Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title:
Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
Description:
Physical Properties of ... between alcohol molecules leading to relatively high ... Physical Properties of Alcohols. The OH group is polar and capable of ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:86
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
1
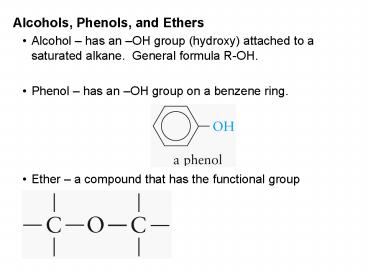
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
- Alcohol has an OH group (hydroxy) attached to
a saturated alkane. General formula R-OH. - Phenol has an OH group on a benzene ring.
- Ether a compound that has the functional group
2
- Naming Alcohols
- Step 1 Name the longest chain to which the OH
group is attached. Use the alkane name of the
chain, drop the e ending, and replace it with
ol. - Step 2 Number the longest chain to give the
lowest number to the carbon with the OH. - Step 3 Locate the OH position.
- Example
OH
CH3CH2CH2CHCH2CH3
6 5 4 3 2 1
3-hexanol
3
- Naming Alcohols, cont.
- Step 4 Locate and name any other groups
attached to the longest chain. - Step 5 Combine the name and location of other
groups, the location of the OH, and the longest
chain into the final name. - Example
OH
CH3
CH3
CH3CH2CH2CHCHCH3
6 5 4 3 2 1
2,4-dimethyl-3-hexanol
4
p. 407
5
p. 407
6
- Classification of Alcohols
7
- Physical Properties of Alcohols, cont.
- The OH group can hydrogen bond between alcohol
molecules leading to relatively high boiling
points. - Hydrogen bonding in pure ethanol
8
- Physical Properties of Alcohols
- The OH group is polar and capable of hydrogen
bonding. - This makes low molecular weight alcohols highly
soluble in water. - Hydrogen bonding in a water-methanol solution
9
- Physical Properties of Alcohols, cont.
- Larger alkanes have greater hydrophobic regions
and are less soluble or insoluble in water. - Water interacts only with the OH group of
1-heptanol
10
- Alcohol Reactions
- The removal of water (dehydration) from an
alcohol is an elimination reaction and produces
an alkene.
11
p. 411
12
- Oxidation the removal of hydrogen atoms.
13
- Alcohol Reactions, cont.
- Primary alcohol oxidation
- Secondary alcohol oxidation
14
- Properties of Ethers
- Much less polar than alcohols.
- Low boiling and melting points because of the
inability to hydrogen bond between molecules. - More soluble in water than alkanes, but less
soluble than alcohols.
15
- Hydrogen bonding of dimethyl ether (a) with
water and (b) no hydrogen bonding in the pure
state