Trendline Analysis - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 20
Title:
Trendline Analysis
Description:
A 'trendline' analysis is used to find the best 'fit' of a function or best ... it follows that the distance between the corresponding tick marks is the same. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:302
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Trendline Analysis
1
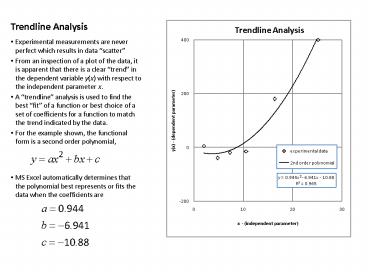
Trendline Analysis
- Experimental measurements are never perfect which
results in data scatter - From an inspection of a plot of the data, it is
apparent that there is a clear trend in the
dependent variable y(x) with respect to the
independent parameter x. - A trendline analysis is used to find the best
fit of a function or best choice of a set of
coefficients for a function to match the trend
indicated by the data. - For the example shown, the functional form is a
second order polynomial, - MS Excel automatically determines that the
polynomial best represents or fits the data when
the coefficients are
2
Trendline Analysis
- The trendline analysis uses a least squares
curve fitting procedure. - the deviation of the ith data point is the
difference between the value of the dependent
variable yi at xi and the curve fitting function
f() evaluated at xi. - the coefficients a, b, and c in f(x) are chosen
to minimized the total sum of the deviations
squared,
3
Transducer Calibration
The function of a water pump is to cause an
increase in the fluid pressure as it passes
through the pump. The pressure increase depends
on the flow rate and the pump speed. In a pump
test, these parameters must be measured.
4
Transducer Calibration
- apply known pressure differentials to the
transducer and measure the corresponding
transducer output voltage - (known pressures might be determined by using
another previously calibrated pressure
measurement system) - Apply a Trendline Analysis to find the best fit
of a linear curve fit equation to the data
- Use the calibrated pressure transducer to
determine unknown pressures by measuring the
transducer output voltage and applying the
calibration relation
5
- Type in the data values shown
- Create the table headings and format the table as
shown - Plot the data on a Scatter Plot (refer to the
previous tutorial as necessary) - Format the plot as shown
- axis range,
- tick mark intervals,
- tick mark type,
- number format
- horizontal vertical grid lines
- data point marker style
6
- Add a Trendline to the plot by
- right-click on a data point marker and select Add
Trendline from the popup window - select a Linear curve fit
- set the Trendline Name for the plot legend
- display the curvefit equation on the plot
- display the r-squared value on the plot
(indicates how well the curve fit matches the
data - the closer it is to one, the better the
fit)
7
- Change the format for the Trendline Label by
- right-clicking on the label
- select Format Trendline Label
- select the Number option group and choose the
Scientific format with 3 decimal places - select the Fill option group and choose a Solid
Fill with the Color set to White - select the Border Color option group and choose a
Solid Line with the Color set to Black
8
We have established the relationship between the
pressure applied to the transducer and its
corresponding voltage output. In a normal
experimental application, an unknown pressure
will be applied to the transducer and the
calibration equation will be used to find the
pressure from the measured voltage.
9
- Start a new worksheet Sheet2
- Create a data table
- type in the measured transducer output voltages
- enter the coefficients determined from the
trendline analysis - enter the formula to calculate the pressures
corresponding to each voltage - complete the table formatting as shown
- Create a plot of the pressures with the
formatting shown
10
Power Law Trendlines
- Many processes of interest to engineers follow a
power-law relationship, - The plot above is for a power-law relationship
with an exponent greater than 1.
11
Log-Log Plots
- Data that follows a power-law is often shown on a
log-log plot. This is the same data that was
presented on the previous slide. - Note that the data follows a linear trend on the
log-log plot.
- On log-log plots, the distance along an axis is
proportional to the log of the parameter.
12
Log-Log Plots
- On log-log plots, the distance along an axis is
proportional to the log of the parameter. - Taking the log of the power-law
relation,note that log y is linear with
respect log x. - Since the difference between log(100) and log(10)
is the same as the difference between log(1000)
and log(100), it follows that the distance
between the corresponding tick marks is the same. - The minor grid lines from 1-10 are 2, 3, 4,etc.
and from 10-100 are 20, 30, 40, etc. - Note that the coordinates for the first 3 points
are (5,75), (10,300), and (15,675).
13
- To find the trendline for data that follows a
power-law relationship - key-in the data and format the table as shown
- create the plot with the formatting features
shown - right-click on one of the data points and select
Add Trendline from the popup menu - set the Trend/Regression Type to Power
- set the Trendline Name to power-law curve fit
- display the equation and R-squared value on the
plot
14
- Format the trendline label as shown
- right-click on the x-axis and select format axis
- turn-on the auto-scaling
- select the Logarithmic Scale
- repeat these selections for the y-axis
15
- select Major Minor Gridlines for the vertical
and horizontal axis
16
The final forma of the plot
17
Exponential Trendlines
- Many processes of interest to engineers follow an
exponential relationship, - The plot above is for an exponential relationship
with a positive exponent . - The process is described as exponential growth.
- The plot above illustrates the typical trend for
an exponential process with a negative exponent. - The process is described as exponential decay.
18
Semi-Log Plots
- Data that follows an exponential variation is
often shown on a semi-log plot. This is the same
data that was presented on the previous slide. - Note that the data follows a linear trend on the
semi-log plot.
- On semi-log plots, the distance along the x-axis
is proportional to the parameter and distance
along the y-axis is proportional to the log of
the parameter
19
Log-Log Plots
- On semi-log plots, the distance along the y-axis
is proportional to the log of the parameter and
along the x-axis, the distance is proportional to
the parameter. - Taking the log of the exponential
relation,note that log y is linear with
respect x.
20
- On Sheet4 of your workbook
- Create and format the data table as shown.
- Create and format the plot as shown you will
choose the Exponential Trendline Type.