Mechanism of labour - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 6
Title:
Mechanism of labour
Description:
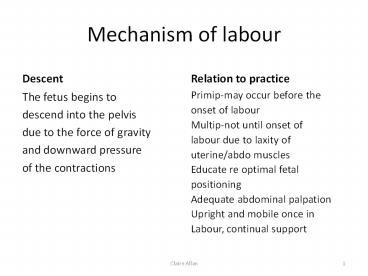
Mechanism of labour Descent Relation to practice The fetus begins to descend into the pelvis due to the force of gravity and downward pressure of the contractions – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1248
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Mechanism of labour
1
Mechanism of labour
- Descent
- Relation to practice
- The fetus begins to
- descend into the pelvis
- due to the force of gravity
- and downward pressure
- of the contractions
- Primip-may occur before the
- onset of labour
- Multip-not until onset of
- labour due to laxity of
- uterine/abdo muscles
- Educate re optimal fetal
- positioning
- Adequate abdominal palpation
- Upright and mobile once in
- Labour, continual support
2
Mechanism of labour
- Flexion
- Relation to practice
- As the fetus descends the chin
- touches the chest (arms begin
- to cross) and the attitude of
- flexion is adopted. This is
- increased further when the
- head meets the resistance of
- the birth canal
- Upright position to assist with
- gravity
- When resting, adopt the left
- lateral position (OFP)
- Observation of the
- contractions-are they regular,
- do they appear to be
- increasing in strength and
- becoming expulsive?
3
Mechanism of labour
- Internal rotation
- Relation to practice
- As the occiput reaches the
- resistance of the pelvic floor, it
- rotates forward 45 degrees.
- The slope of the pelvic floor
- aids this rotation forward and
- allows the head to emerge in
- the longest diameter of the
- pelvis (anterposteior)
- Fully dilated, station of the head
- Vertex may or may not be
- visible
- Upright position-kneeling,
- squatting
- May be spontaneously pushing
- Would you encourage
- mechanical pushing or allow
- for natural descent?
4
Mechanism of labour
- Crowning
- Relation to practice
- The head has crowned when it
- escapes under the pubic arch
- and no longer recedes
- between contractions because
- the widest transverse diameter
- of the head is born
- Extension
- With slight extension the
- bregma, forehead, face and chin
- will pass over the perineum and
- the head is born
- May be
- spontaneously/mechanically
- pushing or still breathing
- through contractions, how
- long can the second stage last?
- Introverted in her behaviour
- and may adopt alternative
- Position, bending towards the
- floor with knees apart
5
Mechanism of labour
- Restitution
- Relation to practice
- When the head is born it will
- turn to the left or the right,
- righting itself with the
- shoulders. The shoulders then
- rotate (similar action to that of
- the head) and lie in the
- anteroposterior diameter of
- the pelvis. Rotation follows
- the same direction as restitution
- No need to do anything, allow
- time for restitution (you may
- see a small part of the anterior
- shoulder). Wait for the next
- contraction to deliver the
- remainder of the body
- (Drs are often too quick in
- trying to deliver the body)
6
Mechanism of labour
- Lateral flexion
- Relation to practice
- In most supine or semi
- recumbent birthing positions
- the anterior shoulder will be
- born first (under the pubic
- arch) and the posterior
- shoulder will pass over the
- perineum
- If the woman is on all fours or
- leaning forward then the
- posterior shoulder may be
- born first due to gravity and
- the effect of the birth canal-
- the curve of carus-this causes
- the trunk of the baby to flex
- sideways as it is born