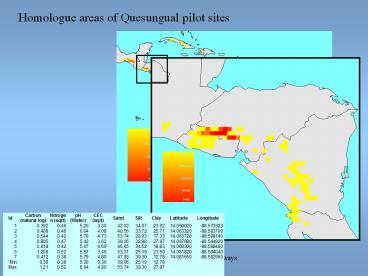
Homologue areas of Quesungual pilot sites
Title:
Homologue areas of Quesungual pilot sites
Description:
Andes and Sao Fco Impact Pathways Workshop. Homologue areas of Quesungual pilot sites ... Andes and Sao Fco Impact Pathways Workshop. Location of pilot sites ... –
Number of Views:47
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Homologue areas of Quesungual pilot sites
1
Homologue areas of Quesungual pilot sites
2
Dominios de Extrapolación(Extrapolation Domains)
- Jorge Rubiano Victor Soto
3
(No Transcript)
4
Spatial Extrapolation Domains Potential areas to
scale up CPWF research projects
5
Objective
- To identify places with similar characteristics
(social and biophysical) to those of pilot
research sites of CPWF Projects in which outputs
are highly probably to replicate
6
Rationale (1)
- We describe an extrapolation domain as the
geographical area that is likely to behave in the
same way as a project site, based on evidence of
its physical and social attributes. Similarity
is defined by the probability that a search site
has the same value as the project site in a
limited number of attributes that are defined by
project specialists as being important.
Attributes commonly used include climate, soil,
land use, socio-economic characteristics, etc.
7
Rationale (1)
- We describe an extrapolation domain as the
geographical area that is likely to behave in the
same way as a project site, based on evidence of
its physical and social attributes. Similarity
is defined by the probability that a search site
has the same value as the project site in a
limited number of attributes that are defined by
project specialists as being important.
Attributes commonly used include climate, soil,
land use, socio-economic characteristics, etc.
8
Rationale (2)
- The assumption is that adoption is related to the
degree of similarity in key variables. The key
variables condition constrain the likelihood that
a given site is favourable for extrapolation. - The degree to which a site is favourable for
extrapolation depends upon the weight of evidence
that the key variable is present. - Maps indicate where similar conditions exist.
9
Methods
- Weights of Evidence
- Homologue
10
Bayesian Approach
H1
H2
H3
11
Bayesian Approach
H2
H1
H3
E1
12
Bayesian Approach
H1
H2
H3
E1
E2
13
Why a Bayesian Approach?
- Using these techniques it is possible to obtain a
probabilistic distribution of the occurrence of
modelled events, and reduce the uncertainty and
sample space for further inquiries. - The Bayesian paradigm offers a natural and
consistent way of framing a problem and achieving
data integration and developing methodological
solutions (Herriges and Kling, 1998). - It answers questions like 'How should a piece of
evidence change what we currently believe?'
(Spiegelhalter et al., 1999). - An advantage of a Bayesian approach is that it
allows explicit recognition of multiple
perspectives (Spiegelhalter et al., 2000).
14
Project 6 Natural resource conservation and
management for increased food availability and
sustainable livelihoods empowering farming
communities with strategic innovations and
productive resources in dryland farming.
- The outputs relating to crops and soils are
- 1) New varieties of staple food crops
developed - 2) Soil and water management practices
developed - 3) Drought probability map
- 4) Manuals on crop production, and soil and
water conservation developed. - The outputs relating to water are
- 1) Appropriate domestic water harvesting
reservoirs designed to meet household water needs - 2) Dugouts enhanced to retain water
- 3) Formal structures for governance of
community water resources developed - 4) Manuals on appropriate water harvesting
systems produced.
15
(No Transcript)
16
Key Variables
- Existence of fish production
- The status of sanitation facilities
- The poverty line as describe by the below UD 1
per/day index, and - Climate and other biophysical conditions
17
Location of pilot sites for project 6 in Africa
18
Location of pilot sites for project 6 in Africa
19
Extent of extrapolation domains
20
Improved Sanitation ()
Improved sanitation includes any of the following
excreta disposal facilities connection to a
public sewer, connection to a septic tank,
pour-flush latrine, simple pit latrine, and
ventilated improved pit latrine. WHO emphasizes
that these data measure access to an improved
excreta disposal system--access to a sanitary
system cannot be adequately measured on a global
scale
Irrigation Number of ha per pixel with
irrigation facilities (pixel size of 2500ha
21
Education Average length of schooling (years)
Children's Health Oral re-hydration therapy
(ORT) use rate ()
Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) use rate refers to
the percentage of children under the age of 5
with diarrhea (in the two weeks preceding data
collection) who received either oral rehydration
therapy (oral rehydration solutions or
recommended homemade fluids) or increased fluids
and continued feeding in order to prevent
dehydration and diarrheal diseases.
22
Population 2000 (x 1000)
23
Probabilities of socio-economic similarities
(ii) Based on agroecological variables
Probabilities of bio-physical similarities
24
Areas with highest SE and BF probabilities in
Africa
25
Probabilities of socio-economic similarities
(ii) Based on agroecological variables
Probabilities of bio-physical similarities
26
Areas with highest SE and BF probabilities in
South America
27
Population and areas with highest SE and BF
probabilities in the tropical world
28
Summary
- Where else in the world current funded projects
are reliable - Integrate diverse sources of information for
targeting new sites - Present a logical and quantitative method explore
geographical impact - Produce basic information for scenario analisis
29
Questions for extrapolation and scenario analyses
- 1. Please provide geographic co-ordinates of
current pilot sites, alternatively details and
exact names of sites. - 2. Caracteristicas y/o problemas claves de los
sitios piloto que son condicion que justifica o
valida la implementacion de su proyecto en otro
lugar por ejemplo - 3. Project outputs expect to be adapted outside
project site? (Productos que se esperan seran
adaptados fuera del sitio de trabajo) - 4. Areas where project outputs will be
disseminated (please quantify in terms of numbers
of expected adopters and changes in yield, etc.,
if possible)? - 5. If crop technologies form part of your
project, what yield and area increases by
irrigation/rainfed crop do you expect and by
when year? - 6. If water productivity increases are part of
your project, what increase do you project from
what baseline productivity or efficiency?, and
for which crop rainfed or irrigated or which
water use sector irrigation, domestic, industry,
etc., and by which year? - 7. Do you expect beneficiaries to engage in other
activities, like crop diversification into which
crops? - 8. Critical factors that affect spread of
outputs?
30
Bayesian Approach
Area173
Pilot sites10
Prior P0.0578
Pattern Area 22 Area of Pilot sites in Pattern
5 Conditional Prob5/220.227
Relational factor of prior and posterior P
5/100.5
Posterior Probability0.522/1730.063