1 Oracle Server Architecture Overview - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title: 1 Oracle Server Architecture Overview
1
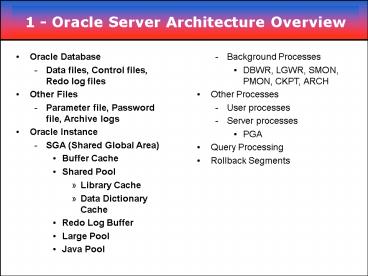
1 - Oracle Server Architecture Overview
- Oracle Database
- Data files, Control files, Redo log files
- Other Files
- Parameter file, Password file, Archive logs
- Oracle Instance
- SGA (Shared Global Area)
- Buffer Cache
- Shared Pool
- Library Cache
- Data Dictionary Cache
- Redo Log Buffer
- Large Pool
- Java Pool
- Background Processes
- DBWR, LGWR, SMON, PMON, CKPT, ARCH
- Other Processes
- User processes
- Server processes
- PGA
- Query Processing
- Rollback Segments
2
1 - Oracle Server Architecture Overview
Oracle Instance
Server Process
SGA (System Global Area)
PGA
DatabaseBuffer Cache
Shared Pool
Redo Log Buffer
Java Pool (optional)
User Process
Large Pool (optional)
DBWR
LGWR
SMON
PMON
CKPT
RECO
Other Files...Parameter, Password, Archive Logs
ARCH
LCKn
Pnnn
Dnnn
SNPn
Oracle Database
Data files
Redo Log Files
Control Files
3
Database Files
- Data files
- Store the data
- Can only be associated with 1 database
- Form logical units called a tablespace
- Redo log files
- Record all of the changes in the database
- Must have at least 2 groups
- Oracle recommends each group have 2 members on
separate devices - Control files
- Database name
- Time stamp of database creation
- Name and locations of all data files and redo log
files
4
Other Files
- Parameter files
- Store hundreds of parameters for the Oracle
Instance - Password file
- Authenticates which users are allowed to start
and stop the database - Archive redo log files
- Copies of the redo log files that are saved so
the database can be recovered to a single point
in time
Other Files...Parameter, Password, Archive Logs
5
The Oracle Instance
- Oracle Instance is comprised of the background
processes and memory structures (SGA - Shared
Global Area)
Oracle Instance
SGA (System Global Area)
DatabaseBuffer Cache
Shared Pool
Redo Log Buffer
Java Pool
Large Pool
DBWR
LGWR
SMON
PMON
CKPT
RECO
ARCH
LCKn
Pnnn
Dnnn
SNPn
6
Shared Pool
- Shared Pool
- Library Cache
- Stores the most recently used SQL statements
- Data Dictionary Cache (Row Cache)
- Stores definitions of objects contained in the
database - Used to validate object names and privileges
- Size is set by the SHARED_POOL_SIZE parameter in
the initialization file (parameter file).
SGA (System Global Area)
DatabaseBuffer Cache
Shared Pool
Redo Log Buffer
Java Pool
Large Pool
7
Buffer Cache
- Area of memory used to store the most recently
used data. Oracle knows which data is most
likely to be used again by maintaining a list of
recently used blocks called the LRU. - Operation
- A request for data is made
- Oracle checks the buffer cache to see if it
exists - If not it grabs the block from disk (physical
read)
SGA (System Global Area)
DatabaseBuffer Cache
Shared Pool
Redo Log Buffer
Java Pool
Large Pool
8
Sizing the Buffer Cache
DB_BLOCK_SIZE 8192
8K
8K
8K
DB_BLOCK_BUFFERS 5
8K
8192 5 40960 Bytes (40K)
8K
9
Redo Log Buffer
- Circular buffer that records all of the changes
occurring in the database - Size
- Defined by LOG_BUFFER parameter
- Should be a multiple of DB_BLOCK_SIZE
- Usually small compared with total SGA size, small
increase can significantly enhance throughput - As of Oracle 8 a 1 MB upper limit has been set on
the background write threshold which limits the
negative impact of a very large redo log buffer - Data is written from the redo log buffer to the
redo log files by the log writer process
10
Large Pool and Java Pool
- Optional areas of memory
- LARGE_POOL_SIZE
Oracle Instance
SGA (System Global Area)
DatabaseBuffer Cache
Shared Pool
Redo Log Buffer
Java Pool
Large Pool
DBWR
LGWR
SMON
PMON
CKPT
RECO
ARCH
LCKn
Pnnn
Dnnn
SNPn
11
Background Processes
- 5 background processes are mandatory
- Database Writer (DBWR)
- Log Writer (LGWR)
- System Monitor (SMON)
- Process Monitor (PMON)
- Checkpoint (CKPT)
- Required as of Oracle 8i
DBWR
LGWR
SMON
PMON
CKPT
RECO
ARCH
LCKn
Pnnn
Dnnn
SNPn
12
Database Writer (DBWR)
- Writes modified (dirty) blocks in the buffer
cache to the data files - Operates in batch mode
- When
- There are too many dirty blocks
- DB_BLOCK_MAX_DIRTY_TARGET
- A process scans a specified number of buffers in
the LRU list without finding a free buffer - A time-out occurs (every 3 seconds)
- A checkpoint occurs
- You can configure additional DBWR processes by
setting the DB_WRITER_PROCESSES parameter in the
parameter file
13
Log Writer (LGWR)
- Writes information in the redo log buffer to the
redo logs - Writes When
- Every time a commit is issued
- When redo log buffer is 1/3 full
- When there is more than 1 MB of changes
- Before DBWR (DB Writer) completes cleaning
modified buffer blocks in the buffer cache by
writing them to the data files - When a timeout occurs (every 3 seconds)
14
System Monitor (SMON)
- Automatically recovers the instance during
instance failure - Rolls forward transactions in the redo logs that
have not been written to disk - Opens the database and makes locked data
available - Rolls back uncommitted transactions
- Space Maintenance Functions
- Coalesces free space
- De-allocates temporary segments
15
Process Monitor (PMON)
- Cleans up failed processes by handling existing
transactions and recovering memory - Rolls back existing transactions
- Releases any locks held by the process
- Releases other resources held by the process
- Checks server and dispatcher processes and
restarts them when necessary
16
Checkpoint (CKPT)
- Used to synchronize data files, mandatory in
Oracle 8i - In Oracle 8 takes it handles the task of updating
the data file headers instead of log writer - Frequent checkpoints increase the speed of
database recovery during instance failure but may
hinder performance - CHECKPOINT_PROCESS True (Before 8i)
17
Connecting to the Database
- A user process always connects to the database
via a server process
Oracle Instance
Server Process
SGA (System Global Area)
PGA
DatabaseBuffer Cache
Shared Pool
Redo Log Buffer
Java Pool
User Process
Large Pool
DBWR
LGWR
SMON
PMON
CKPT
RECO
ARCH
LCKn
Pnnn
Dnnn
SNPn
18
PGA (Program Global Area)
- PGA
- Used by only one process and is not shared
- Gets Created when Server Process Starts.
- Contents
- Stack space
- Session information
- Cursor state
- Sort area
Server Process
PGA
User Process
19
Query Processing
- Parse
- Execute
- Fetch
Oracle Instance
Server Process
SGA (System Global Area)
PGA
DatabaseBuffer Cache
Shared Pool
Redo Log Buffer
Java Pool
User Process
Large Pool
DBWR
LGWR
SMON
PMON
CKPT
RECO
ARCH
LCKn
Pnnn
Dnnn
SNPn
20
Query Processing
- Parse
- SQL statement is passed from user process to
server process - Server process looks in shared pool to see if SQL
already exists - Validates SQL by checking the syntax
- Checks the data dictionary to ensure all of the
objects and columns actually exist - Locks on objects are obtained so the definition
does not change - Checks the users privileges
- Determines the execution plan
- Loads the SQL and the plan into the shared SQL
area - Executecontinued
21
Query Processing
- Parse
- Execute
- Identifies the rows that are selected
- Fetch
- Returns the rows to the user process and ordered
if necessary
22
Rollback Segments
- Record the before image before data is actually
changed in the database - Purpose
- Allows user to roll back a transaction
- Allows other users to see the original image
until the changes have been committed - Allows the database to be recovered if the
instance fails