What is Statistics - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 8
Title: What is Statistics
1
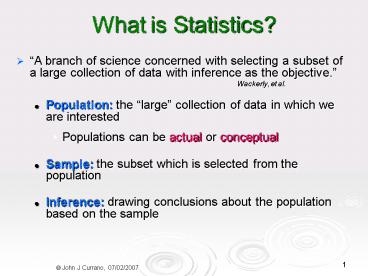
What is Statistics?
- A branch of science concerned with selecting a
subset of a large collection of data with
inference as the objective. Wackerly, et
al. - Population the large collection of data in
which we are interested - Populations can be actual or conceptual
- Sample the subset which is selected from the
population - Inference drawing conclusions about the
population based on the sample
? John J Currano, 07/02/2007
2
- Samples and populations always consist of
numbers. - Sometimes this is clear and straightforward
- What is the mean (average) U. S. household
income ? - What is the mean weight of all 15 oz. boxes of
Cheerios produced by General Mills in the last
month? - Sometimes it is not so clear what the numbers
are or should be, or even if it is a statistical
question - If the election were today, would Candidate X
win? - What is the acceleration due to gravity?
3
- When we make an inference about a population
(e.g., get an estimate of the mean family income
in the U.S.), we would also like to have some
measure of how good the estimate is - How close to the true value is it?
- How certain can we be that it is this close?
- To answer questions like these we need to study
probability and probability distributions.
4
Characterizing a Set of Measurements - Graphical
- Data (200 observations)
- Histogram
- Relative Frequency Histogram
5
Characterizing a Set of Measurements - Graphical
- In both histograms, the area of a rectangle over
a subinterval is proportional to the fraction of
the observations in the subinterval. - A useful variant of the relative frequency
histogram is obtained by scaling the y-axis so as
to make the total area 1 ? multiply all heights
by 1/(total area).
6
Characterizing a Set of Measurements - Graphical
- A relative frequency distribution is a relative
frequency histogram of the population in which
the total area is 1. - Depending on the population, it may look like a
relative frequency histogram, or it may be
smoothed out.
7
Numeric Characterizations of a Sample (p. 8)
- Sample Mean (measure of central tendency)
- Sample Variance (measure of dispersion, spread,
variation) - Sample Standard Deviation, s
- Corresponding Population Parameters
- Mean µ, variance ? 2, standard deviation ?
- will be defined later
8
Empirical Rule (p. 10)
- For a set of measurements (data) coming from a
population whose distribution is approximately
normal (bell- or mound-shaped) with mean ? and
standard deviation ?, the interval - (??, ??) contains approx. 68 of the
measurements - (?2?, ?2?) contains approx. 95 of the
measurements - (?3?, ?3?) contains almost all of the
measurements