Multiple Alignment, Distance Estimation, - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Multiple Alignment, Distance Estimation,
Description:
find oligonucleotide primers for PCR. predict secondary and tertiary ... D12 - D23 - D13 - D12 - D13 D23 - Multiple Alignment by CLUSTALW. Pairwise alignment ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:159
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Multiple Alignment, Distance Estimation,
1
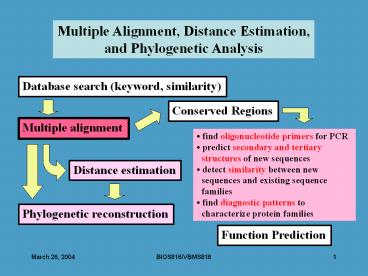
Multiple Alignment, Distance Estimation, and
Phylogenetic Analysis
Database search (keyword, similarity)
Conserved Regions
Multiple alignment
find oligonucleotide primers for PCR predict
secondary and tertiary structures of new
sequences detect similarity between new
sequences and existing sequence families find
diagnostic patterns to characterize protein
families
Distance estimation
Phylogenetic reconstruction
Function Prediction
2
What Do We Assume?
1. The sequences under study have been derived
from a common ancestral sequence
3
What Do We Assume?
2. Deletions, insertions, and substitutions have
occurred in either of the lineages after the
divergence
ATTCTGC
4
What Do We Assume?
NOTE We cannot tell an insertion on one
sequence or a deletion on the other
5
What Do We Assume?
NOTE We cannot tell an insertion on one
sequence or a deletion on the other
ATTCT-C AATCTGC
Insertion or deletion??Indel
6
Alignment Strategy
Protein alignment is easier than DNA
alignment ? DNA has only 4 nucleotide types
(they can match just by chance more
frequently) If DNA sequences are from coding
regions, ? Align them at the protein level
after translation Do not blindly rely on the
default parameter set ? Try different
options! (scoring matrix, gap penalties, etc.)
7
How Do We Align Sequences?
1) Maximize the number of matched pairs
(similarity alignment) 2) Minimize the number of
mismatched pairs (distance alignment) while at
the same time 3) Keep the number of gaps as small
as possible
8
Alignment Score
A simple scheme S m wg, where m the
number of matched pairs w the gap
penalty g the number of gaps
9
Biologically (Evolutionary) Plausible
Alignment Requires More Complex Scoring System
- 1) Gap penalty
- Gap opening or gap creation penalty ? length
independent - Gap extension penalty ? length dependent
- Gap extension penalty lt Gap opening penalty
- (new gaps are NOT easily inserted)
- 2) Weighting scheme
- Identity based ? Identity matrix matched
(identical) vs. mismatched - Similarity based
- Nucleotide alignments Transition weighting
- Protein alignments Gonnet matrices (Gonnet
250 etc.) - Dayhoff matrices (PAM250 etc.)
- BLOSUM matrices (BLOSUM62 etc.)
10
Transition Weighting Scheme
11
Transition Weighting Scheme
12
Transition Weighting Scheme
13
Transition Weighting Scheme
gtgt
14
Alignment Score
A simple scheme S m wg, where m the
number of matched pairs w the gap
penalty g the number of gaps
15
Transition Weighting Scheme
A better scheme S ? s(i, j) wg,
where s(i, j) the similarity score between
nucleotides i and j w the gap penalty g the
number of gaps
?
A C G T
A 1 0 0.5 0
C 0 1 0 0.5
G 0.5 0 1 0
T 0 0.5 0 1
w -1,
16
Multiple Alignment by CLUSTALW Thompson et al.
(1994)
Pairwise alignment (fast approximation or full
dynamic programming)
Generate a distance matrix ( identities
converted to distances)
Construct a guide tree (neighbor-joining
phylogenetic method)
Progressive alignment following the guide
tree (weight matrix, various gap penalties, etc.)
17
Multiple Alignment by CLUSTALW
Pairwise alignment (full dynamic programming)
T T G G A C G A T T G
T
C
G
G
A
G
C
T
G
TTGGACGATTG vs. TCGGAGCTG
18
Multiple Alignment by CLUSTALW
Pairwise alignment (full dynamic programming)
T T G G A C G A T T G
T
C
G
G
A
G
C
T
G
TTGGACGATTG vs. TCGGAGCTG
19
Multiple Alignment by CLUSTALW
Pairwise alignment (full dynamic programming)
T T G G A C G A T T G
T
C
G
G
A
G
C
T
G
TTGGACGATTG vs. TCGGAGCTG
20
Multiple Alignment by CLUSTALW
Pairwise alignment (full dynamic programming)
T T G G A C G A T T G
T
C
G
G
A
G
C
T
G
TTGGACGATTG vs. TCGGAGCTG
21
Multiple Alignment by CLUSTALW
Pairwise alignment (full dynamic programming)
T T G G A C G A T T G
T
C
G
G
A
G
C
T
G
TTGGACGATTG TCGGA-G-CTG
Dynamic programming computes the optimal
alignment based on the scoring scheme (scoring
matrices and gap penalties)
22
Multiple Alignment by CLUSTALW
Pairwise alignment (fast approximation)
Use diagonals only within the window size (w)
k-tuple matches
T T G G A C G A T T G
T
C
G
G
A
G
C
T
G
T T G G A C G A T T G
T
C
G
G
A
G
C
T
G
w2
Top diagonal
Alignment is done only within this band
23
Multiple Alignment by CLUSTALW
Pairwise alignment (fast approximation or full
dynamic programming)
Use dynamic programming option (Slow-Accurate)
unless it is necessary! For faster computation
(but lower resolution) ? Use larger k-tuple
size, fewer top diagonals, smaller window size
24
Multiple Alignment by CLUSTALW
Pairwise alignment (fast approximation or full
dynamic programming)
Generate a distance matrix ( identities
converted to distances)
25
Multiple Alignment by CLUSTALW
Pairwise alignment (fast approximation or full
dynamic programming)
Generate a distance matrix ( identities
converted to distances)
Construct a guide tree (neighbor-joining
phylogenetic method)
Progressive alignment following the guide
tree (weight matrix, various gap penalties, etc.)
26
Multiple Alignment by CLUSTALW
Progressive alignment following the guide tree
Closer sequences are aligned first
Guide tree
27
How gap penalties are determined in ClustalW?
Initial gap penalties GOP (gap opening) and
GEP (gap extension) ? User defined Weight
(scoring) matrix dependent gap penalties
Similarity level dependent gap penalties
Sequence length dependent gap penalties
Position specific gap penalties ? if gaps
already exist ? residue specific (e.g.,
hydrophilic stretches)
28
Multiple Alignment by CLUSTALW
ClustalW implimentations Standalone ClustalW
(text-menu based) GCG (SeqLab) VectorNTI,
MacVector, DNA, etc. Freeware, Shareware
(SEAVIEW, lots more) Web interface (EMBOSS,
etc.) ClustalX (ClustalW with GUI and more)
29
Multiple Alignment by CLUSTALW
Bioinformatics Core Facility Web
server http//biocore.unl.edu/Pise/5.a/clustalw.ht
ml Bioinformatics Web IU Center for Genomics
Bioinformatics http//sunflower.bio.indiana.edu/bi
oweb/seqanal/interfaces/clustalw.html Institut
Pasteur, Biological Software list http//bioweb.pa
steur.fr/seqanal/interfaces/clustalw-simple.html
EMBL-EBI ClustalW Form http//www.ebi.ac.uk/clusta
lw
ClustalX FTP site (Windows, Macintosh,
Linux/Unix) ftp//ftp-igbmc.u-strasbg.fr/pub/Clust
alX/
30
ClustalX Exercise
1. Download the two sample data from the course
web site http//bioinfolab.unl.edu/unlbioinfo/doc
s/bios816/spring_2004/ bglobin.seq - protein
sequences Dloop.seq - DNA sequences Use
either DOS format or non-DOS format whichever the
ones that work for you. ? These sequences are
in FASTA format.
gtHBB_HUMAN VHLTPEEKSAVTALWGKVNVDEVGGEALGRLLVVYPWTQ
RFFESFGDLSTPDAVMGNPKV KAHGKKVLGAFSDGLAHLDNLKGTFATL
SELHCDKLHVDPENFRLLGNVLVCVLAHHFGK EFTPPVQAAYQKVVAGV
ANALAHKYH gtHBB_HORSE VQLSGEEKAAVLALWDKVNEEEVGGEALG
RLLVVYPWTQRFFDSFGDLSNPGAVMGNPKV KAHGKKVLHSFGEGVHHL
DNLKGTFAALSELHCDKLHVDPENFRLLGNVLVVVLARHFGK DFTPELQ
ASYQKVVAGVANALAHKYH
31
ClustalX Exercise (continued)
2. Find ClustalX on your machine and run the
program. 3. Load bglobin.seq data (from File
Menu). 4. Go to Alignment Menu. 5. Choose
Alignment Parameters, then Pairwise Alignment
Parameters. Check the options. 6. Choose
Alignment Parameters, then Multiple Alignment
Parameters. Check the options. 7. Some online
help is available from Help Menu. 8. From
Alignment Menu, choose Run Complete Alignment
to start the multiple alignment.
32
ClustalX Exercise (continued)
- 9. From Quality Menu, try Show Low-Scoring
Segments and Show Exceptional Residues, and
examine what you see. - 10. From File Menu, choose Save Sequences As
Click on PHYLIP format. Change the SAVE
SEQUENCE AS file name to something other than
bglobin.aln. Take a look at the file you just
created. This is the Phylip format of an
alignment. - 11. From Alignment Menu, choose Alignment
Parameters then choose Reset New Gaps Before
Alignment. - ? If you do not choose this option, every time
you redo multiple alignment, gaps will be just
accumulated (old gaps will not be removed
before re-aligned). - 12. Choose Alignment Parameters, then Multiple
Alignment Parameters. Change the options as
below - Gap Opening 1
- Gap Extension 0.1
- Protein Weight Matrix Identity matrix
33
ClustalX Exercise (continued)
13. From Alignment Menu, choose Run Complete
Alignment to do the multiple alignment. Examine
the result. 14. Use the DNA sample data
(Dloop.seq) and repeat the same process.
ClustalW/X has many options. Some options are
not available in ClustalX, but in ClustalW. So
try ClustalW, too. ClustalW is available through
some web sites. The original papers (Thompson
et al. 1994 Thompson et al. 1997) explain all
the details on these options. These papers (pdf
files) are available on the course web site.
The assignment from my lectures will be given in
the next class.