perinatal mortality. - Factors influencing smoking initiation differ
from those of smoking behavior maintenance.
Nicotine dependence, genetic factors, and
psychosocial factors influence maintenance of
smoking behavior. - Nicotine meets the criteria of a highly addictive
drug. Nicotine is a potent psychoactive drug that
induces euphoria, serves as a reinforcer of its
use, and leads to nicotine withdrawal syndrome
when it is absent. Nicotine in cigarette smoke
affects mood and performance and is the source of
addiction to tobacco. Smoking may begin as a
voluntary habit, but eventually it becomes an
addiction.
45
Cancer
- One in every eight deaths worldwide is due to
cancer, which claims twice as many lives as AIDS.
By 2020, three out of every five new cancer cases
will be found in the developing world. In these
countries, 80 to 90 of cancer patients already
suffer from advanced and incurable cancers at the
time of diagnosis. Also in 2020, regions with
traditionally low numbers of cancer deaths could
see alarming increases in mortality rates.
Regions including Northern Africa and Western
Asia, South America, the Caribbean, and South
East Asia could face sharp increases of over 75
in the number of cancer deaths in 2020 as
compared to 2000. - The knowledge about prevention and treatment of
cancer is increasing, yet the number of new cases
grows every year. If current trends continue, 15
million people will discover they have cancer in
2020, two-thirds of them in newly-industrialized
and developing countries.
46
AIDS
- The AIDS epidemic caught scientists off guard.
The medical community has been unable to find
ways to cure or even vaccinate against infection.
AIDS is an acronym that stands for acquired
immunodeficiency syndrome and is an infectious
disease in which the immune system collapses.
This disease is caused by the human
immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Most HIV infections
are sexually transmitted however, another
cluster of infections has come from IV-drug users
sharing needles. HIV infections are atypical of
other viral infections in several ways HIV
typically kills its host around a decade after
infection yet is virtually asymptomatic during
the first several years the viral infection is
not, by itself, the cause of death the virus
specifically infects key cells of the immune
system and thereby ultimately destroys the immune
response the virus can "hide-out" inside cells
for years and then emerge long after any
treatment has stopped. - The number of cases grew rapidly in just a few
years. From blood samples and autopsy reports,
the first case dates to the 1950s. But it was not
until nearly 1980 that it became common enough to
be noticed. Today, 30 million people are infected
worldwide. A huge fraction of Africa's population
in some countries is infected, the epidemic is
spreading exponentially in Asia. (Five years ago,
it was estimated that 10 of Thailand's military
was infected.) Drugs are available that prolong
the life of infected individuals, but the regimen
is rigorous (daily doses of several drugs), and
the virus has been able to evolve resistance to
every drug tried.
47
Plastic Curgery
- Recent surveys discovered that over 69 of women
are concerned with the visible signs of aging,
including fine lines, wrinkles, and dryness. 47
want to improve the look of the skin around their
eyes, and 18 want to improve the look of the
area around their mouths.
48
Influenza
- Strains of flu virus differ from one another
largely in the genes that code for surface
molecules called glycoproteins, which are the
primary targets of the body's immune system in
defending against flu viruses. Evolutionary
changes in immune response against such antigen
molecules are the reason that new vaccines must
be developed against emerging strains of virus.
Vaccines remain the mainstays in our
armamentarium against influenza but they must be
constantly updated to meet with the new strain of
virous that are constantly appearing.
49
SARS
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a
viral respiratory illness caused by a
coronavirus, called SARS-associated coronavirus
(SARS-CoV). SARS was first reported in Asia in
February 2003. Over the next few months, the
illness spread to more than two dozen countries
in North America, South America, Europe, and Asia
before the SARS global outbreak of 2003 was
contained. According to the World Health
Organization (WHO), a total of 8,098 people
worldwide became sick with SARS during the 2003
outbreak. Of these, 774 died. - The main way that SARS seems to spread is by
close person-to-person contact. The virus that
causes SARS is thought to be transmitted most
readily by respiratory droplets (droplet spread)
produced when an infected person coughs or
sneezes. Droplet spread can happen when droplets
from the cough or sneeze of an infected person
are propelled a short distance (generally up to 3
feet) through the air and deposited on the mucous
membranes of the mouth, nose, or eyes of persons
who are nearby. The virus also can spread when a
person touches a surface or object contaminated
with infectious droplets and then touches his or
her mouth, nose, or eye(s).
50
Drug Addictions
- Drug addiction is a complex illness. It is
characterized by compulsive, at times
uncontrollable drug craving, seeking, and use
that persist even in the face of extremely
negative consequences. For many people, drug
addiction becomes chronic, with relapses possible
even after long periods of abstinence. - The compulsion to use drugs can take over the
individual's life. Addiction often involves not
only compulsive drug taking but also a wide range
of dysfunctional behaviors that can interfere
with normal functioning in the family, the
workplace, and the broader community. Addiction
also can place people at increased risk for a
wide variety of other illnesses. These illnesses
can be brought on by behaviors, such as poor
living and health habits, that often accompany
life as an addict, or because of toxic effects of
the drugs themselves. Because addiction has so
many dimensions and disrupts so many aspects of
an individual's life, treatment for this illness
is never simple. - Effective drug abuse and addiction treatment
programs typically incorporate many components,
each directed to a particular aspect of the
illness and its consequences Three decades of
scientific research and clinical practice have
yielded a variety of effective approaches to drug
addiction treatment. - Medications, such as antidepressants, mood
stabilizers, or neuroleptics, may be critical for
treatment success when patients have co-occurring
mental disorders, such as depression, anxiety
disorder, bipolar disorder, or psychosis.
51
Blood Substitutes
- Blood is an essential body fluid. It is
responsible for the transport of oxygen to body
tissues, and for carrying away wastes such as
carbon dioxide. It performs important functions
such as clotting to stop bleeding. It is the
major vehicle for transport of nutrients and
antibodies. Blood is literally a river of life.
Blood is one of the world's most vital medical
commodities The liquid and its derivatives save
millions of lives every year. Yet blood is a
complex resource not completely understood,
easily contaminated, and bearing more than its
share of cultural baggage. Physicians and
scientists alike recognized that a blood
substitute would bypass the risk of a blood-borne
pathogen being passed to a patient during
transfusion. Further advantages to using a blood
substitute in place of normal blood include an
increased shelf life, the elimination of the need
to crossmatch blood types from donor to
recipient, and the ability to transfuse in an
ambulance. The estimated market for a blood
substitute is now between 2 and 12 billion
dollars. the world market for blood and its
derivatives probably does not exceed 18.5
billion per year. About 4.5 million units of
human blood are transfused every year, at a price
of 200 to 350 a pint, a market of 8 billion to
10 billion. Unlike human blood, the synthetic
stuff doesnt have a limited shelf life, and is
free of viruses such as HIV and hepatitis that
can be present in human blood.
52
Diabetes
- Diabetes mellitus is a group of diseases
characterized by high levels of blood glucose
resulting from defects in insulin production,
insulin action, or both. Diabetes can be
associated with serious complications and
premature death, but people with diabetes can
take steps to control the disease and lower the
risk of complications. - Type 1 diabetes was previously called
insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) or
juvenile-onset diabetes. Type 1 diabetes develops
when the body's immune system destroys pancreatic
beta cells, the only cells in the body that make
the hormone insulin that regulates blood glucose. - Type 2 diabetes was previously called
non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM)
or adult-onset diabetes. Type 2 diabetes may
account for about 90 to 95 of all diagnosed
cases of diabetes. It usually begins as insulin
resistance, a disorder in which the cells do not
use insulin properly. Type 2 diabetes is
associated with older age, obesity, family
history of diabetes, history of gestational
diabetes, impaired glucose metabolism, physical
inactivity, and race/ethnicity. Type 2 diabetes
is increasingly being diagnosed in children and
adolescents.
53
Diabetes
- With this new tendency to be obese our society is
becoming more prone to diabetes. This cronical
disease is growing every day and not only adults
and elders are struck by its effects. Nowadays
children due to their habits are more prone to be
diabetic. - Diabetes can affect many parts of the body and
can lead to serious complications such as
blindness, kidney damage, and lower-limb
amputations. - In the US alone about 210,000 people under 20
years of age have diabetes. This represents 0.26
of all people in this age group. Approximately
one in every 400 to 500 children and adolescents
has type 1 diabetes. Over the age of 20 years
old 18.0 million 8.7 of all people in this age
group have diabetes. Over 60 years old 8.6
million 18.3 of all people in this age group
have diabetes.
54
Healthy Holidays
- As people get older the preoccupation with their
physical welfare increases and their life is most
of the times planned around this need. This means
that holidays that can help them take care of
their body as well as their spirit are welcomed.
Izmir has a fine example in the usage of fish to
help cure psoriasis condition. - In a further reflection of consumers' growing
inclination to choose products that are good for
their health, travel packages that combine
medical checkups or treatment with fun and
relaxing activities are enjoying a steady growth
in popularity. A typical package of this sort
involves the traveler being given an extensive
medical checkup at a hospital before enjoying a
relaxing and therapeutic stay at a hot spring
resort. Witnessing a particular boom in
popularity are medical travel package tours
offering positron emission tomography (PET)
scans, a technology that is being used
increasingly in the detection of cancer, with
hotel accommodation included. These packages,
which also include hotel accommodation, are the
result of alliances between travel agencies and
medical institutions in cities throughout Japan.
Such packages offer benefits not only for
consumers - it is well known that early detection
is vital in the treatment of many diseases - but
also for medical institutions and the travel
industry. Hospitals and clinics are also able to
use the expensive medical equipment they own to
derive commercial revenue, while travel agencies
are able to tap a new and expanding market. More
and more medical travel packages are expected to
appear in the years ahead. Many industry analysts
predict that medical tourism will be an
increasingly important element of the travel
industry, because people's awareness of the
importance of preventative health and their
willingness to spend time and money on it are
likely to continue to grow.
55
Genetic Testing
- With the development of new areas of the genetic
field new sorts of test as well as the accuracy
of the current ones increase. Also people become
more confident in the reliability of the results.
New applications of these techniques arise. Not
only for police research purposes, even though
that will happen at a higher rate, but also
university laboratories and other medical
laboratories that can not afford or do not have
the skills or machines to do these tests. - Despite still being in its infancy, the genetic
testing market has the potential for strong
growth in the future, genetic testing generated
revenues totaling 319.9 million in 2000 and is
estimated to reach 877.2 million by 2006 at a
compound annual growth rate of 20.4. Tests that
were uncommon, if not unheard of, a short while
ago are now routinely performed at genomic
testing labs all over the world.
56
Genetic Testing
- The use of genetic tests to measure a persons
predisposition to blood clots, for example, is
increasing at a rate of 150 per year.
Gynecologists are expected to recommend that many
couples planning to have a child be tested for
the cystic fibrosis gene. While the
prenatal-screening area is projected to increase
at an annual rate of 8, the cancer and
predisposition testing markets are expected to
grow at rates of 30 and 29.8, respectively.
Analysts attribute such high growth rates in the
cancer and predisposition testing segments to
continuing developments in genetic research.
57
Health Tecnical Machines
- The market for pre-hospital emergency and trauma
equipment is really healthy, and is expected to
remain that way well through century.
Nevertheless the hospital market for emergency
equipment is in a downturn. That segment of the
market is considered saturated, with revenues
derived primarily from replacement sales.
Understandably, manufacturers have targeted
pre-hospital prospects. As pre-hospital emergency
and trauma equipment becomes increasingly
automated, accurate and user-friendly, it is
being put into the hands of an expanding end-user
base of pre-hospital lay persons and minimally
trained practitioners. That expanded user base,
plus the rapid development and deployment of new,
cost-effective equipment, gives the pre-hospital
emergency market tremendous growth potential.
Manufacturers and marketers are scrambling for
position in the cost-conscious, highly
competitive industry. As prices fall, products
become more accessible, leading to increasing
end-user demand creating a new hot prospects
market.
58
Fitness Machines
- The culture of the body is increasing, as people
get more conscious that their body is a machine
that requires maintenance to work properly. They
also care more about their looks and fitness and
the way how other people see them. This new
concept has driven people to the gym and to buy
devices that enable them to pursue these two
goals, Looking good and being good. - Of course this option has opened a new branch of
the health industry thats the production of such
devices that can help people exercising. This
already significant and growing market presents a
great opportunity for high margins goods.
59
Childhood Obesity
- The rising obesity epidemic reflects the profound
changes in society and in the behavioral patterns
of communities over the last 20 - 30 years.
Individuals may become obese, partly because they
have a genetic predisposition to gain weight
readily when they are exposed to unhealthy diets
and lifestyles. Nevertheless, the fundamental
cause of the obesity epidemic is the change in
behaviors and lifestyles, especially with regard
to diet and physical activity patterns.
Furthermore, for childhood obesity, there is
increasing evidence from a range of studies
indicating the important role of early life
environment in the later risk of obesity.
Intrauterine life, infancy, and the pre-school
period, have all been considered as possible
critical periods during which the regulation of
energy balance may be programmed for the long
term. Obesity is a complex, multi-factorial
disorder and coherent and comprehensive
strategies are needed for its effective and
sustainable prevention and management. - Obesity is now well recognized as a disease in
its own right, one, which is largely preventable
through changes in lifestyle, especially diet and
physical activity. Obesity is a major risk factor
associated with increased morbidity and mortality
from chronic noncommunicable diseases. In many
parts of the world, obesity rates are doubling
every 5 to 10 years and increasing the financial
burden of providing medical care due to resulting
health problems. World Health Statistics 2005
published last month indicate