Decoding Surface Station Plots - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 16
Title:
Decoding Surface Station Plots
Description:
... station circle for manned observations or station triangle for automatic ... whether the station is an automatic (triangle) or manned (circle) observing site. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:75
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Decoding Surface Station Plots
1
Decoding Surface Station Plots
2
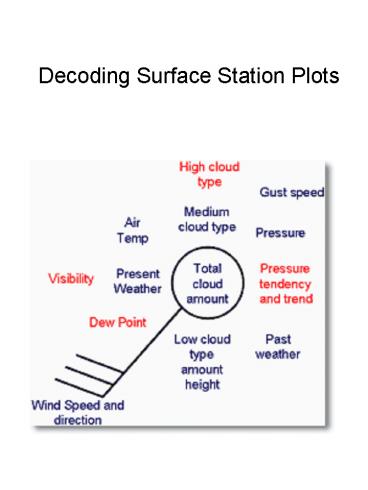
Total cloud amount The total amount of the sky
covered by cloud is expressed in oktas (eighths)
and is plotted within the station circle for
manned observations or station triangle for
automatic stations, by the amount of shading.
3
Air temperature Air temperature is plotted to the
nearest whole degree Celsius, i.e. 23 would
indicate 23 degrees Celsius. (On U.S. maps the
temperature plotted is in degrees
Fahrenheit.) Dew point temperature Dew point
temperature is plotted to the nearest whole
degree Celsius, i.e. 18 would indicate a dew
point of 18 degrees Celsius. (On U.S. maps the
dew point temperature plotted is in degrees
Fahrenheit.)
Wind speed and direction The surface wind
direction is indicated on the station plot by an
arrow flying with the wind. Direction is measured
in degrees from true North. Therefore a wind
direction of 180 is blowing from the south. The
wind speed is given by the number of 'feathers'
on the arrow. Half feathers represent 5 knots
whilst whole feathers indicate 10 knots. A wind
speed of 50 knots is indicated by a triangle.
Combinations of these can be used to report wind
speed to the nearest 5 knots. The symbols used
are given below. Gust Speed Gust speeds are
measured in knots and proceeded by the letter G.
Gust speeds are normally only recorded if they
exceed 25 knots and are plotted as whole knots
i.e. G35 indicates a gust of 35 knots.
4
Sea Level Pressure Pressure is recorded in
millibars and tenths and the last three digits
are plotted. Sea level pressure typically ranges
from 960mb to 1050mb. A general rule of thumb is
to add 10 to the front when the first digit
recorded is a 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 and add 9 to
the front when the first recorded didgit is a 6,
7, 8, or 9. Therefore 1003.1 would be plotted as
031 and 987.1 would be plotted as 871. Pressure
Tendency Pressure trend shows how the pressure
has changed during the past three hours i.e
rising or falling, and pressure tendency shows by
how much it has changed. The tendency is given in
tenths of a millibar, therefore '20' would
indicate a change of two millibars in the last
three hours. Pressure tendency is indicated by
the symbols below. The symbols also show whether
the rise/ fall has been continuous or
discontinuous. That is while the pressure may be
higher than it was 3 hours ago, it may have fell
before it rose, and thus was discontinuous.
5
Visibility Visibility, which is how far we can
see, is given in coded format, in either meters
or kilometers. Visibilities below five kilometers
are recorded to the nearest 100 meters, whilst
those above five kilometers are given to the
nearest kilometer. For visibilities equal to and
less than five km
6
For visibilities greater than five km
In the U.S., visibilities are plotted as
fractions up to 5 miles, and whole numbers from
5-10 miles. Generally the visibility in the U.S.
is only given in instances where the visibility
is less than 10 miles. Thus, when no visibility
is given it is assumed to be greater than or
equal to 10 miles (16km).
7
Current Weather There are 99 symbols used to
describe the current weather a station may be
experiencing Those sybols are given on the next
few tables..
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
Past weather A simplified version of the present
weather plots is used to indicate past weather.
12
High cloud type The type of high cloud present is
provided in coded format, using the symbols below.
13
Medium cloud type The type of medium cloud
present is provided in coded format, using the
symbols below.
14
Low cloud type The type of low cloud present is
provided in coded format, using the symbols
below.
15
Cloud height Cloud heights are measured in
hundreds or thousands of feet, and refer to the
level of the cloud base. The way these are
plotted varies depending on whether the station
is an automatic (triangle) or manned (circle)
observing site.
Table 4 Cloud heights for manned stations
Table 3 Cloud heights for automatic stations
16
Example The decode of this station plot is as
follows