Given: - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 47
Title: Given:
1
- Given
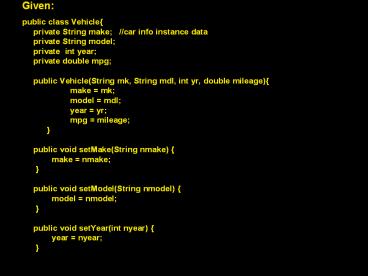
- public class Vehicle
- private String make //car info instance
data - private String model
- private int year
- private double mpg
- public Vehicle(String mk, String mdl, int
yr, double mileage) - make mk
- model mdl
- year yr
- mpg mileage
- public void setMake(String nmake)
- make nmake
- public void setModel(String nmodel)
2
- public String getMake()
- return make
- public String getModel()
- return model
- public int getYear()
- return year
- public double getMileage()
- return mpg
- public String toString()
- return year " " make " "
model
3
- Inheritance extend classes by adding methods
and fields - This is one form of software reuse !!
- Example Car class
- a Car is a Vehicle with trunksize
class Car extends Vehicle new methods
new instance fields
4
- Car automatically inherits all methods and
instance fields of Vehicle - Extended class superclass (Vehicle),
extending class subclass (Car)
Car mycar new Car(Ford,Mustang, 1969)
//assume Car constructor exists
mycar.setMpg(10.5) // OK to use Vehicle method
with Car object
5
An Inheritance Diagram
- Every class extends the Object class either
directly or indirectly
Figure 1An Inheritance Diagram
6
- In subclass, specify added instance fields and
additional methods
public class Car extends Vehicle // data
private boolean convertible
private double trunksize public void
setConvert(boolean conv)
convertible conv
public boolean getConvert()
return convertible
//calculate distance that can currently be
traveled public double distance (double
gallons) return gallons
getMileage() //use superclass method to
access
// private data
inheritied from Vehicle
7
- In subclass, change (override) methods
//class Car continued..
//OVERRIDE the toString method public
String toString() return
getYear() " " getModel() " trunk cap "
trunksize Note again, that
call to inherited public method uses implicit
object (no object need be specified)
//can USE superclass method public String
toString() return
super.toString() "trunk cap trunksize
8
Inheriting Instance Fields
- A subclass has no access to private fields of its
superclass - Subclass must use public interface
- Inherit field All fields from the superclass are
automatically inherited - Add field Supply a new field that doesn't exist
in the superclass - Can't override fields
- What if you define a new field with the same name
as a superclass field? - Each object would have two instance fields of the
same name - this.varname, super.varname
- Fields can hold different values
- Legal but extremely undesirable
9
Inheriting Methods
- Override method
- Supply a different implementation of a method
that exists in the superclass - Must have same signature (same name and same
parameter types) - If method is applied to an object of the subclass
type, the overriding method is executed - Inherit method
- Don't supply a new implementation of a method
that exists in superclass - Superclass method can be applied to the subclass
objects - Add method
- Supply a new method that doesn't exist in the
superclass - New method can be applied only to subclass
objects
10
Invoking a Super Class Method
- Can't just call
- toString() in toString() method of Car
- That is the same asthis.toString()
- Calls the same method (infinite recursion)
- Instead, invoke superclass methodsuper.toString()
Continued
11
Inheritance Hierarchies
- Sets of classes can form complex inheritance
hierarchies - Example
Figure 3A Part of the Hierarchy of Ancient
Reptiles
12
Inheritance Hierarchies ExampleSwing hierarchy
Figure 4A Part of the Hierarchy of Swing User
Interface Components
Continued
13
Subclass Constructors
- super followed by a parenthesis indicates a
call to a superclass constructor - public Car (String mk, String mdll, int yr,
double miles,double trk) - super(mk,mdl,yr,miles)
- trunksize trk
- Must be the first statement in subclass
constructor - If subclass constructor doesn't explicitly call a
super class constructor, default super is
implicitly called - Default constructor constructor with no
parameters - If all constructors of the superclass require
parameters, then the compiler reports an error!
14
Subclass Constructors
- Note Vehicle does not have default constructor
- If we defined Car constructor as follows
- public Car (String mk, String mdll, int yr,
double miles) - setMake(mk)
- setModel(mdl)
- setYear(yr)
- setMpg(miles)
- This method will not compile, as implicit call to
default Vehicle constructor is not possible!!
15
Converting Between Subclass and Superclass Types
- Ok to convert subclass reference to superclass
reference
Car myCar new Car(Chevy, Camaro, 1973)
Vehicle aCar myCar Object theCar myCar
Note all three reference variables are
referring to the same object
16
- Superclass references don't know the full
story - When you convert between a subclass object to its
superclass type - The value of the reference stays the sameit is
the memory location of the object - But, less information is known about the object
aCar.setMpg(7.8) // OK aCar.distance(67)
//NO!! // No--not a method of the class to which
aCar belongs
17
- Why would anyone want to know less about an
object? - To write reusable code when code only needs to
know about superclass features - FOR EXAMPLE ..
- what if we also had a Truck class
- (next slide)
18
Suppose we have a Truck class too
public class Truck extends Vehicle
private boolean trailerHitch private
double bedLength public void
setTrailerHitch(boolean hitch)
trailerHitch hitch
public double getLen()
return bedLength
//calculate Load that can be carried
public double calcLoad (double lbPerCubicFoot)
return (bedLength
lbPerCubicFoot) / etc //
toString etc
19
Class Usage
- //can create and assign to same type reference
- Vehicle v1 new Vehicle(ford,mustang,1966,
28.5) - Car c1 new Car(vw,rabbit, 1978, 35.2)
- Truck t1 new Truck(MAC,pickup, 1968, 16.0)
- //a subclass is the superclass type, but not vice
versa - Vehicle v2 new Car(cadillac,seville, 1988,
16.0) - Vehicle v3 new Truck(MAC,pickup, 1968,
16.0) - Car c2 new Vehicle(gmc,yukon,122, 13.5)
//error - //public superclass methods can be called by
subclass object - v1.setMake(Mercury)
- t1.setMake(Toyota)
- c1.setMake(Nissan)
20
Application can work with Carsa and Trucks using
same code
public class App public static void
main(String args) Vehicle newVehicle
// one list to
store all Vehicles ArrayList
inventory new ArrayList()
//while user wishes to
enter vehicles while(JOptionPane.showInputDia
log("Enter a vehicle?? Y/N").equals("Y"))
String whichone JOptionPane.showInputDialog("
(C)ar or (T)ruck") switch
(whichone.charAt(0) ) //determine which
kind case 'C' newVehicle
new Car() break
case 'T' newVehicle new Truck()
break default
newVehicle new Car() // car assumed as default
type // use same code to
get details for cars trucks
newVehicle.setMake(JOptionPane.showInputDialog("ma
ke?")) newVehicle.setModel(JOptionPane.
showInputDialog( model ?"))
newVehicle.setYear(Integer.parseInt(JOptionPane.sh
owInputDialog ("year?")))
inventory.add(newVehicle)
21
Application can work with Cars and Trucks using
same code
// what is our inventory String output
"" for ( int i0 ii) output output "\n"
inventory.get(i)
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, output)
Simple loop to outputs all Vehicle
information -- The correct version of toString
is selected at run time --- POLYMORPHISM!!
22
Converting Between Subclass and Superclass Types
- Occasionally you need to convert from a
superclass reference to a subclass reference - This cast is dangerous if you are wrong, an
exception is thrown
Vehicle myRide new Car(Chevy, Camaro,
1973) myRide.setConv(true) // will cause
compile error because
// compiler doesnt know its a
Car Can only call setConv with a Car object
Car thisCar (Car) myRide
thisCar.setConv(true)
23
- Solution use the instanceof operator
- instanceof tests whether an object belongs to a
particular type
if (myRide instanceof Car)
Car thisCar (Car) myRide
thisCar.setConv(true)
24
Polymorphism
- Polymorphism ability to refer to objects of
multiple types with varying behavior - Polymorphism at work
- Depending on types of ride, different version of
toString is called
public void printIt(Vehicle ride)
System.out.println( ride.toString() )
25
Access Control
- Java has four levels of controlling access to
fields, methods, and classes - public access
- Can be accessed by methods of all classes
- private access
- Can be accessed only by the methods of their own
class - package access
- The default, when no access modifier is given
- Can be accessed by all classes in the same
package - Good default for classes, but extremely
unfortunate for fields - protected access
- Can be accessed by subclasses and package
26
Recommended Access Levels
- Instance and static fields Always private.
Exceptions - public static final constants are useful and safe
- Some objects, such as System.out, need to be
accessible to all programs (public) - Occasionally, classes in a package must
collaborate very closely (give some fields
package access) inner classes are usually better
27
Recommended Access Levels
- Methods public or private
- Classes and interfaces public or package
- Better alternative to package access inner
classes - In general, inner classes should not be public
(some exceptions exist, e.g., Ellipse2D.Double) - Beware of accidental package access (forgetting
public or private)
28
(No Transcript)
29
Object The Cosmic Superclass
- All classes defined without an explicit extends
clause automatically extend Object
Figure 8The Object Class is the Superclass of
Every Java Class
30
Object The Cosmic Superclass
- Most useful methods
- String toString()
- boolean equals(Object otherObject)
- Object clone()
31
The String toString() Method
String toString() is called whenever you
concatenate a string with an object
import java.awt.Rectangle Rectangle rec1 new
Rectangle(5, 10, 20, 30) System.out.println(rec
1 rec1) //outputs rec1 java.awt.Rectanglex5
,y10,width20,height30"
Object class provides a toString(), so all
objects have one!!
32
What if you dont override the tostring Method ?
- Object class toString() method executed
- Object class knows nothing about the specifics of
your class - Object class toString consists of only two piece
of info it has, class name and hash code (value
based on storage address) - Try it code a class Widget with no toString and
write an application with - 1. Widget myWidget new Widget()
- 2. System.out.println(myWidget)
33
Overriding the tostring Method
- To provide a nicer representation of an object,
override toString
public String toString() return Widget
Size 5 "
Very simple to override toString, just provide a
toString method which returns a String which is
how you would want the object represented
textually.
34
If (coin1 coin2)
- tests for equal location
Two References to Same Objects
35
If (coin1.equals( coin2) )
- Object class equals also tests for equal location
Two References to Same Objects
36
Need to override the equals method so that equal
contents are checked
- equals is intended to test for equal contents
Two References to Equal Objects
Continued
37
Overriding the equals Method
- When redefining equals method, you cannot change
object signature - public boolean equals (Object obj)
Continued
38
Overriding the equals Method
- Equals method should be based on instance data
of two objects .. - public boolean equals (Object obj)
- if (make.equals(obj.make) model
.equals(obj.model ) - year obj.year mpg
obj.mpg) - return true
- else
- return false
But this will not compile because an Object
object does not have make, model, year and mpg
instance fields.
39
Overriding the equals Method
- need to CAST Object obj to a Vehicle object ..
- public boolean equals (Object obj)
- Vehicle vobj (Vehicle) obj
- if (make.equals( vobj.make)
model.equals(vobj.model) - year vobj.year mpg
vobj.mpg) - return true
- else
- return false
40
Overriding the equals Method
- Need to be sure that obj IS an object before you
cast to avoid ClassCastException . - public boolean equals (Object obj)
- if (obj instanceof Vehicle)
- Vehicle vobj (Vehicle) obj
- if (make.equals(vobj.make)
model.equals(vobj.model) - year vobj.year mpg
vobj.mpg) - return true
- else
- return false
- else
- return false
This will work fine for Vehicle objects, but We
will need to use this method when
checking Equality of our subclasses too
need to be more specific when checking for equal
class types
41
Overriding the equals Method
- Need to be sure that obj IS an object before you
cast to avoid ClassCastException . - public boolean equals (Object obj)
- if (getClass().equals(obj.getClass() ))
- Vehicle vobj (Vehicle) obj
- if (make vobj.make model
vobj.model - year vobj.year mpg
vobj.mpg) - return true
- else
- return false
- else
- return false
getClass() is a method inherited from the Object
class which returns a Class object
42
Overriding equals in the Car subclass
- public boolean equals (Object obj)
- if (super.equals(obj) false)
- return false
- else // we now know they
are both Cars, and - // super class
fields are equal - // need to check
additional Car field - Car tobj (Car) obj
- return ( convertible
tobj.convertible -
trunksize tobj.trunksize)
43
Object assignment .
- Copying an object reference gives two references
to same object
Vehicle myCar new Car() Vehicle car myCar
44
Object class has a Object clone() Method
- Object class clone() method returns a copy of the
invoking object - Using the clone() method is inherited from the
object class by all subclasses, BUT ACCESS is
PROTECTED, so method not accessible by
application class.
Vehicle myVec new Vehicle(Toyota , Corolla,
1967, 34.5)
//Vehicle
inherits
// clone method from Object
class Vehicle anotherVec (Vehicle)
myVec.clone()
//BUT application can not
call it!!
This is a security measure added to the Java
language with Java 1.2. At that point the Java
languages popularity as a Web programming
language was becoming apparent.
45
An object can ONLY be cloned IF its class
overrides the Object clone() method
- public class Vehicle
- public Object clone() //same
signature for override - return super.clone() // calls superclass
Objects clone
Vehicle myVec new Vehicle(Toyota , Corolla,
1967, 34.5)
Vehicle
anotherVec (Vehicle) myVec.clone()
BUT . Java has one more security measure for
cloning.
46
An object can ONLY be cloned IF its class
overrides the Object clone() method
- //class which overrides Clone MUST
implementCloneable - public class Vehicle implements Cloneable
- public Object clone()
- try
- return super.clone() //Objects clone
throws checked exception if -
//cloneable not implemented, so must -
// be called within a try/catch block - catch(Exception e)
- return null
47
The Object.clone Method
- Creates shallow copies
Figure 12The Object.clone Method Makes a
Shallow Copy



























![get [PDF] Download If the Gods Had Meant Us to Vote They Would Have Given Us Candidates PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10062341.th0.jpg?_=202406220412)
![READ [PDF] Between Heaven & Hollywood: Chasing Your God-Given Dream PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10067654.th0.jpg?_=20240628051)
![[PDF] DOWNLOAD The Shift: Success is not a given PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10079010.th0.jpg?_=20240716018)
![[PDF READ] Free Given Up For Dead: American GI's in the Nazi Concentra PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10120763.th0.jpg?_=202409050412)