Market Efficiency - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 10
Title:
Market Efficiency
Description:
Rules out Technical Analysis ... Implies that Fundamental Analysis will not provide excess returns. Does not mean Fundamental Analysis is useless. Without it ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:129
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Market Efficiency
1
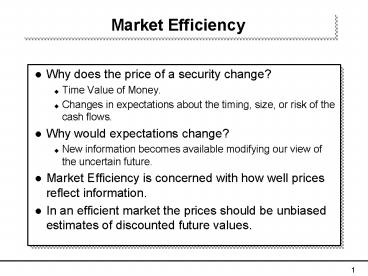
Market Efficiency
- Why does the price of a security change?
- Time Value of Money.
- Changes in expectations about the timing, size,
or risk of the cash flows. - Why would expectations change?
- New information becomes available modifying our
view of the uncertain future. - Market Efficiency is concerned with how well
prices reflect information. - In an efficient market the prices should be
unbiased estimates of discounted future values.
2
Abnormal vs. Expected Returns
- Realized returns are simply the percentage change
in asset value. - Abnormal returns are the realized returns in
excess of the return expected for a level of
risk.
3
Forms of Market Efficiency
- An efficient market will quickly and accurately
reflect available information. - The definition of available information gives
three forms of efficiency - Weak Form - Prices reflect all information
reflected in past prices and volumes. - Semi-Strong Form - Prices reflect all public
information. - Strong Form - Prices reflect all public and
private information.
4
Weak Form Efficiency
- Says you can not make abnormal returns on the
basis of historical data. - Rules out Technical Analysis
- Some trading strategies do make an abnormal
return before trading costs, but not once trading
costs are included. - Empirical evidence generally supports Weak Form
Efficiency.
5
Semi-Strong Form Efficiency
- No abnormal returns on the basis of any public
information (including historical data). - Implies that Fundamental Analysis will not
provide excess returns. - Does not mean Fundamental Analysis is useless.
Without it markets may not be as efficient. - Evidence generally supports Semi-Strong Form
Efficiency, although this is the subject of
considerable debate.
6
Strong Form Efficiency
- Says that there is no information at all that
would allow an abnormal profit. - Implies that even insiders with special knowledge
(e.g., an forthcoming acquisition announcement)
can not make an abnormal profit. - Not much support for Strong Form. The fact that
there are regulations against insider trading
supports this claim.
7
The Three Forms of Efficiency
Semi-Strong Form Efficient
Strong Form Efficient
Weak Form Efficient
8
Points about Efficiency
- The idea of efficiency is that prices will be
fair. - All investments in securities will be zero NPV.
- Intense competition prevents a free lunch.
- Think of efficiency as a matter of degree.
- Just like some cars are more fuel efficient than
others, some markets are more informationally
efficient. - Efficiency may change over time or market
conditions. The availability of computers has
increased our ability to collect, distribute, and
process information quickly.
9
Points about Efficiency
- To be precise, efficiency says there is no way to
profit from available information after
considering information processing and
acquisition costs. - Efficiency does not mean that investments
decisions can be made mindlessly.
10
What you should know?
- How are different forms of market efficiency
defined? Make sure you know how to detect them,
when given a case