Polymer Materials - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 92
Title:
Polymer Materials
Description:
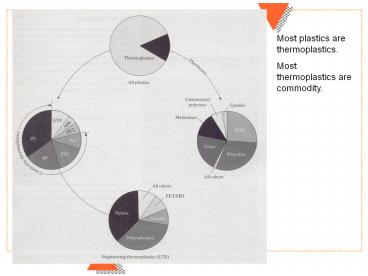
Most plastics are thermoplastics. Most thermoplastics are commodity. * Recall symbol = benzene ring * http://www.lenscompare.com/contact-lens-img/881-safety ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:786
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Polymer Materials
1
Most plastics are thermoplastics. Most
thermoplastics are commodity.
2
Engineering Thermoplastics
- The most common!!
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Polyamides (PA or Nylon)
3
Polymer Materials
- Engineering Resins
- ABS
- Nylon
- Polycarbonate
- Acetal
- Acrylic
- Cellulosics
- Ionomer
4
Polymer Materials
- Engineering Resins (cont)
- PBT
- PET
- PPO
5
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
- ABS
6
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- This is an ethenic engineering plastic
- i.e. basic monomer structure as ethylene just
modifying polystyrene by - Adding plasticizer and copolymers of styrene
butadiene and styrene acrylonitrile to produce a
polystyrene terpolymer of acrylonitrile,
butadiene and styrene (ABS).
7
ABS
butadiene
8
ABS
- Major Uses
- Appliance Housings
- Canoes
- Typewriter Keys
- Pipes Pipe Fittings
- Telephone Housings
9
ABS
- Why would you want to use it?
- Low to Medium Cost
- Good Impact Strength
- Good Chemical Resistance
- High Gloss Surface Finish
- Good Flexural Properties
10
ABS
- Processes
- Injection Molding
- Extrusion
- Blow Molding
- Thermoforming
11
ABS
- Long Term Service Temperature
- Max 135
- Min Already below Tg
12
ABS
13
ABS
- Material Suppliers
- GE
- Monsanto
- DOW
14
Other Styrenic Blends
- HIPS
- SAN
- SMA - Styrene Maleic Anhydride
- EPS
15
Nylon
- PA - Polyamide
16
Nylon
/ copolymer for example, nylon 6/10
copolymers of nylon 6 and 10. The numbers refer
to how many methyl units (-CH2-) occur on each
side of the nitrogen atoms (amide groups). The
difference in number of methyl units influences
the property profiles of the various nylons. See
link below
- Types
- Most Common
- Nylon 6
- Nylon 6/6
- Nylon 6/10
- Nylon 6/12
- Nylon 11
- Nylon 12
http//www.sdplastics.com/nylon.html
http//www.ides.com/generics/Nylon/Nylon_typical_p
roperties.htm
17
Nylon
- Suffixes refer to number of carbon atoms involved
in the condensation polymerization process. EX
18
Nylon
- Crystalline Yes, very flexible
- Hygroscopic Yes (O and N)
- Glass Transition (135 F)
- Flammability Varies depending on additives,
but will usually self extinguish because of N
19
Nylon
- Major Uses
- Structural parts!! (i.e. replacement for cast
aluminum 380 series) - Electrical Connectors
- Gears
- Bearings
- Cable Ties
- Fishing Line
- Automotive Valve Covers/Oil Pans
- Sports/Exercise Equipment
20
Nylon
- Why would you want to use it?
- High Strength among the highest of all
engineering plastics - Good Heat Resistance
- Good Chemical Resistance
- Excellent Wear Resistance
- Good Fatigue Resistance
21
Nylon
- Processes
- Injection Molding
- Extrusion
- Blow Molding
- Rotational Molding
- Thermoforming
22
Nylon 6
23
Nylon 6/6 most common
24
Nylon
- Material Suppliers
- Dupont
- Hoechst Celanese
- Monsanto
- BASF
- Bayer
25
More on Nylon
- One of the first engineering plastics (30s).
- Crystalline thermoplastic
- Can have tensile properties comparable to soft
aluminum. - Types 6 and 6/6 are the most common!!
- Biggest disadvantage tendency to absorb
moisture after prolonged period
26
Su 35 ksi!!
27
Polycarbonates (PC)
28
- Polycarbonate
- Crystalline No, too rigid
- Hygroscopic Yes (O)
- Glass Transition High (300 F)
- Flammability No (High number of double carbon
bonds will extinguish soot)
29
Polycarbonates (PC)
- Polycarbonates are amorphous linear polyesters
with excellent moldability. - Good impact strength, temperature resistance.
- Transparent (aka Plexiglas)
- Tensile strength similar to ABS and nylon except
impact strength can be 10X greater! ButCosts
more and susceptible to environmental stress
cracking.
30
Polycarbonates (PC)
- Uses include
- Helmets (football and hard hats), face shield,
power tool housings, cell phones, automotive
dashboards, window cranks, small gears, etc.
31
Acetal
32
- Polyoxymethylene (Acetal or POM)
- Crystalline Yes, very flexible
- Hygroscopic Yes (O)
- Glass Transition Low (-100 F)
- Flammability Yes (only C and O bonds)
33
Acetal
- Major Uses
- Gears
- Bearings
- Faucet Components
- Fuel Pump Components
- Refrigerator Clips
- Zippers
34
Acetal
- Why would you want to use it?
- Low to Medium Cost
- Good Chemical Resistance
- High Strength
- Excellent Fatigue
- Good Creep Resistance
- Lubricity
- Dimensional Stability at High Temperature
35
Acetal
- Processes
- Injection Molding
- Extrusion
- Blow Molding
- Rotomolding
36
Acetal
- Long Term Service Temperature
- Max 200
- Min -100
37
Acetal
38
Acetal
- Material Suppliers
- DuPont
- Hoechst Celanese
- BASF
- LNP
39
Acrylic
- PMMA
40
- Polymethylmethacrylate (Acrylic)
- Crystalline No, too rigid (dual methyl groups)
- Hygroscopic Yes (O)
- Glass Transition High (220 F)
- Flammability Yes (only C-H and CO bonds)
41
Acrylic
- Major Uses
- Sheet
- Windows
- Displays
- Signs
- Surgical Instruments
42
Acrylic
- Why would you want to use it?
- Low Cost
- Good Chemical Resistance
- Hardness
- Good Creep Resistance
- Transparency
- Best Polymer for Weatherability
43
Acrylic
- Processes
- Casting
- Injection Molding
- Extrusion
- Thermoforming
44
Acrylic
- Long Term Service Temperature
- Max 80
- Min Already below Tg
45
Acrylic
46
Acrylic
- Material Suppliers
- AtoHaas
- Continental
- DuPont
- ICI
47
Cellulosic
48
Cellulosic
- Major Uses
- Tool Handles
- Safety Glasses
- Tooth Brush Handles
- Automotive and Furniture Trim
- Toys
- Tubing
- Writing Instruments
49
Cellulosic
- Why would you want to use it?
- Low Cost
- Medium Chemical Resistance
- Hardness
- Transparency
- Rigid
50
Cellulosic
- Processes
- Casting
- Injection Molding
- Extrusion
51
Cellulosic
- Long Term Service Temperature
- Max 220
- Min Already below Tg
52
Cellulosic
53
Cellulosic
- Material Suppliers
- Albis
- Eastman
- Kleer
- Rotuba
54
Ionomer
55
Ionomer
- Major Uses
- Golf Ball Covers
- Automotive Bumper Pads
- Film for Food and Drugs
56
Ionomer
- Why would you want to use it?
- Good Resilience
- Good Flexibility
- Abrasion Resistance
- Good Chemical Resistance
57
Ionomer
- Processes
- Injection Molding
- Extrusion
58
Ionomer
- Long Term Service Temperature
- Max 100
- Min -40
59
Ionomer
60
Ionomer
- Material Suppliers
- Amoco
- BASF
61
THERMOSETS
62
Polymer Materials
- Thermoset
- EPOXY
- Melamine
- Urea
- Phenolic
- Polyester
- Vinyl Ester
63
EPOXY
64
EPOXY
- Major Uses
- Encapsulating Electronic Components
- Bobbins for Coil Windings
- Adhesives
65
Epoxy
- Why would you want to use it?
- High Mechanical Strength
- Outstanding Adhesive Properties
- Good Resistance to Heat
- Good Chemical Resistance
66
Epoxy
- Processes
- Compression/Transfer Molding
- Injection Molding
67
Epoxy
68
Epoxy
- Material Suppliers
- Ciba-Geigy
- Dow
- Shell
69
Melamine (Amino)
70
Melamine
- Major Uses
- Molded Dinnerware
- Electric Shaver Housings
- Buttons
- Ashtrays
- Connector Bodies
71
Melamine
- Why would you want to use it?
- High Surface Hardness
- Good Heat Resistance
- Good Flame Resistance
- Resists Chipping and Breaking
72
Melamine
- Processes
- Compression/Transfer Molding
- Injection Molding
73
Melamine (Alpha Cellulose)
74
Melamine
- Material Suppliers
- American Cynamid
- BIP
- Bud Co.
75
Urea (Amino)
76
Urea
- Major Uses
- Control Housings
- Wiring Devices
- Control Buttons
- Knobs
77
Urea
- Why would you want to use it?
- High Surface Hardness
- Good Heat Resistance
- Good Flame Resistance
- Resists Chipping and Breaking
78
Urea
- Processes
- Compression/Transfer Molding
- Injection Molding
79
Urea (Alpha Cellulose)
80
Urea
- Material Suppliers
- American Cynamid
- BIP
- Bud Co.
81
Phenolic
82
Phenolic
- Major Uses
- Electrical Products
- Connectors
- Cooking ware (recall plate)
- Ashtrays
- Utensil Handles
- Elecrtic Motor Components
- Knobs
83
Phenolic
- Why would you want to use it?
- Good Heat Resistance
- Good Flame Resistance
- Good Rigidity
- Good Creep Resistance
84
Phenolic
- Processes
- Compression/Transfer Molding
- Injection Molding
85
Phenolic (Wood Floor)
86
Phenolic
- Material Suppliers
- Amoco Electronic
- Rogers
- Plenco
87
Vinylester
88
Vinylester
- Major Uses
- Pipe
- Electrical Equipment
- Grating
- Exhaust Stacks
- Washer Drums
- Chemical Tanks
89
Vinylester
- Why would you want to use it?
- Good Heat Resistance
- Excellent Bonding to Fibers
- Good Chemical Resistance
- Good Rigidity
- Good Creep Resistance
90
Vinylester
- Processes
- Hand Lay-Up
- Compression/Transfer Molding
- Injection Molding
91
Vinylester (15 Glass Fiber)
92
Vinylester
- Material Suppliers
- Premix
- Glastic
- Reichold