The Components of a Companys Macroenvironment - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 18
Title:
The Components of a Companys Macroenvironment
Description:
Good substitutes exist or new ones emerge. Surge in availability of supplies occurs ... Just-in-time deliveries. Electronic order processing. Electronic invoice ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:176
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Components of a Companys Macroenvironment
1
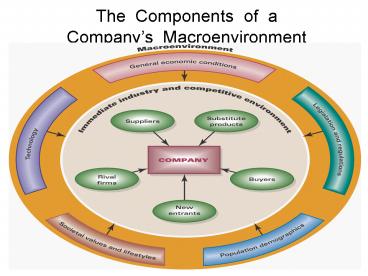
The Components of aCompanys Macroenvironment
2
Identifying the Industrys Strategy-Shaping
Business and Economic Features
- Market size and growth rate
- Buyer needs and requirements
- Number of rivals
- Scope of competitive rivalry
- Degree of product differentiation
- Product innovation
- Production capacity
- Pace of technological change
- Vertical integration
- Economies of scale
- Learning and experience curve effects
3
- Porters Five Forces Model
4
Is the Entry of AdditionalCompetitors a
Serious Threat ?
- Seriousness of threat depends on
- Size of pool of entry candidatesand available
resources - Barriers to entry
- Reaction of existing firms
- Evaluating threat of entry involves assessing
- How formidable entry barriers are for each type
of potential entrant and - Attractiveness of growth and profit prospects
5
Common Barriers to Entry
- Sizable economies of scale
- Cost and resource disadvantages independent of
size - Brand preferences and customer loyalty
- Capital requirements and/or otherspecialized
resource requirements - Access to distribution channels
- Regulatory policies
- Tariffs and international trade restrictions
6
When Is the Threat of Entry Stronger ?
- Theres a sizable pool of entry candidates
- Entry barriers are low
- Industry growth is rapid and profit potential is
high - Incumbents are unwilling or unable to contest a
newcomers entry efforts - When existing industry members have a strong
incentive to expand into new geographic areas or
new product segments where they currently do not
have a market presence
7
The Strength of CompetitivePressures from
Substitute Products
Concept
- Substitutes matter when customers are attracted
to the products of firms in other industries
Examples
- Eyeglasses and contact lensvs. laser surgery
- Sugar vs. artificial sweeteners
- Newspapers vs. TV vs. Internet
8
Competitive Pressures From Suppliersand
Supplier-Seller Collaboration
- Whether supplier-seller relationships represent
aweak or strong competitive force depends on - Whether suppliers can exercisesufficient
bargaining leverage toinfluence terms of supply
in their favor - Nature and extent of supplier-sellercollaboration
in the industry
9
When Is the Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Stronger ?
- Industry members incur high costs in
switchingtheir purchases to alternative
suppliers - Needed inputs are in short supply
- Supplier provides a differentiated inputthat
enhances the quality of performanceof sellers
products or is a valuable partof sellers
production process - There are only a few suppliers of a specific
input - Some suppliers threaten to integrate forward
10
When Is the Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Weaker ?
- Item being supplied is a commodity
- Seller switching costs to alternative suppliers
are low - Good substitutes exist or new ones emerge
- Surge in availability of supplies occurs
- Industry members account for a bigfraction of
suppliers total sales - Industry members threaten to integrate backward
- Seller collaboration with selected suppliers
provides attractive win-win opportunities
11
Competitive Pressures Can Be Createdby
Effective Seller-Supplier Collaboration
- Forging strategic partnershipswith select
suppliers to - Reduce inventory and logistics costs
- Speed availability of next-generationcomponents
- Enhance quality of parts being supplied
- Squeeze out cost savings for both parties
- can lower costs or enhance product
differentiation - Utilizing supply chain partnerships to lower
costs and/or enhance product differentiation puts
rivals under increased competitive pressure - Sellers who do a significantly better job than
rivals of managing supply chain partnerships may
even achieve competitive advantage
12
When Is the BargainingPower of Buyers
Stronger ?
- Buyer switching costs to competing brands
orsubstitutes are low - Buyers are large and can demand concessions
- Large-volume purchases by buyers are important to
sellers - Buyer demand is weak or declining
- Only a few buyers exists
- Identity of buyer adds prestigeto sellers list
of customers - Quantity and quality of informationavailable to
buyers improves - Buyers have ability to postpone purchases until
later - Buyers threaten to integrate backward
c
c
13
Competitive Pressures Can Be Createdby
Effective Seller-Buyer Collaboration
- Collaborative partnerships may result in mutual
benefits due to - Just-in-time deliveries
- Electronic order processing
- Electronic invoice payments
- Data sharing
- When a company delivers added value to customers
via its collaborative efforts, rivals come under
increased competitive pressure to provide
equivalent benefits or risk loss of customer
patronage - Competitive advantage potential may accrue to
sellers who do a better job than rivals of
managing partnerships with customers
14
Strategic Implications of theFive
Competitive Forces
- Competitive environment is unattractive fromthe
standpoint of earning good profits when - Rivalry is vigorous
- Entry barriers are lowand entry is likely
- Competition from substitutes is
strong - Suppliers and customers haveconsiderable
bargaining power
15
Strategic Implications of theFive
Competitive Forces
- An industrys competitive environment is ideal
from a profit-making standpoint when - Rivalry is moderate
- Entry barriers are highand no firm is likely to
enter - Good substitutesdo not exist
- Suppliers and customers arein a weak bargaining
position
16
Coping With theFive Competitive Forces
- Objective is to craft a strategy to
- Insulate firm fromcompetitive pressures
- Initiate actions to producesustainable
competitive advantage - Allow firm to be the industrys mover and
shaker with the most powerful strategy that
defines thebusiness model for the industry and
that may shape the rules of competition and
market engagement
17
The Factors Driving IndustryChange and
Their Anticipated Impact
- Industries change because forcesare driving
industry participantsto alter their actions - Driving forces are themajor underlying causesof
changing industry andcompetitive conditions
18
Analyzing Driving Forces
- Identify forces likely to exert
greatestinfluence over next 1 - 3 years - Usually no more than 3 - 4 factorsqualify as
real drivers of change - Assess impact
- Are the driving forces causing demand for product
to increase or decrease? - Are the driving forces acting to make competition
more or less intense? - Will the driving forces lead to higher or lower
industry profitability?