Defining Data Warehouse Structures - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title:
Defining Data Warehouse Structures
Description:
Melons. 2002. Measures Dimension. Products Dimension. Q4. Q3. Q2. Time Dimension. Apples. Cherries ... Melons. Cherries. Grapes. Defining a Cube Slice. Ave ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:166
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Defining Data Warehouse Structures
1
Defining Data Warehouse Structures
2
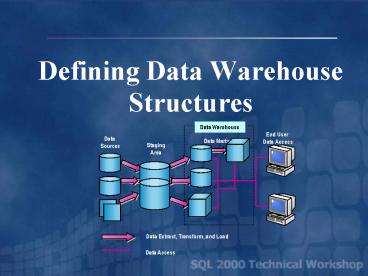
Data Warehouse Structures Overview
Data Warehouse
OLAP
End User Data Access
Data Marts
3
The Star Schema
4
Describing Dimensions
- Describing Business Entities
- Containing Attributes That Provide Context to
Numeric Data - Presenting Data Organized into Hierarchies
5
Identifying Primary Keys
- Primary Keys
- Identify Uniqueness
- Are the Dimension Columns Referenced in the Fact
Table - Two Candidates
- Application Keys (app suffix) Are Source Data
Values That Identify Uniqueness - Surrogate Keys (key suffix) Are System-generated
Integers That Identify Uniqueness
6
Defining Hierarchies
- Understanding Benefits of Hierarchies
- Allow end users to view data at different levels
of summarization - Provide drill down / drill up paths of analysis
Drill Down
Drill Up
- Implementing Hierarchies
- Denormalized star schema dimensions
- Normalized snowflake dimensions
7
Snowflaked Dimension Tables
- Defines Hierarchies by Using Multiple Dimension
Tables - Is More Normalized than a Single Table Dimension
8
Describing Fact Tables
Inventory Data By Inventory Date, Product, and
Warehouse
Sales Data By Product, Customer, and Order Date
9
Identifying Fact Table Components
DimensionTables
Sales_fact Table
Foreign Keys
customer_dim
201 ALFI Alfreds
customer_key
product_key
time_key
quantity_sales
amount_sales
201
25
134
400
10,789
product_dim
25 123 Chai
The grain of the sales_fact table is defined by
the lowest level of detail stored in each
dimension associated with the fact table The
grain of the sales_fact table is sales data by
customer ID, product ID, and order date
10
Defining Foreign Keys
FOREIGN KEY Constraint
FOREIGN KEY Constraint
product_key
customer_key
order_date_key
customer_dim_key
time_dim_key
FOREIGN KEY Constraint
product_dim_key
- Physically implement the relationship between FK
columns of the fact table and PKs of dimension
tables - Enforce referential integrity between the
dimension tables and the fact table
11
Relational Schemas and OLAP
Data Warehouse
OLAP
OLAP
End User Data Access
Data Marts
12
OLAP Database Components
- Numeric Measures
- Data values or facts that users analyze
- Dimensions
- Business categories that provide context to
numeric measures - Sourced from columns in star schema dimensions
- Members are organized into hierarchies
- Cubes
- Combine dimensions and measures into one
conceptual model - Logical storage medium for an OLAP database
13
Relational Dimensions vs. OLAP Dimensions
REGIONWestEastSTATE REGIONCA WestOR WestMA
EastNY East
REGION West CA OREast MA NY
OLAP
Relational
14
OLAP Dimension Fundamentals
Year
Time Dimension Table
Quarter
Month
RELATIONAL
OLAP
15
Dimension Family Relationships
- Drinks is the Parent of Tea and Coffee
- Tea and Coffee are Children of Drinks
- Tea and Columbian are Descendants of Drinks
- Tea and Drinks are Ancestors of Earl Grey
- Tea and Coffee are Siblings
- Lemon and Columbian are Cousins
- All are dimension Members
16
Cube Measures
- Are the Numeric Values of Principal Interest
- Correspond to a Fact Tables Facts (or Measures)
- Intersect All Dimensions at All Levels
- Are Aggregated at All Levels of Detail
- Form a Dimension
17
The Cube
Time Dimension
Products Dimension
Measures Dimension
18
Querying a Cube
Q1
Q2
Time Dimension
Q3
Grapes
Cherries
Q4
Melons
Apples
Products Dimension
Sales Units
Ave Units
Sales Dollars
Net Price
Measures Dimension
19
Defining a Cube Slice
Q1
Q2
Time Dimension
Q3
Grapes
Cherries
Q4
Melons
Apples
Products Dimension
Sales Dollars
Net Price
Ave Units
Sales Units
Measures Dimension