Sales and Operations Planning - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title:
Sales and Operations Planning
Description:
Operations Planning Chapter 14 How Sales and Operations Planning fits the Operations Management Philosophy Sales and Operations Planning Sales and operations planning ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:143
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Sales and Operations Planning
1
Sales and Operations Planning
- Chapter 14
2
How Sales and Operations Planning fits the
Operations Management Philosophy
Operations As a Competitive Weapon Operations
Strategy Project Management
Process Strategy Process Analysis Process
Performance and Quality Constraint
Management Process Layout Lean Systems
Supply Chain Strategy Location Inventory
Management Forecasting Sales and Operations
Planning Resource Planning Scheduling
3
Sales and Operations Planning
- Sales and operations planning (SOP) The process
of planning future aggregate resource levels so
that supply is in balance with demand. - Staffing plan A sales and operations plan of a
service firm, which centers on staffing and other
human resourcerelated factors. - Production plan A sales and operations plan of a
manufacturing firm, which centers on production
rates and inventory holdings.
4
Aggregation
- The sales and operations plan is useful because
it focuses on a general course of action,
consistent with the companys strategic goals and
objectives, without getting bogged down in
details. - Product family A group of customers, services,
or products that have similar demand requirements
and common process, labor, and materials
requirements. - A company can aggregate its workforce in various
ways as well, depending on its flexibility. - The company looks at time in the aggregate
months, quarters, or seasonsrather than in days
or hours.
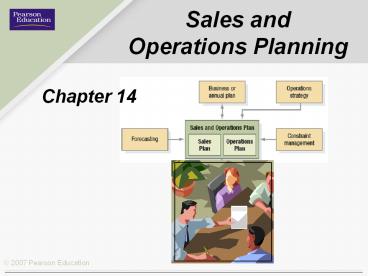
5
The Relationship of Sales and Operations
Plansto Other Plans
6
Managerial Inputs from FunctionalAreas to Sales
and Operations Plans
7
Plan Objectives
- Six objectives usually are considered during
development of a plan - Minimize Costs/Maximize Profits
- Maximize Customer Service
- Minimize Inventory Investment
- Minimize Changes in Production Rates
- Minimize Changes in Workforce Levels
- Maximize Utilization of Plant and Equipment
8
Reactive Alternatives
- Reactive alternatives are actions that can be
taken to cope with demand requirements. - Anticipation inventory is inventory that can be
used to absorb uneven rates of demand or supply. - Workforce adjustment Hiring and laying off to
match demand. - Workforce utilization Use of overtime and
undertime. - Vacation schedules Use of plant-wide vacation
period, vacation blackout periods.
9
Reactive Alternatives
- Subcontracting Outsourcing to overcome
short-term capacity shortages. - Backlogs, Backorders, and Stockouts
- Backlog An accumulation of customer orders that
have been promised for delivery at some future
date. - Backorder A customer order that cannot be filled
immediately but is filled as soon as possible. - Stockout An order that is lost and causes the
customer to go elsewhere.
10
Aggressive Alternatives
- Aggressive alternatives are actions that attempt
to modify demand and, consequently, resource
requirements. - Complementary products Services or products that
have similar resource requirements but different
demand cycles. - Creative Pricing Promotional campaigns designed
to increase sales with creative pricing.
11
Planning Strategies
- Chase strategy A strategy that involves hiring
and laying off employees to match the demand
forecast. - Level-utilization strategy A strategy that keeps
the workforce constant, but varies its
utilization to match the demand forecast. - Level-inventory strategy A strategy that relies
on anticipation inventories, backorders, and
stockouts to keep both the output rate and the
workforce constant. - Mixed strategy A strategy that considers and
implements a fuller range of reactive
alternatives than any one pure strategy.
12
Constraints and Costs
- The planner usually considers several types of
costs when preparing sales and operations plans. - Regular-Time Costs These costs include
regular-time wages plus contributions to
benefits, Social Security, retirement funds, and
pay for vacations and holidays. - Overtime Costs Overtime wages typically are 150
percent of regular-time wages. - Hiring and Layoff Costs Include the costs of
advertising jobs, interviews,training programs,
exit interviews, severance pay, and lost
productivity. - Inventory Holding Costs
- Backorder and Stockout Costs
13
Chase StrategyApplication 14.1
14
Level-Utilization StrategyApplication 14.2
15
Mixed StrategyApplication 14.3
- Key Ideas
- ? Hire only 7 in quarter 3, making maximum use
of overtime to compensate. - ? Reduce the amount of undertime in quarter 3.
- ? Reduce the layoffs required in quarter 4.
16
Sales and Operations Planning as a Process
- Sales and operations planning is a
decision-making process, involving both planners
and management. - The process itself, typically done on a monthly
basis, consists of six basic steps.
17
Decision Support Tools
- Spreadsheets can be used, including ones that you
develop on your own. - Input values
- Derived values
- Utilized time
- Calculated values
- The Transportation method of production planning
to solve production planning problems assumes
that a demand forecast is available for each
period, along with a possible workforce
adjustment plan.
18
Planning Using a Spreadsheet
19
SOP Spreadsheetfor a Make-to-Stock Family