Allostratigraphy/Sequence Stratigraphy
1 / 34
Title:
Allostratigraphy/Sequence Stratigraphy
Description:
Allostratigraphy/Sequence Stratigraphy Subdivision of the stratigraphic record otbo bounding discontinuities Bounding discontinuities define Depositional Sequences –
Number of Views:665
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Allostratigraphy/Sequence Stratigraphy
1
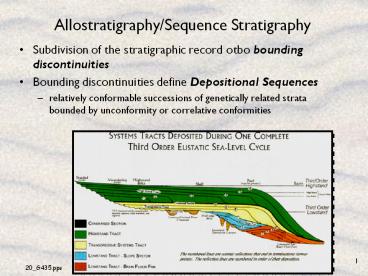
Allostratigraphy/Sequence Stratigraphy
- Subdivision of the stratigraphic record otbo
bounding discontinuities - Bounding discontinuities define Depositional
Sequences - relatively conformable successions of genetically
related strata bounded by unconformity or
correlative conformities
2
Utility of Depositional Sequences
- If bounding discontinuities are produced by
isochronous events (at least basin-wide) then
these material (or non-material) features can be
used for correlation since they are isochronous. - How are sequence bounding unconformities
recognized and correlated in different places?
3
Depositional Sequences/Sequence Boundaries
- Importance and utility first recognized in the
analysis of seismic reflection profile date and
reflection terminations
4
Basin Fill and Accommodation Space
- Sedimentary Basins
- Topographic/Bathymetric versus
- Geological
- Sites of Thick (1000's of meters) sediment
accumulation over Long Time Periods (Ma--gt
mega-annum millions of years). - Sedimentary basins accumulate sedimentary fill
due to available - Accommodation Space
- Space available below base level for sediment
accumulation - The thickness and type of sedimentary deposit
formed in a sedimentary basin is controlled by - Sediment supply
- Accommodation space for that sediment
5
First Principles and ControlsSequence
Stratigraphy
- Accommodation is defined by
- The Equilibrium Profile
- The theoretical, steady state (no gain or loss of
sediment) depositional surface in any environment - Controlled by various factors, including
- Hydrodynamic gradient of the system
- Substrate and sediment load characteristics
- and
6
First Principles and ControlsSequence
Stratigraphy
- Base Level
- Points coinciding with theoretical equilibrium
profile along an actual depositional profile
- Erosion occurs above and deposition occurs below
base level
Posamentier and Allen, 1999
7
Accommodation Space
- Produced (in an idealized shallow marine
environment) by - Rise in sea level relative to the depositional
surface - Sediment accumulates to sea level (or base level
for the more general case) if sufficient supply
exists
8
Creation of Accommodation Space Eustatic vs.
Relative Sea Level Change
- Eustacy and Accommodation
- World wide change in the elevation of sea level
relative to a fixed point in the earths interior
9
Creation of Accommodation Space Eustatic vs.
Relative Sea Level Change
- Relative Sea Level Change and Accommodation
- Tectonic Accommodation
- Local thermal or mechanical processes resulting
in - Up or down motion of the depositional surface
relative to a fixed point in the earths interior
in local areas effected by those tectonic events - Sediment Supply Accommodation
- Sediment input in excess of space made available
by tectonic or eustatic change
10
(No Transcript)
11
Aggradation, Progradation, and Retrogradation
- Stacking patterns of sedimentary basin fill due
to relative sea level and sediment input
influence on accommodation - Aggradation
- Progradation
- Retrogradation
12
Aggradation
- Sediment input accommodation
- Not common for long periods
13
Progradation/Regression
- Sediment input gt accommodation
- Facies prograde and shift offshore
- Regression
14
Forced Regression
- Rapid Relative Sea Level Fall
- Negative accommodation
- Facies shift basinward
- Erosion occurs in landward areas
- Regression and Unconformity Surface
15
Transgression/Retrogradation
- Relative Sea Level Rise
- Accommodation created in excess of sediment
input - Facies shift landward
16
Effects of Changing Accommodation on the
Stratigraphic Record
- Transgression/Regression
- Water depth/shoreline changes interpreted from
vertical changes in grain size (CUS/FUS) or
sedimentary facies in local sections - Onlap/Offlap
- Landward/basinward shift in shoreline due to
relative sea level change - The fundamental geometric aspect of the
sedimentary record upon which relative sea level
change is interpreted
17
Wheeler DiagramsTime/Space relationships of
Unconformity
- Space/Space Stratigraphic Cross Section
- Time/Space Chronostratigraphic Chart
18
Data Types for Sequence Analysis
- Geological
- From bore holes
- (Typically from offshore, subsurface areas)
- Geophysical
- Seismic reflection profile data
19
(No Transcript)
20
Cycles of Relative Sea Level Change
Fichter and Poche, 2001
Nichols, 1999
21
(No Transcript)
22
The Geologic Record, Relative Sea Level, and
Eustacy
- Eustatic Sea Level
- The Holey Grail of stratigraphic studies
23
Cycles of Relative Sea Level, Base Level, and
Accommodation Space
- Cycles of relative sea level,
- Migration of base level up and down the
depositional surface, and - Variations in accommodation space can be directly
related to the variation in
Strata Geometry and Sedimentary Facies
24
(No Transcript)
25
In Fichter and Poche, 2001 After Mitchum and Van
Wagoner, 1990
26
In Fichter and Poche, 2001 After Mitchum and Van
Wagoner, 1990
27
Depositional Sequences
- Relatively Conformable
- Genetically Related (abide by Walther's Law)
- Bounded by Unconformity or Correlative Conformity
- isochronous with respect to unconformity
- Depositional Sequences are Chronostratigraphic
Units - the defining Sequence Boundary defines older
(below) and younger (above) strata - Chronostratigraphic Units
- geological time significant
28
Depositional Systems Tracts
- Use of Depositional Sequence concepts to predict
stratal geometry
- Three dimensional assemblage of sedimentary
facies genetically linked by their origin in
related depositional environments - Basically Waltherian World
29
Low Stand Systems Tract
- Forced Regression
- Subaerial exposure and formation of a
- Sequence Boundary
- Offlap
- Basinward shift in facies belts
30
Transgressive Systems Tract
- Retrogradation
- Flooding of the shelf and onlap
- Landward shift in facies belts
31
Maximum Flooding SurfaceCondensed Section
- Between TST and HST (highstand systems tract)
- Represented by a change from retrogradation to
aggradation/progradation - The surface or thin succession characterized by
evidence for slow rates of sedimentation
32
Highstand Systems Tract
- Progradation (accommodation lt sediment input)
- Regressive successions
- Onlap and offlap/down-lap
33
Basic Depositional Sequence/Systems Tract Model
for a Generic, Clastics-Dominated Continental
Margin
34
Stratigraphic Expression of Relative Sea Level
Cycles
- The Sequence Model
- A tool for predicting stratigraphic architecture
- Methodology for basin wide correlation
- May be used for interregional correlation through
recognition of Eustatic Cycles