Transformers - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 23
Title:
Transformers
Description:
Equivalent circuit referred to the LT side of a 250/2500 single phase transformer is shown in fig. The load impedance connected to HT is 380+j230 . – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:288
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Transformers
1
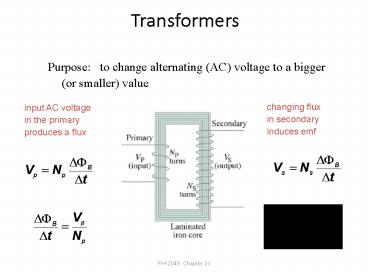
Transformers
Purpose to change alternating (AC) voltage to
a bigger (or smaller) value
changing flux in secondary induces emf
input AC voltage in the primary produces a flux
2
Principle of Transformer Action
3
Principle of Transformer Action
- Principal of Transformer Action
- Principle of electromagnetic induction.
- Ideal t?o ?inding transformer
- ?inding resistances are negligible
- Fluxes confined to magnetic core
- Core lose negligible
- Core has constant permeability
- V1 I1 MMF N1Ie
- Core flux f follo?s, Ie very closely.
- Ie f sinusoidal
- f fmax sin?t
4
Principle of Transformer Action
5
Transformers
- Nothing comes for free, however!
- Increase in voltage comes at the cost of current.
- Output power cannot exceed input power!
- power in power out
6
Transformers Sample Problem
- A transformer has 330 primary turns and 1240
secondary turns. The input voltage is 120 V and
the output current is 15.0 A. What is the output
voltage and input current?
step-up transformer
7
(No Transcript)
8
(No Transcript)
9
Ideal Transformer on an inductive load
10
- The exciting current leads the flux by hysteretic
angle,
11
Transformer on LOAD
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
(No Transcript)
15
(No Transcript)
16
(No Transcript)
17
(No Transcript)
18
(No Transcript)
19
- Equivalent circuit referred to the LT side of a
250/2500 single phase transformer is shown in
fig. The load impedance connected to HT is
380j230?. For a primary voltage of 250V, compute - the secondary terminal voltage
- primary current and power factor
- Power output and efficiency
20
Equivalent circuit referred to the LT side of a
250/2500 single phase transformer is shown in
fig. The load impedance connected to HT is
380j230?. For a primary voltage of 250V,
compute
- the secondary terminal voltage
- primary current and power factor
- Power output and efficiency
- Z'L (380j230) (N1 / N2)2
- (380j230) (250/2500)2
- 3.8j2.3
- Total impedance in the primary
- Secondary terminal voltage I2ZL
21
- Im V1/jXm 250?0/250?90 1?-90 0-j1
- I'e Ic Im 0.5 (0-j1) 0.5-j1
- I'1 I'1 Ie 40- j300.5- j1 51?-37.4
- b) Primary current I1 51A
- Primary p.f cos?1 cos37.4 0.794
lagging - (c) Load p.f
- cos?2 380/ (38022302 ) 0.855
- Power Output V2I2cos?2 222050.855
- 9500 Watts
- Power Output I'12RL 5023.8 9500 Watt
- Core Loss ,PC v12 / RC Ic2 RC 0.520.2 500
Watts - Power Input V1I1cos?1 250510.794 10123.5
22
(No Transcript)
23
(No Transcript)